File

Human Anatomy and Physiology I
Camden County College
John-Paul Vermitsky
The Muscles that YOU WILL NEED TO KNOW for the EXAM. Be sure to also identify where each muscle is located.
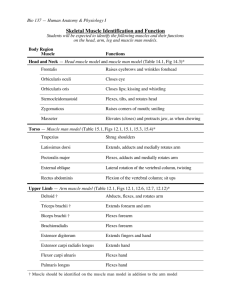
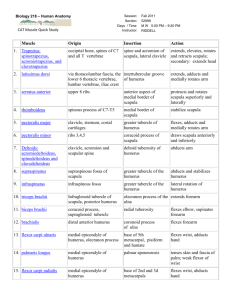
Muscle
Epicranius
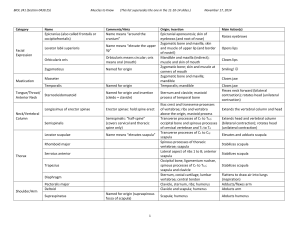
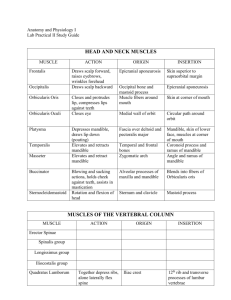
Frontalis
Occipitalis
Orbicularis oculi
Zygomaticus
Levator labii superioris
Depressor labii inferioris
Depressor anguli oris
Orbicularis oris
Mentalis
Buccinator
Platysma
Masseter
Temporalis
Sternocleidomastoid
Splenius capitus
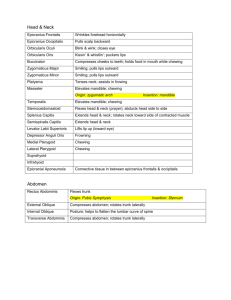
Rectus abdominus
External oblique
Internal oblique
Transverse abdominis
Diaphragm
External intercostals
Internal intercostals
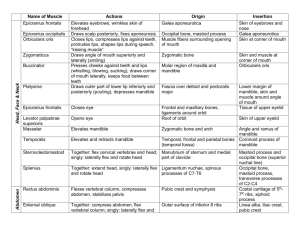
Trapezius
Rhomboideus major
Levator scapulae
Serratus anterior
Pectoralis minor
Pectoralis major
Coracobrachialis
Deltoid
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Function/Action
Consists of the occipitalis and frontalis muscles connected by the aponeurosis
Raises eyebrows and wrinkles forehead horizontally.
Pulls scalp posteriorly
Closes the eye
Pulls angle of mouth upward
Opens the lips; raises the upper lip.
Draws lower lip inferiorly
Antagonist of the zygomaticus; draws corners of mouth downward and laterally.
Closes and puckers the lips; shapes lips during speech
Protrudes lower lip and wrinkles the chin.
Compresses cheeks inward
Draws angle of mouth downward; opens mouth
Raises the mandible
Raises the mandible
Contraction of both muscles flexes head toward the chest; contraction of one muscle turns head away from contracting muscle
Contraction of both muscles extends head; contraction of one muscle turns head toward same side as contracting muscle
Tightens abdominal pelvic wall; compresses internal organs; flexes the vertebral column
Tightens abdominalpelvic wall and compresses internal organs
Tightens abdominalpelvic wall and compresses internal organs
Tightens abdominalpelvic wall and compresses internal organs
Forms floor of thoracic cavity; lowers during contraction, causing inspiration
Raises ribs upward and outward during inspiration
Draws ribs downward and inward during expiration
Elevates clavicle; adducts and elevates scapula; extends head
Adducts and elevates scapula
Elevates scapula
Pulls scapula downward and anteriorly
Pulls scapula anteriorly and downward
Adducts humerus; draws it forward across chest
Adducts and flexes humerus
Abducts, flexes, and extends humerus
Assists deltoid in abducting humerus
Rotates humerus laterally
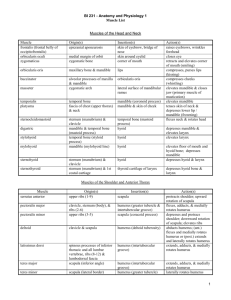
Latissimus dorsi
Teres major
Teres minor
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Brachioradialis
Triceps brachii
Flexor carpi radialis
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Palmaris longus
Extensor carpi radialis longus
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Extensor digitorum
Iliacus
Psoas major
Gluteus maximus
Gluteus medius
Tensor fascia latae
Adductor longus
Adductor magnus
Qadraiceps Femoris
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Vastus intermedialis
Hamstrings
Biceps femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Gracilis
Sartorius
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Peroneus longus
Tibialis anterior
Extensor digitorum longus
Medial pterygoid
Lateral pterygoid
Genioglossus
Hyoglossus
Styloglossus
Scalenes
Erector spinae
Adducts and extends humerus; rotates humerus medially
Extends, adducts, and rotates humerus medially
Rotates humerus laterally
Flexes and rotates forearm laterally; supination
Flexes forearm
Flexes forearm
Extends forearm
Flexes and abducts wrist
Flexes and adducts wrist
Flexes wrist
Extends and abducts the wrist
Extends and adducts wrist
Extends fingers
Flexes thigh
Flexes thigh
Extends and rotates thigh laterally
Abducts and rotates thigh medially
Flexes and abducts thigh
Adducts, flexes, and rotates thigh laterally
Adducts, flexes, and rotates thight laterally
A composite thigh muscle formed of four parts that are usually described as separate muscles. Each muscle has a common tendon that attaches to the patella and continues as the patellar ligament to the tibial tuberosity. Consists of the
Rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis and vastus intermedius.
Extends the leg and flexes the thigh
Extends leg
Extends leg
Extends leg
Three distinct muscles of the posterior thigh; consists of the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and the semimembranosus
Flexes and rotates leg laterally; extends thigh
Flexes and rotates leg medially; extends thigh
Flexes and rotates leg medially; extends thigh
Flexes and rotate leg medially; extends thigh
Flexes thigh; rotates leg medially and thigh laterally as when crossing legs
Planter flexes foot and flexes leg
Planter flexes foot
Plantar flexes and everts foot; supports arch
Dorsiflexes and inverts foot
Dorsiflexes and everts foot; extends toes
Synergist of temporalis and masseter muscles in elevation of mandible; side to side movements of the mandible with the laeral pterygoid
Protrudes mandible; provides forward sliding and side to side grinding movements of the lower teeth
Primarily protrudes tongue
Depresses tongue and draws its sides
Retracts and elevates the tongue
Elevates the first two ribs (aiding in inspiration); flexes and rotates the neck
Prime movers of back extension; consists of the iliocostalis,
Iliocostalis
Longissimus
Spinalis
Semispinalis
Quadratus lumborum
Bulbospongiosus
Ischiocavernosus
Coccygeus
Rhomboids
Levator scapulae
Suppinator
Iliopsias
Iliacus
Psoas major
Extensor digitorum brevis
Flexor digitorum brevis
Abductor hallucis
Abductor digiti minimi longissimus, spinalis
Extend vertebral column; maintain erect posture; acting on one side, bend vertebral column to same side
Extend the vertebral column and acting on one side bend it laterally
Extends the vertebral column
Extends the vertebral column and head and rotates them to opposite sides
Flexes the vertebral column laterally when acting separately; when acting together they maintain posture
Empties the male urethra; assists in the erection of the penis in males and clitoris in females
Retards venous drainage and maintains erection of penis or clitoris
Supports pelvic vicera
Act together to retract scapula, thus “squaring shoulders”; stabilizes scapula
Elevates and adducts scapula in concert with trapezius
Assists biceps brachii to forcibly supinate forearm
Iliopsias is a composite of two closely related muscles (iliacus and psoas major) whose fibers pass under the inguinal ligament to insert via a common tendon on the femur
Prime mover for flexing thigh or for flexing trunk on thigh during a bow
Prime mover for flexing thigh or for flexing trunk on thigh during a bow; also effects lateral flexion or vertebral column; important muscle in posture
Helps extend toes at metatarsophalangeal joints
Flex toes
Abducts great toe
Abducts and flexes little toe
Camden County College
Anatomy & Physiology I
The Muscles Quiz
Name ____________________________________ Date ______________________________
1.
A fascicle is a a.
Muscle b.
Bundle of muscle fibers enclosed by a connective tissue sheath c.
Bundle of myofibrils d.
Group of myofilaments
2.
The function of the T tubules in muscle contraction is to a.
Make and store glycogen b.
Release calcium into the cell interior and pick it up again c.
Transmit the action potential deep into the muscle cells d.
Form proteins
3.
During muscle contraction, ATP is provided by (a) a coupled reaction of ADP and creatine phosphate, (b) aerobic respiration of glucose, (c) anaerobic glycolysis: i.
____Which provides ATP faster? ii.
____Which does (do) not require that oxygen be available? iii.
____Which provides the highest yield of ATP? iv.
____Which results in the formation of lactic acid? v.
____Which has carbon dioxide and water products? vi.
____Which is most important in endurance sports?