Y4-Y5 Block B Unit 1
advertisement

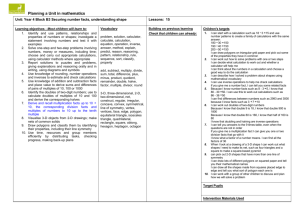
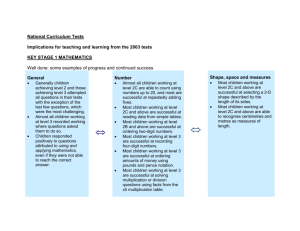
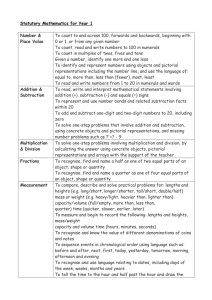
Learning overview: Year 4 Block B unit 1 Children rehearse and improve their recall of number facts. They use their understanding of the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction to state the addition facts corresponding to any subtraction fact, and vice versa. They know, or can derive quickly, all addition and subtraction facts for each number to 20, and continue to play games and solve puzzles to practise recalling these facts. They combine known facts with understanding of place value to add and subtract multiples of 10, 100 and 1000. For example, they use the fact that 19 – 5 = 14 to establish that 190 – 50 = 140, 1900 – 500 = 1400, and 19 000 – 5000 = 14 000. Children round numbers to the nearest 10 and 100 and then round money to the nearest pound. They recognise that rounding helps them to estimate the result of a calculation. They also realise that they can use their understanding of inverses to check the accuracy of calculations. Children rehearse their knowledge of the 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 times-tables. They count in steps of 6 from zero and investigate the patterns of multiples in the 100square. They use the patterns to answer questions such as: Will 72 be in the pattern? How do you know? They answer questions such as: How many sixes are in 54? and What is the missing number in 6 × = 54? They compare the multiples of 6 with the multiples of 3 and spot that the former are double the latter. When they solve word problems involving numbers, money or measures, children decide what calculation to do and how to do it: mentally, on paper or using a calculator. They set their solution back in the context of the problem to judge whether it is reasonable. They solve problems such as: For her party Asmat spent £2.88 on apples, £3.38 on bananas and £3.76 on oranges. Will a £10 note cover the cost? Explain your reasoning. A chocolate bar costs 19p. How many bars can be bought for £5? How many lengths of 9 cm can I cut from 183 cm of ribbon? Children extend their knowledge of 2-D shapes. They name equilateral triangles, isosceles triangles and heptagons, and know that polygons are closed flat shapes with straight sides. They learn that polygons can be regular or irregular and that a regular polygon has equal sides and equal angles. They explore polygons that have equal sides but unequal angles, and those that have equal angles but unequal sides. They describe properties of polygons using correct mathematical vocabulary, such as: has more than one right angle, is regular, has two or more sides of equal length, is a quadrilateral, etc. They classify polygons, using Carroll or Venn diagrams when appropriate. They justify their reasoning, explaining to others why some shapes may not fit their chosen criteria. Using their understanding of the properties of 2-D shapes, children investigate problems such the maximum number of right angles in a triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, … Children extend their knowledge of properties of 3-D shapes. They identify the shapes of faces of common 3-D shapes, and count the number of faces, edges and vertices (corners) of cubes, cuboids, pyramids and prisms. From their experience of handling 3-D shapes and describing their properties, they visualise mental images of the shapes. They can name a 3-D shape which has been secretly hidden in a drawstring bag. They look at drawings of 3-D shapes and relate them to real shapes. By unfolding packets they begin to understand how a net folds up to create a 3-D shape. Children contribute throughout to class discussions. They listen to the responses of others and identify the main points of the speaker. They compare their solutions and suggest alternatives Securing number facts, understanding shapes Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Learning overview: Year 5 Block B unit 1 Children rehearse multiplication facts to 10 × 10 and the related division facts. They discuss the facts that they can recall rapidly and strategies to help them derive those they struggle to recall, for example doubling 4 times-table facts to work out 8 times-table facts. They respond to questions such as: The product of two numbers is 24. What could the numbers be? They record their answers systematically to derive all pairs of factors for the number 24. They use squared paper or peg boards to create all the different arrays possible using 10, 11, 12, … squares or pegs. They use this to list all of the factors of 10, 11, 12, … They investigate which numbers can create a square array and learn that these are called square numbers; for example, 16 is a square number because it is equal to 4 × 4. Children classify numbers according to their properties, recording the classifications in Venn and Carroll diagrams. For example, they place the numbers 1 to 30 on a Venn diagram. They describe patterns in their diagram and respond to questions such as: What do you notice about numbers that are multiples of both 2 and 5? They learn the vocabulary common multiple and suggest general statements based on similar relationships, for example: All common multiples of 3 and 4 are multiples of 12. They test these statements by finding examples that match them. Children use known multiplication facts and place value to find related facts. For example, they use 8 × 4 = 32 to find the answer to 80 × 4, explaining that 80 is ten times as big as 8 so the answer will be ten times 32, or 320. They predict the answer to 80 × 40, explaining how they worked this out, then check their prediction using a calculator. They find related division facts, e.g. recognising that 3200 ÷ 400 = 8 because 8 × 400 = 3200. Children use similar strategies and their understanding of inverse operations to find the missing numbers in calculations such as: 20 × = 600 2800 ÷ 70 = ÷ 50 = 300 Children use rounding to suggest sensible estimates to addition and subtraction calculations. For example, they predict whether the answer to 3217 – 1682 is (a) 1635, (b) 1535 or (c) 1435. They use efficient written methods for addition and subtraction of whole numbers, estimating first. They use their knowledge of number facts, rounding and inverses to find the missing digits in calculations such as 367 – 192 = 1539. Children visualise and describe 3-D shapes according to a range of properties including: the shapes of faces, the number of faces, edges and vertices, and whether the number of edges meeting at each vertex is the same (as in a cube) or different (as in a square-based pyramid). They solve problems involving 3-D shapes, for example finding all of the possible nets for an open cube or sorting a set of 3-D shapes using an ICT ‘binary tree’ program. Children extend their knowledge of the properties of 2-D shapes. For example, they investigate the properties of rectangles. They measure the length of the two diagonals, commenting on what they notice. They measure the distance from the point where the diagonals cross each other to each of the four vertices. Children predict and test which other shapes have diagonals of equal length or diagonals that bisect each other Securing number facts, understanding shapes Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Securing number facts, understanding shapes Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Year 4 objectives 1999 links Year 5 objectives Year 4 38, 42 44, 46 & Year 5 45, 47 Year 5 linked objectives are located in block D unit 1 Use knowledge of addition and subtraction facts and place value to derive sums and differences of pairs of multiples of 10, 100 or 1000 Because I know sums like 3 7 10, I also know 30 70 100 300 700 1000 3000 7000 10 000 Because I know differences like 6 - 4 2, I also know 60 - 40 20, 600 - 400 200 6000 4000 2000 1999 links Derive and recall multiplication facts up to 10 × 10, the corresponding division facts and multiples of numbers to 10 up to the tenth multiple I can work out division facts for the 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 times-tables I can count in 6s from zero to 60 Use knowledge of rounding, number operations and inverses to estimate and check calculations I can round numbers in a calculation to help me estimate the answer to the calculation Visualise 3-D objects from 2-D drawings; make nets of common solids If I see a drawing of a cube or a pyramid I can visualise the solid shapes I can make a net for an open cube and fold it to check that it is correct Draw polygons and classify them by identifying their properties, including their line symmetry I know facts about regular polygons such as the number of sides and number of angles I can pick out irregular polygons that have at least one right angle Focus of using and applying Report solutions to puzzles and problems, giving explanations and reasoning orally and in writing, using diagrams and symbols I can explain to the class how I solved a problem I can draw a diagram to show how I solved a problem Identify and use patterns, relationships and properties of numbers or shapes; investigate a statement involving numbers and test it with examples I can use what I know about polygons to group them into regular and irregular polygons Solve one-step and two-step problems involving numbers, money or measures, including time; choose and carry out appropriate calculations, using calculator methods where appropriate I can work out how to solve problems with one or two steps I can decide what calculation to work out and whether a calculator will help me I can think about the numbers in a calculation and choose a good way to do the calculation Focus on speaking and listening: Listen to a speaker and make notes on the talk I can listen to and understand how other people solved a problem. I can decide which method I think is the best Securing number facts, understanding shapes Year 4 18 and Year 5 19, 59 Year 4 72 Year 4 104 Year 4 102, 104 Year 4 76 Use efficient written methods to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places I can explain each step when I write addition and subtraction calculations in columns Recall quickly multiplication facts up to 10 × 10 and use them to multiply pairs of multiples of 10 and 100; derive quickly corresponding division facts I can use tables facts to multiply multiples of 10 and 100 and to find linked division facts Identify pairs of factors of two-digit whole numbers and find common multiples (e.g. for 6 and 9) I can find pairs of factors that multiply to make a given number I can find a number that is a multiple of two different numbers Use knowledge of rounding, place value, number facts and inverse operations to estimate and check calculations I can check whether a calculation is correct and explain how I did this Year 5 49, 51 Year 5 59, 65 Year 5 21 Year 5 73 Identify, visualise and describe properties of rectangles, triangles, regular polygons and 3-D solids; use knowledge of properties to draw 2-D shapes and identify and draw nets of 3-D shapes I can describe the important features of shapes such as rectangles I know the important features of a cube. I can use these to draw its net Year 5 103, 105 & Year 6 105 Focus of using and applying Explore patterns, properties and relationships and propose a general statement involving numbers or shapes; identify examples for which the statement is true or false I can sort numbers or shapes according to their properties and explain how I sorted them Year 5 17,19,21, 79, 81 Year 4 16, 18, 78, 80 Year 4, 56,74,8 2, 84, 86, 88, 100 and Year 5 75 Focus on speaking and listening: Identify different question types and evaluate impact on audience I know that when my teacher asks certain mathematical questions there may be more than one answer. I try to think of all the possible answers Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Securing number facts, understanding shapes Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Y4 previous learning: Check that children can already: recall addition and subtraction facts for each number to 20 • recall multiplication and division facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 10 times-tables • say a subtraction fact that is the inverse of an addition fact, and a multiplication fact that is the inverse of a division fact, and vice versa • identify the calculation needed to solve a one-step problem • name common 2-D and 3-D shapes, and recognise a 3-D shape from a 2-D drawing of it • draw a line of symmetry in a 2-D shape • choose their own criterion for sorting a set of shapes Y4 vocabulary for this unit Additional Y5 vocabulary for this unit problem, solution, calculator, calculate, calculation, equation, operation, inverse, answer, method, explain, predict, reason, reasoning, pattern, relationship, rule, sequence, sort, classify, property formula, criterion/criteria, generalise, general statement add, subtract, multiply, divide, sum, total, difference, plus, minus, product, quotient, remainder, factor, multiple, divisor, round integer, square number, divisible by, operation, inverse, double, halve, estimate, approximate vertex, vertices, face, edge side, parallel, perpendicular, angle, degree (°), acute, obtuse, protractor, angle measurer, names of shapes, , scalene triangle, octahedron 3-D, three-dimensional, 2-D, two-dimensional, net, construct, regular, irregular, concave, convex, symmetrical, line of symmetry, vertex, vertices, face, edge, polygon, equilateral triangle, isosceles triangle, quadrilateral, rectangle, square, oblong, hexagon, heptagon, octagon Securing number facts, understanding shapes Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Year 4 Block B Identify and use patterns, relationships and properties of numbers or shapes; investigate a statement involving numbers and test it with examples Block A unit 1 Block B unit 1 Block C unit 1 Block D unit 1 Block E unit 1 Block A unit 2 Solve one-step and two-step problems involving numbers, money or measures, including time; choose and carry out appropriate calculations, using calculator methods where appropriate Block B unit 2 Block C unit 2 Block D unit 2 Block E unit 2 Block A unit 3 Block B unit 3 Block C unit 3 Block D unit 3 Block E unit 3 Use knowledge of rounding, number operations and inverses to estimate and check calculations Report solutions to puzzles and problems, giving explanations and reasoning orally and in writing, using diagrams and symbols Use knowledge of addition and subtraction facts and place value to derive sums and differences of pairs of multiples of 10, 100 or 1000 Identify the doubles of two-digit numbers; use these to calculate doubles of multiples of 10 and 100 and derive the corresponding halves Derive and recall multiplication facts up to 10 × 10, the corresponding division facts and multiples of numbers to 10 up to the tenth multiple Draw polygons and classify them by identifying their properties, including their line symmetry Visualise 3-D objects from 2-D drawings; make nets of common solids Securing number facts, understanding shapes Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Year 5 Block B Explore patterns, properties and relationships and propose a general statement involving numbers or shapes; identify examples for which the statement is true or false Block A unit 1 Block B unit 1 Block C unit 1 Block D unit 1 Block E unit 1 Block A unit 2 Block B unit 2 Block C unit 2 Block D unit 2 Block E unit 2 Block A unit 3 Block B unit 3 Block C unit 3 Block D unit 3 Block E unit 3 Represent a puzzle or problem by identifying and recording the information or calculations needed to solve it; find possible solutions and confirm them in the context of the problem Use knowledge of place value and addition and subtraction of two-digit numbers to derive sums and differences and doubles and halves of decimals (e.g. 6.5 ± 2.7, half of 5.6, double 0.34) Recall quickly multiplication facts up to 10 × 10 and use them to multiply pairs of multiples of 10 and 100; derive quickly corresponding division facts Identify pairs of factors of two-digit whole numbers and find common multiples (e.g. for 6 and 9) Use knowledge of rounding, place value, number facts and inverse operations to estimate and check calculations Use efficient written methods to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places Use a calculator to solve problems, including those involving decimals or fractions (e.g. to find 34 of 150 g); interpret the display correctly in the context of measurement Identify, visualise and describe properties of rectangles, triangles, regular polygons and 3-D solids; use knowledge of properties to draw 2-D shapes and identify and draw nets of 3-D shapes Complete patterns with up to two lines of symmetry; draw the position of a shape after a reflection or translation Securing number facts, understanding shapes Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Week Mental/Oral (rehearse, recall, 1 refine, reason, revisit, read) Objectives Activity Main Activity Objectives Key vocabulary Plenary Direct teaching Key questions Activities - (considering lower, middle and higher achievers) Indicate organisation and support. Resources (incl ICT) Review, reflect. Key questions Mon Tues Wed Thur Fri Assessment and future action Securing number facts, understanding shapes Homework Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Week Mental/Oral (rehearse, recall, 2 refine, reason, revisit, read) Objectives Activity Main Activity Objectives Key vocabulary Plenary Direct teaching Key questions Activities - (considering lower, middle and higher achievers) Indicate organisation and support. Resources (incl ICT) Review, reflect. Key questions Mon Tues Wed Thur Fri Assessment and future action Securing number facts, understanding shapes Homework Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block Week Mental/Oral (rehearse, recall, 3 refine, reason, revisit, read) Objectives Activity Main Activity Objectives Key vocabulary Plenary Direct teaching Key questions Activities - (considering lower, middle and higher achievers) Indicate organisation and support. Resources (incl ICT) Review, reflect. Key questions Mon Tues Wed Thur Fri Assessment and future action Securing number facts, understanding shapes Homework Year 4 and Year 5 Block B Unit 1 (Autumn term): 3 week block