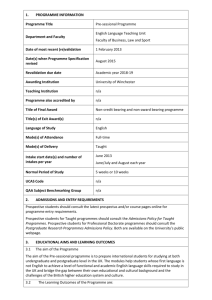
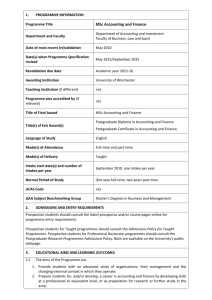
Kis and Kid-Kis proteins interact specifically with region I on the 115

Supplemental figure 1 Kis and Kid-Kis proteins interact specifically with region I on the 115-bp parD region I fragment. (A, B) show the hydroxyl radical footprinting analyses of the interactions of Kis (4.8
M) or a combination of Kid (4.8
M) and Kis
(2.4
M) with the 115-bp parD region I fragment (2 nM). Protections in the coding (A) and non coding (B) strands are indicated by black bars and dots. Lanes 1 and 4 show the cleavage patterns of the DNA without protein. Lanes 2 and 3 show the regions protected by Kis or Kid-Kis, respectively. Maxam-Gilbert AG ladder sequence is included. The sequence of the protected region is indicated. (C) Summary of the protected sites in parD region I by Kis and Kid-Kis complexes (bars and dots). The 18-bp symmetric element is boxed and the dyad symmetry axe is indicated with a broken line. The parD promoter elements, -35, extended -10 and the transcription initiation point, are in blue.
Supplemental figure 2 Interaction of Kis and Kid-Kis with parD region I and parD region II fragments. Shown is electrophoretic mobility shift assay of the binding of
Kis alone (7.5
M)or Kid and Kis (equimolar 7.5 or 15
M) to parD region I or II (375 nM). Lanes 1 and 5, complexes formed between Kis and region I and II, respectively.
Lanes 2-3 and 6-7 complexes formed between equimolar Kid-Kis mixtures (lane 2 and 6
15
M and lane 3 and 7 7.5
M) and parD region I and II, respectively. Lanes 4 and 8 present the negative controls without proteins. The specific complexes obtained are indicated with cVIII, cIX and cX.