Final Exam Review
advertisement

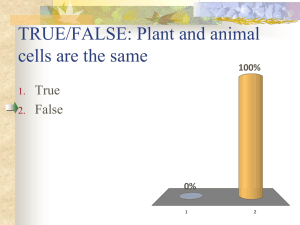
Final Exam Review 1. Cell without a nucleus 2. Function of cell membrane 3. Reading graphs 4. What do enzymes to do reactions? 5. What factors affect how well an enzyme works? 6. Examples of eukaryotic cells 7. Function of mitochondria 8. Function of Golgi apparatus 9. What is a hypothesis? 10. Difference between plant and animal cells 11. Function of the nucleus 12. Where does protein synthesis take place? 13. Which cells are made by meiosis? 14. What is a female’s genotype? 15. Punnett squares and probability 16. What is independent assortment? 17. Cross TT and tt 18. Determine offspring of TT and Tt 19. What is homozygous dominant? 20. Role of tRNA 21. Compare and contract RNA and DNA 22. How are DNA, RNA and proteins related? 23. Determine the codons: CCG GCC AUU 24. What do CCC and AGU have in common? 25. Replicate: TACCGGTAA 26. How are different proteins different from each other? 27. Determine # of chromosomes if haploid number is 18. 28. If diploid number is 40, how many would be in the gametes? 29. What is artificial selection? 30. What is ecological succession? 31. How might an invasive species affect an ecosystem? 32. How does sexual reproduction affect genetic variation? 33. How are variation and natural selection related? 34. What is survival of the fittest? 35. What is punctuated equilibrium? 36. What is geographic isolation? 37. What are the building blocks of proteins? 38. What are homologous structures? 39. What is biodiversity? 40. What factors can cause a population to decrease in size? Keep Going! Final Exam Review 1. Cell without a nucleus 2. Function of cell membrane 3. Reading graphs 4. What do enzymes to do reactions? 5. What factors affect how well an enzyme works? 6. Examples of eukaryotic cells 7. Function of mitochondria 8. Function of Golgi apparatus 9. What is a hypothesis? 10. Difference between plant and animal cells 11. Function of the nucleus 12. Where does protein synthesis take place? 13. Which cells are made by meiosis? 14. What is a female’s genotype? 15. Punnett squares and probability 16. What is independent assortment? 17. Cross TT and tt 18. Determine offspring of TT and Tt 19. What is homozygous dominant? 20. Role of tRNA 21. Compare and contract RNA and DNA 22. How are DNA, RNA and proteins related? 23. Determine the codons: CCG GCC AUU 24. What do CCC and AGU have in common? 25. Replicate: TACCGGTAA 26. How are different proteins different from each other? 27. Determine # of chromosomes if haploid number is 18. 28. If diploid number is 40, how many would be in the gametes? 29. What is artificial selection? 30. What is ecological succession? 31. How might an invasive species affect an ecosystem? 32. How does sexual reproduction affect genetic variation? 33. How are variation and natural selection related? 34. What is survival of the fittest? 35. What is punctuated equilibrium? 36. What is geographic isolation? 37. What are the building blocks of proteins? 38. What are homologous structures? 39. What is biodiversity? 40. What factors can cause a population to decrease in size? Keep going!!! 41. What does an energy pyramid look like? 42. How much energy is transferred? 43. What is the ultimate source of all food? 44. What is the body’s first line of defense? 45. What are antibodies? 46. How do vaccines work? 47. What are the structures of a bacteriophage? 48. What is a virus made of? 49. How do viruses reproduce? 50. How do nutrients get to cells? (Which systems are involved?) 51. What does the circulatory system do? 52. What is a nerve impulse? 53. Which two systems coordinate and integrate all body activities? 54. What is the function of the nervous system? 55. How are mutations involved with evolution? 56. If two animals are very closely related, how different will their DNA be? 57. What is Darwin’s theory of evolution? 58. What is an ecosystem? 59. What is an herbivore? 60. What organism recycles nitrogen back to the atmosphere? 61. What is required to keep photosynthesis going? 62. What does the HIV virus attack? Why is this important for someone with the disease? 63. What is released at a synapse? 64. What is homeostasis? 65. What are sensory neurons? Motor neurons? There are 80 questions on the Final Exam Bring a pencil and an eraser Bring your Bio book to turn in Bring something quiet to work on! 41. What does an energy pyramid look like? 42. How much energy is transferred? 43. What is the ultimate source of all food? 44. What is the body’s first line of defense? 45. What are antibodies? 46. How do vaccines work? 47. What are the structures of a bacteriophage? 48. What is a virus made of? 49. How do viruses reproduce? 50. How do nutrients get to cells? (Which systems are involved?) 51. What does the circulatory system do? 52. What is a nerve impulse? 53. Which two systems coordinate and integrate all body activities? 54. What is the function of the nervous system? 55. How are mutations involved with evolution? 56. If two animals are very closely related, how different will their DNA be? 57. What is Darwin’s theory of evolution? 58. What is an ecosystem? 59. What is an herbivore? 60. What organism recycles nitrogen back to the atmosphere? 61. What is required to keep photosynthesis going? 62. What does the HIV virus attack? Why is this important for someone with the disease? 63. What is released at a synapse? 64. What is homeostasis? 65. What are sensory neurons? Motor neurons? There are 80 questions on the Final Exam Bring a pencil and an eraser Bring your Bio book to turn in Bring something quiet to work on!