Bio 1010 Evolution & Diversity, Section Two Exam, Spring 2011

Bio 1020 Intro’ Bio’ II, Section One Exam, Spring 2012 (Watch for negatives like the word “not.”)
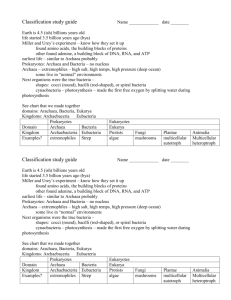
1. Which of the following statements is true regarding Bacteria and Archaea in general?
A. Bacteria and Archaea are in the same monophyletic clade, the Prokaryotes, sometimes called the
Monera
B. Bacteria and Archaea all live in association with other organisms as disease causing pathogens
C. Bacterial cell membranes and cell walls are biochemically the same as those in Archaea
D. Bacterial ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequences are very different than those in Archaea
2. One more time, which of the following statements is true regarding Bacteria and Archaea?
A. They all contain several membrane bound organelles, e.g. mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum
B. Different species of Bacteria and Archaea have evolved to live in every conceivable habitat
C. They all contain DNA packaged with proteins as chromosomes, contained in a nucleus
D. They are all basically the same, with little variety in their DNA, metabolism, or lifestyle
3. The first organisms on Earth that could photosynthetically produce oxygen were:
A. Ancestral moss and fern-like plants
B. Ancestral aerobic Proteobacteria
C. Ancestral Cyanobacteria
D. Ancestral Algae
4. The Endosymbiotic Theory asserts that chloroplasts were originally:
A. Some ancestral aerobic Proteobacteria cell
B. Some ancestral Cyanobacteria cell
C. Some ancestral Eukaryote cell
D. Some ancestral Archaea cell
5. The Endosymbiotic Theory asserts that mitochondria were originally:
A. Some ancestral aerobic Proteobacteria cell
B. Some ancestral Cyanobacteria cell
C. Some ancestral Eukaryote cell
D. Some ancestral Archaea cell
6. Bacterial and archaeal genomes consist of:
A. A single ‘naked,’ circular DNA molecule and, perhaps, one or more smaller plasmids
B. A single ‘naked,’ circular RNA molecule and, perhaps, one or more smaller plasmids
C. A single ‘naked,’ linear DNA molecule and, perhaps, one or more smaller plasmids
D. Several discrete linear packages of DNA and protein called chromosomes
7. The ‘nano-factory’ structure that assembles proteins in all life forms is called:
A. The cytoplasm
B. An endospore
C. A ribosome
D. A plasmid
8. Many Bacteria, and some Archaea, have a sticky, slimy, protective layer outside of everything; this is the:
A. Glycocalyx (capsule)
B. Flagellum
C. Cell wall
D. Pilus
9. Many Bacteria and Archaea have structures used for adhering to other objects; these are:
A. Glycocalyxes (capsules)
B. Cell walls
C. Flagella
D. Pili
10. Some Bacteria and Archaea have structures used for locomotion in response to chemotaxis; these are:
A. Glycocalyxes (capsules)
B. Cell walls
C. Flagella
D. Pili
1
11. An accessory circular DNA molecule in bacteria and archaea that often carries genes for sex, drug resistance, and/or pathogenicity is:
A. The cytoplasm
B. An endospore
C. A ribosome
D. A plasmid
12. Some Bacteria can go dormant, creating tough, thick-walled structures to survive harsh environments; this is:
A. A glycocalyx (capsule)
B. The cell membrane
C. An endospore
D. The cell wall
13. Which of the following statements is true about methods of bacterial and archaeal classification?
A. Since most can be grown in culture, metabolisms (medium requirements) works best for classification
B. Stain response (e.g. +/- Gram stain) and morphology (rod, sphere, etc.) works best for classification
C. Molecular phylogenetics (DNA or RNA sequence-based) works best for classification
D. Electron microscopy techniques work best for classification
14. Which of the following statements is not true about Carl Woese single-handedly revolutionizing biology?
A. He demonstrated that Bacteria and Archaea are so different that they deserve different Domains of life
B. He analyzed the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequence from bacteria and archaea
C. He analyzed complete genome sequences from bacteria and archaea
D. His ideas were ridiculed by many scientists, for many years
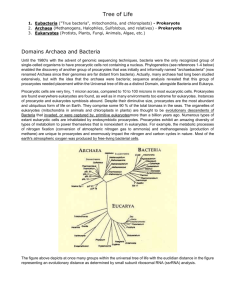
15. Which of the following statements is true according to molecular phylogenetics of the ‘Tree of Life’?
A. Upon rooting, we see Archaea are more closely related to Bacteria, than they are to Eukaryotes
B. The most ancestral branches, those closest to the root, mainly live in very cold environments
C. Bacteria and Archaea have much more biodiversity than Eukaryota
D. Horizontal gene transfer is extremely rare
16. An organism that occupies a very hot environment (generally above around 120º F) is called):
A. A psychrophile
B. A thermophile
C. An acidophile
D. A halophile
17. An organism that occupies a very acidic environment (generally with a pH below 5 or so) is called:
A. A psychrophile
B. A thermophile
C. An acidophile
D. A halophile
18. Pick the true statement from the following regarding Bacteria and Archaea in the global biosphere:
A. An insignificant amount of the Earth’s carbon is ‘tied up’ in Bacteria and Archaea
B. There are way more humans on Earth than either Bacteria or Archaea
C. There are ten times more human cells than microbial cells in our body
D. The entire biosphere is ultimately dependent upon them
19. Which of the following statements is not true regarding bacterial and archaeal metabolism?
A. Many of them can switch their metabolism depending on the environment they occupy
B. They have evolved to use every conceivable carbon and energy source on Earth
C. Some are autotrophs and others are heterotrophs
D. They all require oxygen to live
20. Which of the following is true regarding — if all the animals, plants, and fungi of the world went extinct, then:
A. The biogeochemical cycles of the ecosphere would continue in their usual fashion
B. The Archaea and Bacteria would continue to exist all over the Earth
C. The Archaea and Bacteria would also go extinct
D. All life on Earth would end
21. Pick the statement from the following that is true regarding microbial mats and biofilms:
A. The same genes are active in microbes living in mats and biofilms as are active when living solitary
B. Biofilms can be important medically because they sometimes cause hard-to-treat infections
2
C. Microbial mats and biofilms usually only consist of a single microbial species
D. All microbial mats and biofilms are harmful, one way or another
22. Bacteria have ________________ Phyla (or what could be considered Kingdoms) than (as) Archaea.
A. About the same number of
B. Many more (many means more than around ten here)
C. Many less
D. A few more (few means less than around six here)
23. In the Bacteria, the ____________ group usually come out as the most basal, ancestral clade in phylogenies.
A. Archaea
B. Aquaficae
C. Cyanobacteria
D. Proteobacteria
24. Archaea have been found in all the following environments except :
A. Mars
B. Very cold environments, e.g. Antarctica
C. Garbage landfills, swamps, and marshes
D. Hot springs, hydrothermal and volcano vents, and old mines
25. Which of the following statements is not true regarding methane gas production?
A. Some Archaea make methane, called swamp gas, in marshes and swamps
B. Methane is also a byproduct of cellulose digestion in cows
C. Archaea in cow’s digestive systems make methane
D. Methane is only made from petroleum
26. The hydrothermal vent Archaea and Bacteria that begin the food chain in that ecosystem:
A. All require sunlight for their survival
B. Require glucose or some other sugar for their survival
C. Survive by consum ing the ‘rain’ of detritus that falls from upper layers of the ocean
D. Require inorganic substances such as hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide or monoxide
27. Bacteria and Archaea are being used in the oil and mining industries for all of these things except :
A. The bioremediation of old mining sites’ waste dumps to reduce toxic and radioactive metal content
B. To extract valuable metals such as copper from low-grade ore (tailings) heaps
C. To clean up crude oil spills in land and ocean environments
D. To dig deeper shafts into the Earth
28. A chemoautotrophic Bacteria or Archaea only requires this to survive:
A. Light and carbon dioxide
B. Inorganic compounds
C. Organic compounds
D. Oxygen
29. Horizontal gene transfer in Bacteria or Archaea is:
A. Only accomplished through one mechanism
B. Only occurs between members of the same species
C. No longer occurring, although it was very common during the early evolution of life
D. A very common occurrence that happens all the time, even between different domains of life
30. Bacteria and Archaea asexually reproduce very efficiently. Pick the best response from the following:
A. Some can produce a new generation as fast as every day
B. Some can produce a new generation as fast as every hour
C. Some can produce a new generation as fast as every 20 minutes
D. Some can produce a new generation as fast as every minute
31. Horizontal gene transfer in Bacteria or Archaea by the uptake of ‘naked’ DNA without cell-to-cell contact is:
A. Transformation
B. Transposition
C. Transduction
D. Conjugation
3
32. Horizontal gene transfer in Bacteria or Archaea, where DNA is transferred through a sex pilus, is:
A. Transformation
B. Transposition
C. Transduction
D. Conjugation
33. Horizontal gene transfer in Bacteria or Archaea mediated by a virus called a bacteriophage is:
A. Transformation
B. Transposition
C. Transduction
D. Conjugation
34. Traits such as antibiotic resistance or virulence can arise via spontaneous mutation, but also:
A. Can rapidly spread through a bacterial population via horizontal gene transfer
B. Can arise as a direct response to the use of antimicrobial drugs
C. Are restricted to only those cells in which the occur
D. Are rapidly lost in the cells where they occur
35. Different ways that bacteria can enter or exit a human to cause disease do not include which of the following?
A. Contaminated semen, vaginal fluids, urine, or feces
B. Contaminated food, water, or air
C. Open injuries or bites in the skin
D. Getting chilled by cold weather
36. Symptoms characteristic of bacterial disease do not result from which of the following?
A. The host’s own immune system actively fighting the infection
B. Interactions between host cells and bacterial cells
C. Bacterial endotoxins and exotoxins
D. Bacterial DNA release
37. The bacterium that causes humans to get ulcers is:
A. Neisseria
B. Rhizobium
C. Escherichia coli
D. Heliobacter pylori
38. Which of the following statements is not true Escherichia coli :
A. It has a strain named 0157:H7, that can cause severe gastrointestinal disease
B. It is very well understood and is used extensively for genetic engineering
C. It is a normal, usually harmless, symbiont of the human large intestine
D. All strains of it cause disease
39. Temperatures lower than around 35º F (about 2º C) __________ most bacteria that cause food poisoning.
A. Induces horizontal gene transfer in
B. Speeds up reproduction
C. Causes dormancy in
D. Can kill
40. Which statement is true regarding the evolution of antibiotic resistance in pathogenic bacteria?
A. This phenomenon is accelerated by humans not completing their entire antibiotic prescription regime
B. This phenomenon happens in the absence of bacterial mutation or horizontal gene transfer
C. This phenomenon is avoided by the supplementation of animal feeds with antibiotics
D. This phenomenon will go away with the development of new antibiotics
41. Which of the following is not true about Staphylococcus aureus , the causative agent of a ‘staph’ infection?
A. Some strains have independently evolve d the pathogenicity genes for “toxic shock syndrome”
B. Phylogenetic analyses show they seldom undergo horizontal gene transfer of these genes
C. Some strains, called MRSA, have evolved resistance to many antibiotics
D. Staphylococcus aureus is a very common bacterium
42. Which of the following statements is true about the original photosynthetic organisms on Earth?
A. These organisms changed the atmosphere from an oxidizing to a reducing mix
B. The atmosphere achieved current oxygen levels around 6,000 years ago
4
C. Aerobic bacteria and archaea evolved before photosynthetic ones
D. These organisms were likely the ancestors of Cyanobacteria
43. Which of the following statements is true about nitrogen fixation?
A. Nitrogen gas in the atmosphere is directly used by animals in the biosynthesis of organic compounds
B. Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting ammonia, nitrates, and nitrites to nitrogen gas
C. Many forms of life can fix nitrogen — animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, and archaea
D. All life on Earth is dependent upon nitrogen fixation
44. Which of the following statements is not true about nitrogen fixation by the bacterium Rhizobium ?
A. It occurs in the root nodules of legume (peas, beans, clover, alfalfa, etc.) plants
B. The relationship requires a number of important bacterial and host genes
C. The relationship is a clear demonstration of coevolutionary symbiosis
D. It decreases soil productivity drastically
45. I showed several examples of biogeochemical cycles on Earth, which of the following statements is true?
A. Bacteria and/or archaea have nothing to do with any of these biogeochemical cycles
B. Bacteria and/or archaea affect all these cycles, including nitrogen, sulfur, and iron
C. Bacteria and/or archaea only affect metal and salt cycles on Earth
D. Bacteria and/or archaea only affect the nitrogen cycle on Earth
46. Which of the following statements is true regarding symbiotic Bacteria and/or Archaea in our bodies?
A. The symbionts restrict pathogenic bacteria growth by competing for the limited available resources
B. Most Bacteria and Archaea cause disease; those that don’t provide little benefit to humans
C. Adult humans have very few Bacteria and/or Archaea within and on their bodies
D. Babies acquire bacterial and archaeal symbionts well before birth
47. Many (perhaps most) animal-bacterial and/or archaeal symbioses:
A. Are involved in helping the host gain nutrition, e.g. allowing the digestion of otherwise indigestible foods
B. Do not affect either the symbiont or the host in any appreciable manner
C. Have nothing to do with fat storage regulation or vitamin production
D. Harm the host animal, particularly its immune system
48. Probiotics refers to:
A. Eating ‘good’ bacteria to supplement your usual intestinal population
B. Taking your antibiotic for as long as it has been prescribed
C. Creating oil-based products with bacteria
D. Eating only raw, vegetarian food
49. An insect bacterial symbiont named Wolbachia :
A. Is being experimented with as a potential biological control agent against mosquitoes
B. Affects many systems in insects, but not reproduction
C. Affects fewer than 10% of all insect species
D. Helps insects digest their food
50. Bacteria are particularly important in the manufacture of many products; which of these do n’t they make?
A. Transgenic Bacteria can make drugs like human insulin, growth hormone, and blood-clotting factors
B. Important industrial solvents, various cleaning enzymes, and pharmaceuticals such as antibiotics
C. Processed foods, including vinegars, sauerkrauts, pickles, olives, yogurts, and cheeses
D. Hard liquor, wine, and beer
5