Effect of Recombination on Trait variability and QTL Mapping
advertisement

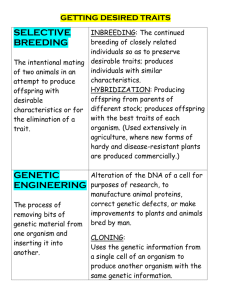
Effect of diverse germplasm and pedigree structure on quantitative traits A large number of genes typically explain why two plant genotypes differ for vegetative and reproductive traits. We can study the genetic architecture of complex traits by crossing two plant genotypes and creating two descendant populations with different genetic histories. If traits do have a complex genetic architecture, then the descendant population that has undergone several cycles of recombination should have greater variation than the descendant population that has not undergone several cycles of recombination. In addition, if traits are genetically complex, we expect to identify more loci that influence them within the descendant population that has undergone several cycles of recombination than within the descendant population that has undergone less recombination. We are using this approach to examine the genetic architecture of several vegetative and reproductive traits in corn, Zea mays. In a separate project, we are also examining the genetic diversity of maize in collaboration with Dr. Liz Lee (University of Guelph).