Repatha
advertisement

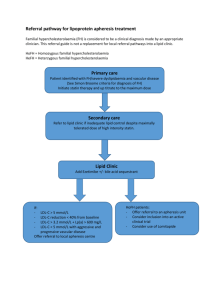
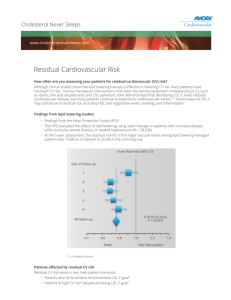
New Drug Introduction: Repatha™ / Evolocumab Pharmacology Manufacturer Approval Date Indications Contraindications Black Box Warnings Warnings and Precautions Pregnancy/Lactation Pharmacokinetics Human monoclonal IgG2 antibody that binds to proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9) and inhibits circulating PCSK9 from binding to the low density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R), preventing PCSK-9 mediated LDL-R degradation and allowing LDL-R to recycle back to the liver cell surface. By inhibiting the binding of PCSK9 to LDLR, evolocumab increases the number of LDL-Rs available to clear LDL from the blood thus lowering LDL-C levels Amgen August 27, 2015 Indicated as an adjunct to diet and; - Maximally tolerated statin therapy for treatment of adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) or clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD) who require additional lowering of LDL-C - Other LDL-lowering therapies in patients with homozygous hepercholesterolemia (HoFH) who need additional lowering of LDL-C Serious hypersensitivity to evolocumab or any component of the formulation None Allergic reactions like rash and urticarial have occurred. Discontinue treatment if signs or symptoms of serious allergic reactions occur, and treat according to standard of care and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve No human studies. Animal studies show it crosses the placenta. Previous experience indicates monoclonal antibodies cross the placenta during 2nd and 3rd trimester. Even though IgG is present in human milk data shows it does not enter neonatal and infant circulation in substantial amounts. Risks vs. benefits should be considered. A – Estimated absolute bioavailability 72%, median Cmax: 3-4 days D – Mean steady state volume of distribution 3.3 L (SD 0.5) M – Non-saturable proteolytic pathway E – Half life estimated to be 11 to 17 days Drug Interactions – Object Drugs An approximately 20% decrease in the Cmax and AUC of evolocumab was observed in patients co-administered with a high-intensity statin regimen. This difference is not clinically meaningful and does not impact dosing recommendations. Adverse Effects -Nasopharyngitis (10.5) [ 9.6] Cough (4.5) [3.6] -Upper resp tract infection (9.3) [6.3] Injection site reaction (5.7) [5.0] -Influenza (7.5) [6.3] Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: measure LDL-C 4-8 weeks after initiation of evolocumab Signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction or adverse reaction No laboratory monitoring suggested HeFH or primary hyperlipidemia with CVD: 140 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks or 420 mg subcutaneously once monthly. Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: 420 mg once monthly No adjustment needed in mild to moderate impairment. No data available in severe renal impairment No adjustment needed in mild to moderate impairment. No data available in severe hepatic impairment Treatment(%) Placebo[%] Monitoring Efficacy Monitoring Toxicity Dosing Renal Adjustment Hepatic Adjustment Cost: Source: Medscape.com, date accessed 01/11/2016 Dose(s) Repatha™ – Evolocumab 140 mg, 420 mg injection Repatha™ - Evolocumab 75 mg, 150 mg injection Praluent - Alirocumab 1 year $14,000 $14,600 Summary Repatha™, evolocumab, a human monoclonal IgG2 antibody, is a PCSK9 inhibitor that reduces LDL-C by increasing the number of available LDL-Rs Evolocumab is indicated as adjunct treatment in adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional lowering of LDL-C Suggested subcutaneous dosing is 140 mg every 2 weeks or 420 mg every month Common adverse drug reactions include respiratory and injection-site reactions Suggested monitoring: LDL-C 4 to 8 weeks after starting therapy in patients with HoFH References: 1. https://www.repatha.com 2. Repatha [evolocumab] package insert. Amgen Inc. Aug. 2015. 3. Evolocumab Facts and Comparisons online.factsandcomparisons.com (Accessed January 2015). 4. Blom DJ et. al. A 52 week placebo controlled trial of Evolocumab in hyperlipidemia. N Engl J Med. 2014: 370 (19); 1809-1819 Date Prepared: 01/11/2016 Editor: Peter G. Koval, Pharm.D., BCPS Author: Persida Tahiri, Pharm.D. Candidate, UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy