** BASIC TISSUES HANDOUT ** EPITHELIUM SIMPLE
advertisement

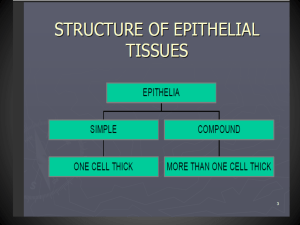
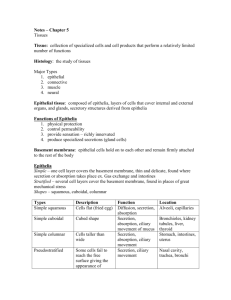
** BASIC TISSUES HANDOUT ** EPITHELIUM (Classification is based upon two criteria: (1) Cell Shape and (2) Number of cell layers) SIMPLE Squamous (aka: Non-stratified) Cuboidal Columnar *INTERMEDIATE SUB-TYPES Pseudostratified * Pseudostratified STRATIFIED Squamous Transitional Cuboidal Columnar Transitional * Note: Functionally, all EPITHELIA are either: a) Protective (linings or coverings) b) Secretory c) Absorptive (or adapted for filtration) d) Specialized (glands, taste buds, etc.) __________________________________________________________________________________ CONNECTIVE TISSUE (Classification is based upon “texture” of the matrix) SOFT Embryonic: Mesenchyme (aka: “C.T. Proper”) Mucous (“Wharton’s Jelly”) Adult: (Loose) Areolar C. T. Adipose C.T. Dense, Collagenous C.T. Elastic C.T. Reticular C.T. FIRM Cartilages: Hyaline Cartilage C.T. Fibrocartilage C.T. Elastic Cartilage C.T. RIGID Bone (aka: Osseous C.T.) Dental tissues: Enamel C.T.; Dentin C.T.; Cementum C.T. FLUID Blood Lymph Note: Chief components to consider in all C.T.’s are: (1) Cells and (2) the Matrix. Matrix is the intercellular material that consists of Ground substance and fibers. (1) Cells may be: Fibroblasts; Adipocytes; Chondrocytes; Osteocytes (-blasts, -clasts); Macrophages; Mast cells; Red Blood Cells; White Blood Cells; Lymphocytes. (2) Ground substance consists of glycosaminoglycans (GAG’s) such as hyaluronic acid, keratandermatan- and chondroitin sulfates; and proteoglycans such as mucins, mucoids, + chondroproteins. (3) Fiber types are named for the fibrous protein of which each is composed: Collagen Fibers (Protein collagen); Reticular Fibers (Protein reticulin); Elastic Fibers (Protein elastin) __________________________________________________________________________________ MUSCLE Skeletal (Striated, attached to bones, voluntary control) Cardiac (Striated, makes up the heart, involuntary control) Smooth (Non-striated, comprises muscular viscera, involuntary control) NERVE (Functional cells: Neurons Supporting cells: Neuroglia) Neurons: Structural classification: Unipolar, Bipolar, Multipolar Functional classification: Sensory, Motor, or Interneuron (afferent), (efferent) Neuroglia: CNS: Astrocytes, Oligodendrocytes, Microglia, Ependyma PNS: Schwann Cells (Neurilemmocytes), Satellite cells __________________________________________________________________________________