AP World History
advertisement

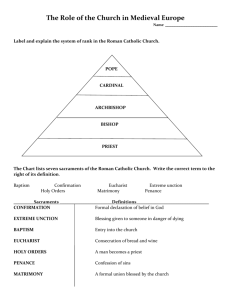
Continuity & Change Over Time (CCOT) Essay Europe 600-1750 Question: analyze the social and economic continuities and changes that occurred in Europe between 600 and 1750. Taylor During the time period between 600 and 1750, economic and social continuities and changes impacted Western Europe immensely. One particular economic alteration was the decline of feudal manoralism, prevalent in the early medieval era, as a result of the restoration of commerce following the Crusades. Another major change was the socioeconomic impact of the Age of Exploration circa 1500, which would establish European Hegemony. While economic transformations occurred throughout Western Europe, the influence of the Roman Catholic Church was continuous despite fluctuations in its authority. After the fall of the Roman Empire in 476 CE, Western Europe became divided into the Germanic Kingdoms that characterized the Middle Ages. Trade languished during this time as a result of the constant warfare (feuds) and political instability that ensued after the fall of Rome. For this reason, self-sufficient manors managed by local warlords developed. Rigid social stratification defined the period with a hierarchy comprised of Kings, Noblemen, Knights and peasantry. Socially, living conditions were unfavorable, and the Black Plague ran rampant devastating the European populace circa 1350. Between 1100 and 1300, Western Europeans embarked upon a series of religious quests against Muslims, known as the Crusades. European soldiers fighting in the Middle East were intrigued by foreign goods and the Muslim preservation of long forgotten Greco-Roman ideals. Amazed at such riches and ideas, they returned home to introduce and expose Western Europeans to what they had discovered. As a result, commerce was resumed and interregional trade networks were created to obtain foreign “luxury” goods that were at increased demand. Fortunately the war had forged European contacts with the Middle East via the Mediterranean Sea, which allowed for merchandise to be acquired from lands as far as China without extended voyages. As trade once again began to flourish, Europe saw the decline of manoralism. This was due to the rise in the merchant class which challenged the power of the Aristocracy, thereby weakening their influence. Increased business in port cities caused urbanization in several areas in addition to an emerging middle class. Burgeoning trade and economic prosperity allowed for the resurgence of Greco-Roman intelligence and culture in what is known as the Renaissance, which spanned from the fourteenth to the seventeenth century. In the midst of the Renaissance, world trade was prosperous and vast. Nations established personal control through the commercial contacts that they established. In an effort to shorten certain trading routes and obtain a more surmountable amount of natural resources, many nations entered the Age of Exploration circa 1500. Christopher Columbus, in an effort to discover a more efficient route from Western Europe to India, accidently unearthed the Americas in 1492. His discovery led many other European nations to pursue imperialistic endeavors in what had become known as the New World. Two Spanish conquistadors, Cortez and Pizarro, made a profound impact on the areas they conquered in the New World. In Mexico, the native Aztecs were overpowered by Cortez’ forces. A majority fell ill from susceptibility to European diseases, while the rest were placed into coercive labor systems. Similar fates were bestowed upon the Incas subjected to Pizarro’s control. The Spanish created these colonies as a source of raw materials and cheap labor to support their expanding economic endeavors. To assert control over the native populations, the encomienda and mita systems were utilized. These systems, originally devised as a means of converting natives to Christianity, were in reality, inhumane, harsh organizations that devastated local populations. Through coercive labor systems and colonization, European nations were able to lay the foundation they needed to attain hegemony during this time period. Between 600 and 1750, the Roman Catholic Church continued to play a constant role in Western Europe. During the feudal period, the church developed its strong authority due to the decentralized political nature of Western Europe. In this instance Christianity acted as a unifying force amongst the several divided kingdoms of the age. Upon entry into the Crusades in 1095, the Church’s influence was at its peak as European soldiers rallied in opposition to Muslim forces encroaching on Byzantine territory. Those who fought returned from the conflict to spark interests in worldly luxury products and thought laying foundation for the European golden age or Renaissance. Intellectual movements spurred by Renaissance thought led many to question the morality of the Catholic Church, specifically in regards to the sale of indulgences. Martin Luther, a Catholic monk, witnessed firsthand the lavish way in which clergy were allowed to live due to their increased secular power. He strongly disapproved of their practices and pursued reform through his 95 theses. The Church’s failure to comply with his proposals resulted in his decision to begin the Protestant Reformation. This division in the Catholic Church combined with an increase in monarchal authority temporarily decreased the church’s influence. Circa 1500, the Age of Exploration transmitted material goods as well as cultural and spiritual ideals. The Spanish conquistadors who conquered regions of Latin America instilled upon the natives their Roman Catholic faith thus replacing their polytheistic worship. What at first was evidence of religious exploitation, as seen in the coercive labor systems established, was transformed into a force of social stability that dominated everyday life. The spread of Christianity to the New World once again established the Catholic Church as a religious authority with substantial influence. Economic and social patterns between 600 and 1750 were transformed due to several changes and continuities throughout Western European society. The European decline in feudalism was impacted immensely by the resurgence in commercial activities following the Crusades. The prosperity that ensued from increased world contacts laid the foundation for eager explorers to trail their ambitions during the Age of Exploration. Their discoveries and conquests would then establish European Hegemony at the expense of many aboriginal people subjected to coercive labor. Throughout this time the Roman Catholic Church continually held a place in society despite fluctuations in their authority and support.