CHEM 5013
advertisement
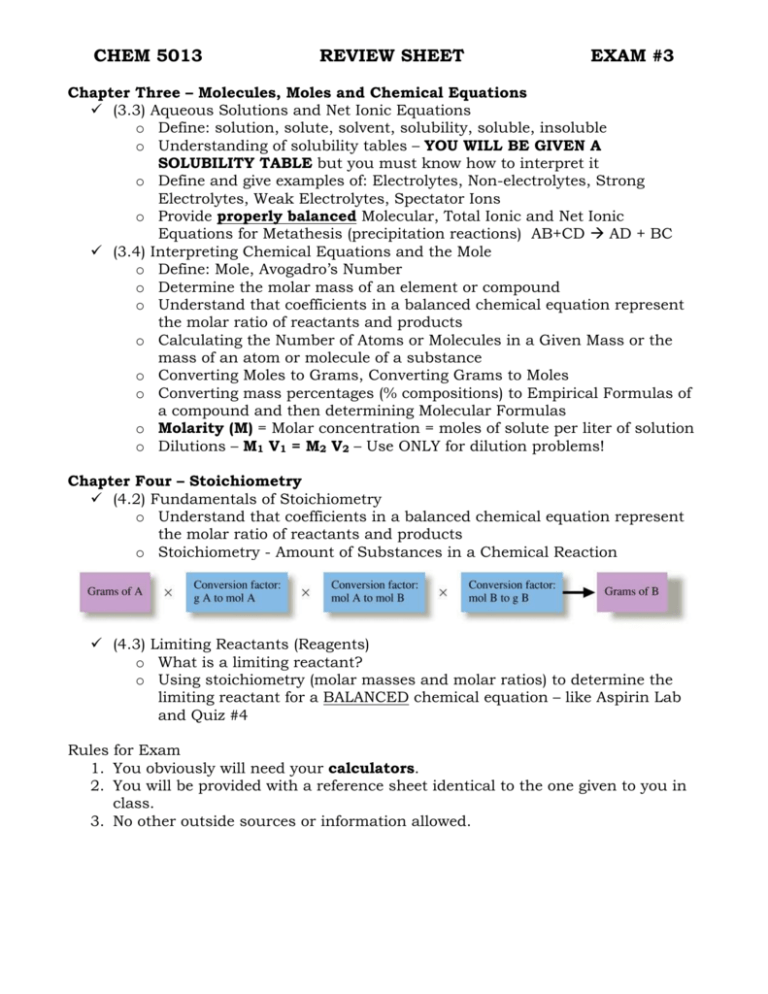
CHEM 5013 REVIEW SHEET EXAM #3 Chapter Three – Molecules, Moles and Chemical Equations (3.3) Aqueous Solutions and Net Ionic Equations o Define: solution, solute, solvent, solubility, soluble, insoluble o Understanding of solubility tables – YOU WILL BE GIVEN A SOLUBILITY TABLE but you must know how to interpret it o Define and give examples of: Electrolytes, Non-electrolytes, Strong Electrolytes, Weak Electrolytes, Spectator Ions o Provide properly balanced Molecular, Total Ionic and Net Ionic Equations for Metathesis (precipitation reactions) AB+CD AD + BC (3.4) Interpreting Chemical Equations and the Mole o Define: Mole, Avogadro’s Number o Determine the molar mass of an element or compound o Understand that coefficients in a balanced chemical equation represent the molar ratio of reactants and products o Calculating the Number of Atoms or Molecules in a Given Mass or the mass of an atom or molecule of a substance o Converting Moles to Grams, Converting Grams to Moles o Converting mass percentages (% compositions) to Empirical Formulas of a compound and then determining Molecular Formulas o Molarity (M) = Molar concentration = moles of solute per liter of solution o Dilutions – M1 V1 = M2 V2 – Use ONLY for dilution problems! Chapter Four – Stoichiometry (4.2) Fundamentals of Stoichiometry o Understand that coefficients in a balanced chemical equation represent the molar ratio of reactants and products o Stoichiometry - Amount of Substances in a Chemical Reaction (4.3) Limiting Reactants (Reagents) o What is a limiting reactant? o Using stoichiometry (molar masses and molar ratios) to determine the limiting reactant for a BALANCED chemical equation – like Aspirin Lab and Quiz #4 Rules for Exam 1. You obviously will need your calculators. 2. You will be provided with a reference sheet identical to the one given to you in class. 3. No other outside sources or information allowed. Advice Study the practice problems on the website and the quizzes – many problems will be similar to the problems found there. Study your lecture notes and textbook sections provided above as well as the labs (Reactions in Aqueous Solutions, Determination of a Chemical Formula, Solutions, Dilutions and Acidimetry) Valuable Hint (Reminder!!!): Chemistry is a subject which builds upon itself. You will need to use information that you learned for Exams 1 and 2 in order to solve some problems on Exam 2. Specifically, it is assumed that you know how to provide correct chemical formulas given the name of a compound and that you can provide the name of a compound given the chemical formula. It is also assumed that you will know how to convert from one unit to another (ex. mL to cm3 or mL to L). Also, know the density formula!!! Example: You should be able to provide a correct formula for calcium carbonate (CaCO3) or Sodium Nitrate (NaNO3)