summary table of meteorological hazards
advertisement
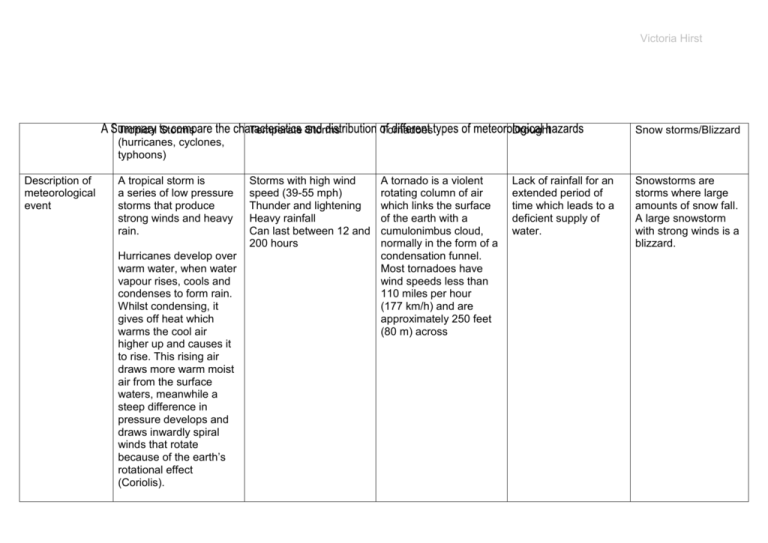
Victoria Hirst Description of meteorological event Tropical Storms (hurricanes, cyclones, typhoons) Temperate Storms Tornadoes Drought Snow storms/Blizzard A tropical storm is a series of low pressure storms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Storms with high wind speed (39-55 mph) Thunder and lightening Heavy rainfall Can last between 12 and 200 hours A tornado is a violent rotating column of air which links the surface of the earth with a cumulonimbus cloud, normally in the form of a condensation funnel. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than 110 miles per hour (177 km/h) and are approximately 250 feet (80 m) across Lack of rainfall for an extended period of time which leads to a deficient supply of water. Snowstorms are storms where large amounts of snow fall. A large snowstorm with strong winds is a blizzard. Hurricanes develop over warm water, when water vapour rises, cools and condenses to form rain. Whilst condensing, it gives off heat which warms the cool air higher up and causes it to rise. This rising air draws more warm moist air from the surface waters, meanwhile a steep difference in pressure develops and draws inwardly spiral winds that rotate because of the earth’s rotational effect (Coriolis). Victoria Hirst Distribution Started above ocean waters warmer than 26˚C Altitude: approx. 5km More than 500km from the equator so that the effect of the earth’s rotation is big enough. They occur above warm sections of the Pacific, Atlantic or Indian oceans. Prevailing winds transport the cyclones into middle latitudes. Cyclones are pushed by jet streams (strong air currents) from west to east. In the northern hemisphere, hurricanes rotate anti-clockwise, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere. 30-60 degrees latitude Tornadoes occur most frequently in USA Places - North America Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany Northern Asia: China, Russia However, they do occur on all continents in various forms. Most common in rural areas. Mainly in latitudes between 30 and 65 degrees north 446 droughts between 1968 and 1992: 62.8% in Africa 11.8% in Asia 3.4% in Europe 3.4% in Oceania Permanent droughts are found in the arid regions of the world, such as Australia, Libya, and Tunisia. Seasonal droughts are found in many areas on the margins of arid regions where precipitation levels change seasonally. Contingent drought occurs when lower than average rainfall conditions persist for months or years in areas where rainfall is expected to be higher, therefore the appropriate infrastructure to cope with less rainfall. Found in high and mid-latitudes, blizzards can be very widespread. They are most common in Russia and Central and Northeastern Asia, Northern Europe, Canada, Northern USA and Antarctica. Victoria Hirst Scale Type of hazard Subsequent hazards? Localised, but can be transported to other regions, making it more large scale. Sudden impact Heavy rain, strong winds, tornadoes and storm surges. These can cause loss of protective rainforest canopies, floods or landslides. Localised Localised Can be on a large scale Localised Sudden impact Large, occasionally destructive, waves Flooding caused by heavy rains. Thunderstorms caused by the change in air pressure Destruction caused by strong winds Sudden impact Thunderstorms and gale force winds Creeping hazard Soil erosion which can lead to landslides Sudden impact Avalanches