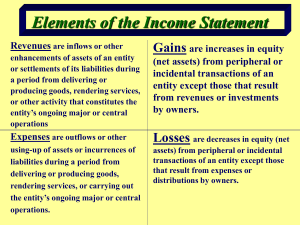
WHAT IS MANAGEMENT
advertisement

Other Teaching Tools 12.3 Video Notes 12.4 Brief Chapter Outline and Learning Goals 12.5 Lecture Outline and Lecture Notes 12.7 Career and Study Skills Notes 12.29 CAREER DEVELOPMENT: Create a Career Plan 12.29 STUDY SKILLS: Make Good Career Planning Habits a Life Skill 12.31 Lecture Links 12.32 LECTURE LINK 12-1 Managerial Accounting and the Budgeting Process 12.32 LECTURE LINK 12-2 Auditing the Audit Process 12.33 LECTURE LINK 12-3 The Power of the Internal Auditor 12.35 LECTURE LINK 12-4 It’s the Earnings that Count 12.35 LECTURE LINK 12-5 Using the Statement of Cash Flows 12.36 LECTURE LINK 12-6 Knowing the Numbers 12.37 Bonus Internet Exercises 12.39 BONUS INTERNET EXERCISE 12-1 Annual Reports Online 12.39 BONUS INTERNET EXERCISE 12-2 CPA Certification 12.40 Critical Thinking Exercises 12.41 CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-1 Budgetary Control 12.41 CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-2 Preparing a Balance Sheet 12.44 CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-3 The Pizza Stand 12.46 CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-4 Comparing Industry Ratios 12.50 12.1 CHAPTER UNDERSTANDING FINANCIAL INFORMATION AND ACCOUNTING 12 Bonus Cases 12.54 BONUS CASE 12-1 Getting Through the Hard Times at Hard Rock 12.54 BONUS CASE 12-2 Survival of the Financially Fittest 12.56 BONUS CASE 12-3 Chicago Rush: When the Goal Line Meets the 12.58 Bottom Line (Video Case) 12.2 BONUS CASE 12-4 The Best Laid Plans Often Go Awry 12.60 BONUS CASE 12-5 Managing by the Numbers 12.62 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual OTHER TEACHING TOOLS For a description of each of these valuable teaching tools, please see the Preface in this manual. Student Learning Tools Student Online Learning Center (OLC) www.mhhe.com/diasbusiness Student Study Guide Spanish Translation Glossary (OLC) Spanish Translation Quizzes (OLC) Instructor Teaching Tools Annotated Instructor’s Resource Manual IRCD (Instructor’s Resource Manual, Test Bank, PowerPoints, EZtest) Asset Map Online Learning Center (OLC) www.mhhe.com/diasbusiness PageOut PowerPoint Presentations (on IRCD and OLC) Test Bank Business Videos on DVD Enhanced Cartridge option Spanish Translation Glossary (OLC) CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.3 VIDEO NOTES Twenty videos are available, geared to individual chapter topics. The teaching notes for these videos are also included in the Video Notes section of this Instructor’s Resource Manual, beginning on page V.1. VIDEO 12: “Chicago Rush: When the Goal Line Meets the Bottom Line” This video features the Chicago Rush, an arena football team. On the field and off the field, numbers are critical. The video shows how Chicago Rush’s management uses accounting to provide key financial information to stakeholders. (BONUS CASE 12-3, “Chicago Rush: When the Goal Line Meets the Bottom Line” on page 12.58 of this manual relates to this video.) 12.4 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual BRIEF CHAPTER OUTLINE AND LEARNING GOALS CHAPTER 12 Understanding Financial Information and Accounting I. INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTING II. THE IMPORTANCE OF FINANCIAL INFORMATION ► A. LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 Describe the importance of financial information and accounting. What Is Accounting? III. AREAS OF ACCOUNTING ► LEARNING OBJECTIVE 2 Define and explain different areas of accounting. A. Managerial and Financial Accounting B. Auditing C. Tax Accounting D. Government and Not-for-Profit Accounting E. Accounting Tools F. Sarbanes-Oxley Act IV. THE SIX-STEP ACCOUNTING CYCLE ► LEARNING OBJECTIVE 3 List the steps in the accounting cycle. V. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS ► LEARNING OBJECTIVE 4 Explain how the major financial statements differ. A. The Accounting Equation B. The Balance Sheet C. 1. Assets 2. Liabilities The Income Statement 1. Revenue CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.5 2. Cost of Goods Sold (Cost of Goods Manufactured) 3. Operating Expenses and Net Profit or Loss D. The Statement of Cash Flows E. A Word about Depreciation VI. ANALYZING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS: RATIO ANALYSIS ► LEARNING OBJECTIVE 5 Explain the importance of ratio analysis in reporting financial information. A. Liquidity Ratios B. Leverage (Debt) Ratios C. Profitability (Performance) Ratios D. 1. Earnings per Share 2. Return on Sales (Net Profit Margin) 3. Return on Equity Activity Ratios VII. SUMMARY 12.6 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE AND LECTURE NOTES CHAPTER OPENING PROFILE R. J. Julia Booksellers (Text pages 384-385) Roxanne Coady, a former corporate accountant, started a new business—R.J. Julia Booksellers. Coady’s business was successful for its first five years, with growth of 30-75%. However, after that the company began experiencing problems. Coady belatedly put her accounting knowledge to use and discovered that her love of books had affected her business decision making. She began studying the firm’s financial statements on a regular basis, refocusing on the bottom line. LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTING A. Businesspeople need to understand the business’s financial numbers. B. Basic accounting information can help businesses better understand and control their operations. C. This chapter presents basic accounting information and explains the basic accounting statements and what they mean to business. II. THE IMPORTANCE OF FINANCIAL INFORMATION ► LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1 Describe the importance of financial information and accounting. (Text pages 386-387) A. All individuals need a basic working knowledge of accounting. 1. Accounting has a unique language. 2. Many people use accounting information, not just managers. B. What Is Accounting? 1. ACCOUNTING is the recording, classifying, summarizing, and interpreting of financial events and transactions to CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting LECTURE NOTES POWERPOINT 12-1 Chapter Title (Refers to text page 384) POWERPOINT 12-2 Learning Objectives (Refers to text page 385) POWERPOINT 12-3 The Importance of Financial Information (Refers to text pages 386387) TEXT REFERENCE Real World Business Apps (Box in text on page 387) John Miller opened a candle store and has expanded his product line. He soon decided that handling his own recordkeeping was more complicated than he anticipated. He has decided to call in an accountant to help manage his finances. 12.7 LECTURE OUTLINE LECTURE NOTES provide management and other interested parties with the information they need to make good decisions. a. Financial transactions include: i. buying and selling goods and services; ii. acquiring insurance; iii. paying employees; iv. using supplies. b. Transactions are usually classified into groups with common characteristics. c. An accounting system is the method used to record and summarize accounting data into reports. 2. Purposes of accounting: a. To give managers basic financial information so they may make better decisions; b. To report financial information to people outside the firm such as owners, creditors, suppliers, employees, investors, and the government. C. Accounting is used to measure and report financial information to the various stakeholders about the economic activities of the firm. III. AREAS OF ACCOUNTING ► 12.8 LEARNING OBJECTIVE 2 Define and explain different areas of accounting. (Text pages 388-393) BONUS CASE 12-1 Getting Through the Hard Times at Hard Rock Theme-dining businesses encountered difficulties in the early 2000s. To survive, Hard Rock Café recruited a new financial manager and changed its financial reporting and information structure. (See complete case, discussion questions, and suggested answers on page 12.54 of this manual.) BONUS CASE 12-2 Survival of the Financially Fittest “Non-profit” may mean no profit, but non-profit organizations need money to function. Financial management at non-profits is complicated and challenging. (See complete case, discussion questions, and suggested answers on page 12.56 of this manual.) POWERPOINT 12-4 Areas of Accounting (Refers to text pages 388389) INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE A. The accounting profession is divided into five areas. B. Managerial and Financial Accounting 1. Definitions a. MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING provides information and analysis to managers within the organization to assist them in decision making. b. FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING generates information for use outside the organization. c. Managerial accounting is concerned with: i. measuring and reporting costs of production, marketing, and other functions (cost accounting); ii. preparing budgets (planning); iii. checking whether or not units are staying within their budgets (controlling); iv. designing strategies to minimize taxes (tax accounting). d. The information prepared by financial accounting is used by: i. company owners, managers, and employees; ii. creditors and lenders; iii. employee unions, customers, suppliers, government agencies, and the general public. 2. Financial accountants are responsible for preparing the ANNUAL REPORT, CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting LECTURE NOTES LECTURE LINK 12-1 Managerial Accounting and the Budgeting Process In addition to the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, managers need other forms of financial information, especially information for budgeting and cost accounting. (See complete lecture link on page 12.32 of this manual.) CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-1 Budgetary Control This exercise is a continuation of LL 12-1 above. It asks the student to analyze a company’s monthly budgetary report to determine which expenses are over or under budget. (PPT 12-5 below can be used with this exercise. Also see complete exercise on page 12.41 of this manual.) POWERPOINT 12-5 Budgetary Control Weinstein Manufacturing Inc. (Use with CTE 1-1 above. Refers to text pages 388-389) BONUS INTERNET EXERCISE 12-1 Annual Reports Online This Internet exercise asks the student to explore the annual report of a specific company by visiting the company’s Web site. (See complete exercise on page 12.39 of this manual.) 12.9 LECTURE OUTLINE 3. 12.10 LECTURE NOTES a yearly statement of the financial condition, progress, and expectations of an organization. Professions: a. A CERTIFIED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTANT (CMA) is a professional accountant who has met certain educational and experience requirements, passed a qualifying exam in the field, and has been certified by the Institute of Certified Management Accountants. b. A CERTIFIED PUBLIC ACCOUNTANT (CPA) is an accountant who has passed a series of examinations established by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) and does accounting work for no one particular firm. c. A PRIVATE ACCOUNTANT is an accountant who works for a single firm, government agency, or nonprofit organization, on the payroll of the company or organization. d. A PUBLIC ACCOUNTANT is an accountant who does not work for a specific company. e. Public accountants help firms by: i. designing an accounting system for a firm; ii. helping select the correct computer and software to run the system; BONUS CASE 12-3 Chicago Rush: When the Goal Line Meets the Bottom Line (Video Case) This bonus case ties in with the video available for use with this chapter. The Chicago Rush of the Arena Football League generates a lot of statistics, both on the field and financial. (See complete case, discussion questions, and suggested answers on page 12.58 of this manual.) BONUS INTERNET EXERCISE 12-2 CPA Certification This Internet exercise directs students to the AICPA Web site to investigate the requirements and details of the Uniform CPA Examination. (See complete exercise on page 12.40 of this manual.) INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE iii. analyzing the financial strength of an organization. 4. Professional accounting assures the users of financial information that financial reports of organizations are accurate. a. The independent FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD (FASB) is the group that oversees accounting practices. b. Users know the information is reported professionally if financial reports are prepared in accordance with GENERALLY ACCEPTED ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES (GAAP), a set of principles followed by accountants in preparing results. C. Auditing 1. AUDITING is the job of reviewing and evaluating the records used to prepare the company’s financial statements. a. Accountants within the organization often perform internal audits to make sure the organization is using proper accounting procedures. b. Public accountants also conduct independent audits of accounting records. 2. An INDEPENDENT AUDIT is an evaluation and unbiased opinion about the accuracy of company’s financial statements. 3. A certified internal auditor (CIA) is an CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting LECTURE NOTES POWERPOINT 12-6 Auditing (Refers to text pages 389-391) LECTURE LINK 12-2 Auditing the Audit Process To remedy some of the problems revealed by recent accounting scandals, Congress passed the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. (See complete lecture link on page 12.33 of this manual.) LECTURE LINK 12-3 The Power of the Internal Auditor The largest bankruptcy in U.S. history started when an internal auditor followed an unexplained piece of financial information. (See complete lecture link on page 12.35 of this manual.) 12.11 LECTURE OUTLINE LECTURE NOTES accountant who has a bachelor’s degree and two years of experience in internal auditing, and who has passed an exam administered by the Institute of Internal Auditors. D. Tax Accounting 1. All levels of government require that the business submit tax returns, filed at specific times and in a precise format. 2. A tax accountant is an accountant trained in tax law and responsible for preparing tax returns and developing tax strategies. 3. As the burden of taxes grows, the role of the tax accountant becomes more important. E. Government and Not-for-Profit Accounting 1. Government and not-for-profit accounting is the accounting system used by organizations whose purpose is not generating a profit. 2. The purpose of these organizations is to serve ratepayers, taxpayers, and others according to a duly approved budget. 3. Users of government accounting information, such as citizens and special interest groups, want to ensure that government is making the proper use of taxpayers’ money. 4. GOVERNMENTAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD (GASB) is the group that sets standards for govern- 12.12 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE F. mental agencies’ accounting practices. 5. Not-for-profit organizations need trained accountants since contributors want to see exactly how and where the funds are being spent. a. BOOKKEEPING is the recording of business transactions. b. Accountants classify and summarize financial data according to formal standards. Accounting Tools 1. A JOURNAL is the record book in accounting (can also be a computer program). a. Transactions for each day, week, or month are kept in the journal. b. The journal’s main purpose is to have a chronological listing of the business transactions that take place. 2. DOUBLE-ENTRY BOOKKEEPING is the concept of writing (or typing) every transaction in two places. a. Accountants can check one list against the other to make sure they add up to the same amount. b. In double-entry bookkeeping, two entries in the journal are required for each company transaction. 3. A LEDGER is a specialized accounting book or computer program in which information from accounting journals is accumulated into specific categories. 4. Recording transactions into categories CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting LECTURE NOTES POWERPOINT 12-7 Accounting Tools (Refers to text pages 391393) TEXT REFERENCE Thinking Critically: The Enron Fallout Fell Out Years Ago (Box in text on page 392) The most important legacy of the corporate scandals of the 1990s is the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) that dramatically changed corporate responsibility for financial reporting. 12.13 LECTURE OUTLINE LECTURE NOTES allows managers to easily find the data needed to make decisions. G. Sarbanes-Oxley Act 1. The SARBANES-OXLEY ACT, signed into law in 2002 after many accounting scandals, requires higher standards of accounting practices and auditing firms. 2. Criticisms: a. Businesses feel the standards are too stringent and limit their ability to make business decisions. b. Supporters feel that the law protects the American public, but does not go far enough. SELF CHECK QUESTIONS (Text page 393) 1. Define accounting. 2. What is the difference between managerial accounting and financial accounting? 3. Name and describe the five working areas of accounting. IV. THE SIX-STEP ACCOUNTING CYCLE ► LEARNING OBJECTIVE 3 List the steps in the accounting cycle. (Text pages 393-394) A. The accounting cycle is a six-step procedure for preparing and analyzing the major financial statements. B. The six-step accounting cycle includes: 1. Step 1. Analyzing and categorizing documents; 2. Step 2. Putting the information into journals; 12.14 TEXT FIGURE 12.1 The Steps in the Accounting Cycle (Box in text on page 394) POWERPOINT 12-8 The Six-Step Accounting Cycle (Refers to text pages 393-394) INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE 3. 4. 5. 6. LECTURE NOTES Step 3. Posting that information into ledgers; Step 4. Preparing a TRIAL BALANCE (a summary of all the data in the account ledgers to check whether the figures are correct and balanced); Step 5. Preparing an income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows; Step 6. Analyze the financial statements and determine the financial health of company. V. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS ► LEARNING OBJECTIVE 4 Explain how the major financial statements differ. (Text pages 394-406) A. A FINANCIAL STATEMENT is the summary of all transactions that have occurred over a particular period. 1. These indicate a firm’s financial health and stability. 2. The key financial statements are: a. The balance sheet, which reports the firm’s financial condition on a specific date; b. The income statement (or profit and loss statement, or “P&L” for short, reports revenues, expenses, and profits (or losses) for a specific period of time; c. The statement of cash flows, which provides a summary of money coming into and going out of the firm. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting POWERPOINT 12-9 Financial Statements (Refers to text pages 394396) TEXT REFERENCE Study Skills: Make Good Study Habits a Life Skill (Box in text on page 395) An additional exercise and discussion is available page 12.31 of this manual. 12.15 LECTURE OUTLINE LECTURE NOTES 3. The differences among the financial statements: a. The balance sheet details what the company owns and owes on a certain day. b. The income statement shows what a firm sells its products for and what its selling costs are over a specific period. c. The statement of cash flows shows the difference between cash coming in and cash going out of a business. B. The Accounting Equation 1. If you owe no money (liability) the sum of your assets is your equity. 2. If you incur a liability, your assets are equal to what you owe plus what you own. 3. In accounting terms: assets = liabilities + owners’ equity 4. Owner’s equity is a way of stating the difference between what is owned versus what is owed. 5. The fundamental accounting equation—owner’s equity and liabilities will always be the same number as assets—is the basis for the balance sheet. C. The Balance Sheet 1. A BALANCE SHEET is the financial statement that reports a firm’s financial condition at a specific time. a. The term balance sheet implies a 12.16 POWERPOINT 12-10 The Balance Sheet (Refers to text pages 396398) INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE 2. balance between two figures– assets on one side and liabilities and owners equity on the other. b. To create your personal balance sheet, you add up everything you own, and then subtract the money you owe others. c. A balance sheet can help managers make business decisions. d. Understanding the balance sheet gives managers a picture of the company’s financial health. ASSETS are economic resources (things of value) owned by the company. a. Assets include productive, tangible items that generate income, as well as intangibles of value. b. Intangiblessuch as brand names, trademarks, and copyrightscan be among the firm’s most valuable assets. c. Assets are characterized based on LIQUIDITY, how fast an asset can be converted into cash. i. For example, an ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE is the amount of money owed to the firm that it expects to be paid within one year. ii. Current assets are items that can or will be converted to cash within one year. iii. Fixed assets are long-term assets that are relatively per- CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting LECTURE NOTES TEXT FIGURE 12.2 Classification of Assets (Box in text on page 397) 12.17 LECTURE OUTLINE 3. 12.18 LECTURE NOTES manent, also referred to as property, plant, and equipment. iv. Intangible assets are longterm assets (e.g., patents, trademarks, copyrights) that have no real physical form but do have value. LIABILITIES are what the business owes to others (debts). a. Current liabilities are debts due in one year or less. b. Long-term liabilities are debts not due for one year or longer. c. Common liability accounts: i. Accounts payable are current liabilities involving money owed for merchandise and services purchased on credit but not paid for yet. ii. Notes payable are short-term or long-term liabilities that a business promises to repay by a certain date. iii. Bonds payable are long-term liabilities that represent money lent to the firm that must be paid back. d. Equity i. The value of things you own (assets) minus the amount of money you owe others (liabilities) is called equity. ii. The value of what stockholders own in a firm (minus lia- TEXT FIGURE 12.3 Sample Very Vegetarian Balance Sheet (Box in text on page 399) CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-2 Preparing a Balance Sheet This exercise directs students to use a given list of accounts to create a balance sheet. (See complete exercise on page 12.44 of this manual.) INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE bilities) is called stockholders’ equity (or shareholders’ equity). iii. OWNERS’ EQUITY is the amount of the business that belongs to the owners minus any liabilities owned by the business. iv. The formula for owners’ equity: owners’ equity = assets - liabilities. e. The balance sheet shows all the assets the company has and also what it owes. D. The Income Statement 1. The INCOME STATEMENT (also called the profit and loss statement) summarizes: a. all the resources (called revenue) that have come into the firm from operating activities; b. the money resources that were used up; c. the expenses incurred in doing business; d. what resources were left after all costs and expenses, including taxes, were paid out. 2. Net income or net loss is revenue left over after all costs and expenses, including taxes, are paid. a. The income statement reports the results of operations over a particular period of time. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting LECTURE NOTES POWERPOINT 12-11 The Income Statement (Refers to text pages 398403) 12.19 LECTURE OUTLINE LECTURE NOTES b. 3. 4. 12.20 The income statement is arranged according to the following formula: revenue – cost of goods sold = gross profit (gross margin) – operating expenses = net income before taxes – taxes = net income (or loss) c. The income statement includes valuable financial information for stockholders, lenders, investors, and employees. REVENUE is the value of what is received for goods sold, services rendered, and other financial sources. a. There is a difference between revenue and sales. b. Most revenue comes from sales, but other sources of revenue include rents earned, interest earned, and so forth. c. GROSS SALES are the total of all sales the firm completed. d. NET SALES are gross sales minus returns, discounts, and allowances. COST OF GOODS SOLD (COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED) is a measure of the cost of merchandise sold, or the cost of raw materials and supplies used for producing items for resale. a. The cost of goods sold includes the purchase price plus any costs TEXT FIGURE 12.4 Sample Very Vegetarian Income Statement (Box in text on page 400) LECTURE LINK 12-4 It’s the Earnings That Count When one entrepreneur approached venture capitalists for expansion capital, he learned that revenue was not as important as the bottom line, net profit. (See complete lecture link on page 12.35 of this manual.) INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE 5. associated with obtaining and storing the goods. b. Most retailers don’t have to consider the cost of raw materials, so their main concern is purchase price and storage cost. c. GROSS PROFIT (GROSS MARGIN) is how much a firm earned by buying (or making) and selling merchandise, without expenses. d. The gross margin doesn’t tell you everything—you must subtract expenses to determine net profit or loss. Operating expenses and net profit or loss a. OPERATING EXPENSES are costs involved in operating a business, such as rent, utilities, and salaries. b. Operating expenses can be classified into two categories: i. Selling expenses are expenses related to the marketing and distribution of the firm’s goods or services. ii. General expenses are administrative expenses of the firm. iii. There are also non-operating expenses, such as interest. c. After all expenses are deducted, the firm’s net income before taxes is determined. i. After allocating for taxes, you get to the bottom line, the net CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting LECTURE NOTES TEXT FIGURE 12.5 Example of Cost of Goods Sold for a Retail Store (Box in text on page 402) CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-3 The Pizza Stand A student organization plans to operate a pizza stand during the homecoming weekend. This exercise asks students to prepare a budget and calculate expected profit. (See complete exercise on page 12.46 of this manual.) 12.21 LECTURE OUTLINE LECTURE NOTES income (or perhaps net loss). ii. This figure is what the firm incurred from revenue minus sales returns, costs, expenses, and taxes. iii. Net income can also be referred to as net earnings or net profit. d. Businesses need to keep track of how much money they earn, spend, how much cash they have on hand, and so on. 6. Users of financial information are very interested in the flow of cash into and out of a business. E. The Statement of Cash Flows 1. The STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS reports cash receipts and disbursement related to the firm’s three major activities. a. Operations: cash transactions associated with running the business; b. Investments: cash used in or provided by the firm’s investment activities; c. Financing: cash raised from the issuance of new debt. 2. Accountants analyze all of the cash changes that have occurred from operating, investing, and financing to determine the firm’s net cash position. 3. The statement of cash flows is different from the income statement. a. The statement of cash flows 12.22 POWERPOINT 12-12 The Statement of Cash Flows (Refers to text pages 403-406) LECTURE LINK 12-5 Using the Statement of Cash Flows Companies do not go out of business because they report net losses—they fail because they run out of cash. (See complete lecture link on page 12.36 of this manual.) BONUS CASE 12-4 The Best Laid Plans Often Go Awry This case discusses how offering credit to customers affected the finances of a pottery import firm. (See complete case, discussion questions, and suggested answers on page 12.60 of this manual.) INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE shows the cash position, how much money is on hand at any given time. b. Companies don’t want to have too much money on hand, but do need to have enough to pay their expenses. 4. A business can increase sales and increase profit and still have cash flow problems. A Word About Depreciation 1. DEPRECIATION is the systemic writeoff of the cost of a tangible asset over its estimated useful life. 2. Assets such as equipment and machinery are considered depreciable subject to accounting rules. 3. Companies are permitted to recapture the cost of assets using depreciation as a business operation expense. 4. There are several ways to calculate depreciation. F. SELF CHECK QUESTIONS (Text page 406) 1. What does an income statement show? What about a statement of cash flow? 2. How are these statements useful for small businesses? 3. What is the accounting equation? 4. What is depreciation? LECTURE NOTES TEXT FIGURE 12.6 Sample Very Vegetarian Statement of Cash Flows (Box in text on page 404) BONUS CASE 12-5 Managing by the Numbers This case discusses how financially knowledgeable workers helped improve one company’s finances. (See complete case, discussion questions, and suggested answers on page 12.62 of this manual.) TEXT REFERENCE Career Development: Create a Career Plan (Box in text on page 405) An additional exercise and discussion is available on page 12.29 of this manual. TEXT REFERENCE Ethical Challenge: The Accounting Hot Seat (Box in text on page 406) The owner of a small cabinet builder has asked the accountant to shift revenues from one fiscal year back to the previous one. What is the legal and/or ethical thing to do? VI. ANALYZING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS: RATIO ANALYSIS ► LEARNING OBJECTIVE 5 Explain the importance of ratio analysis in reporting financial information. (Text pages 406-413) A. Accountants use financial information to CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.23 LECTURE OUTLINE LECTURE NOTES perform financial calculations, called ratios. 1. Financial ratios help in analyzing the actual performance of the company compared to its financial objectives. 2. RATIO ANALYSIS is the assessment of a firm’s financial condition and performance through calculations and interpretations of financial ratios developed from the firm’s financial statements. 3. They also give insight into the firm’s performance compared to other firms in the industry. 4. There are four types of ratios businesses use to measure financial performance. a. liquidity (speed of changing assets into cash); b. debt (leverage); c. profitability; d. business activity. B. Liquidity Ratios 1. Liquidity ratios measure the company’s ability to turn assets into cash to pay its short-term debts. 2. These short-term debts are expected to be repaid within one year. 3. The current ratio is the ratio of a firm’s current assets to its current liabilities. a. current ratio = current assets current liabilities b. 12.24 POWERPOINT 12-13 Analyzing Financial Statements: Ratio Analysis (Refers to text pages 406408) Usually, a company with a current ratio of 2 or greater is considered INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE a safe credit risk. c. The ratio should be compared to that of competing firms within the industry and to the company’s current ratio in the previous year. 4. The acid-test ratio (or quick ratio) measures the cash, marketable securities (stocks and bonds), and receivables of the firm, compared to its current liabilities. a. acid-test ratio = (cash + accounts receivable + marketable securities) ÷ current liabilities b. A number between 0.50 and 1.0 is usually considered satisfactory. C. Leverage (Debt) Ratio 1. Leverage (debt) ratios measure the degree to which a firm relies on borrowed funds in its operations. 2. The debt to owners’ equity ratio measures the degree to which the company is financed by borrowed funds that must be repaid. a. debt to owners’ equity ratio = total liabilities owners’ equity b. A ratio above 100% shows that a firm has more debt than equity. 3. It is important to compare ratios to those of other firms in the same industry and to the company’s ratios in previous years. D. Profitability (Performance) Ratios 1. Profitability (performance) ratios CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting LECTURE NOTES POWERPOINT 12-14 Leverage (Debt) Ratios (Refers to text pages 408-413 TEXT FIGURE 12.7 Industry Ratio Averages 12.25 LECTURE OUTLINE 2. 3. 4. 12.26 LECTURE NOTES measure how effectively a firm is using its various resources to achieve profits. Management’s performance is often measured by using profitability ratios. a. Basic earnings per share (basic EPS) measures the amount of profit earned by a company for each share of common stock it has outstanding. Earnings per share a. The diluted earnings per share (diluted EPS) ratio measures the amount of profit earned by a company for each share of outstanding common stock, but also takes into consideration stock options, warrants, preferred stock, and convertible debt securities that can be converted into common stock. b. EPS is an important ratio because earnings help stimulate growth. c. earnings per share = net income after taxes num. com. stock outstanding d. A larger number would mean the company either has high net income or does not have any outstanding stock. Return on sales (net profit margin) a. This measures the return on sales based on how much profit a company earns for every dollar it generates in revenue. b. return on sales = net income (Box in text on page 409) TEXT REFERENCE Career Spotlight: So You Want to Be … an Accounting Professional (Box in text on page 412) TEXT FIGURE 12.8 Putting Together Ratio Analysis (Box in text on page 412) INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE OUTLINE net sales c. This ratio is an indicator of the company’s ability to generate income from sales. 5. Return on equity a. The higher the risk involved in an industry, the higher the return investors expect. b. It is calculated by comparing a company’s net income with its total owner’s equity. c. return on equity = net income after taxes total owners’ equity d. It is best to compare this ratio with other firms in the same industry. E. Activity Ratios 1. Activity ratios measure how well a company converts its resources to profits. 2. Inventory turnover ratio measures the speed of inventory moving through the firm and its conversion into sales. 3. The more efficiently a firm manages its inventory, the higher the return. a. inventory turnover ratio = cost of goods sold average inventory b. In most retail firms, a turnover of 4 would be acceptable. c. A lower than average inventory turnover ratio often indicates obsolete merchandise on hand or poor buying practices. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting LECTURE NOTES LECTURE LINK 12-6 Knowing the Numbers Employees at Setpoint know more about their company’s finances than most investors do. See complete lecture link on page 12.37 of this manual. TEXT REFERENCE Real World Business Apps (Box in text on page 413) John Miller has met with an accountant about his financial situation. Ashley, the accountant, has explained the role of the certified public accountant and has given John an overview of the financial reporting system. CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-4 Comparing Industry Ratios An investor is considering investing in a regional hotel chain. This exercise lets students compare the financial results for four possible investments. (See complete exercise on page 12.50 of this manual.) 12.27 LECTURE OUTLINE LECTURE NOTES F. Finance professionals use several other specific ratios to learn more about a firm’s financial condition. SELF CHECK QUESTIONS (Text page 413) 1. What is the current ratio used for? 2. What does debt to owners’ equity tell us? 3. What is the major benefit of performing a ratio analysis using the financial statements? VII. SUMMARY 12.28 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual CAREER AND STUDY SKILLS NOTES CAREER DEVELOPMENT BOX: Create a Career Plan (Text page 412) Instructor’s Notes for Text Box Twelve:(Objectives to consider and implement to increase students’ knowledge, usage, and understanding of the concepts). At some point, all successful students will think through the career process and learn to establish some sort of plan. Without much help, this plan might have very low expectations, and not be very helpful to the student’s career. To help in this process, showing students how to do career planning and helping them write career goals is an important function! STUDENT EXERCISE: Review the following outline regarding career planning. Have students spend time developing their answers and discuss their career plans in class. Make note of the various answers and thoughts that each students formulates about their own career ideas. Career Planning & Forecasting Short-Medium-Long Range Goals One of the most important elements to writing your career plan is the ability to have a sense of the goals you have set for yourself and for your career. How you arrive at these goals is discussed throughout this text. How you move successfully toward these goals are the methods of short-term, medium range, and long-term goals. The question that is most asked is how do I begin to set career and personal goals? From this question the real work begins. If you are not familiar with this process, start with basic goals. Questions like the following must first be asked: (1) What type of job would you like to have in the next year, five years, and ten years? (job description, pay, title, etc.) (2) What industry would this job/career be in? (3) What is the state of affairs of this industry (new, high growth, slow growth but stable, stagnant, losing sales, and companies that compete)? (4) What are the types of job(s) available which use your skills as they are today? (5) What new or better skills would you need to enhance your chance of getting the type of job you would like? (6) Name five companies you would like to work for in the industry you are interested in. (7) Name two other jobs/industries that would be your second and third choices if you do not get work in the job/industry of your preference. (8) Find someone working in the position you would like to have over the next year and find out what they do (job duties) and how their position functions in the company. Find a per- CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.29 son doing the job/work you would like to be doing in the next five years and ten years and interview them with the same set of questions. (9) Note your success in jobs you currently hold or have held in the past. (10) How can you use these success/skills in your current or future job? (11) What areas could you improve upon to accentuate your career? (12) What personal goals do you have for the next year, five years, and ten years? (13) How do these personal goals accentuate your job/career? (14) How do these personal goals change the job opportunities you might consider? (15) How do you feel about your career to date? (16) If you change what you are currently doing, what would that be? Explain. (17) What help/assistance would benefit you in your career? (18) How willing are you to change current skills/attitudes to better your career? (19) What feedback have you gotten so far from immediate bosses on your job performances? (20) What are the positives? What are the negatives? Where can you improve? Long-term goals are met with high success when a person can (1) identify what they are in some detail, (2) use a format to express long-term, mid-term and short-term goal setting, (3) understand that mid-term goals are a measure of how successful you have been in pursuit of your long-term goals; and short-term goals are the yearly objectives to reaching mid-term and long-term goals. Based on this, use the following to express your long-term, mid-term and short-term goals: 12.30 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual STUDY SKILLS BOX: Make Good Career Planning Habits a Life Skill (Text page 395) Instructor’s Notes for Text Box Twelve:(Objectives to consider and implement to increase students’ knowledge, usage, and understanding of the concepts). A successful interview, well written résumé, and good etiquette habits are a real positive for any and all students. To refresh your career assessment and implementation, here is a reminder of the basics of what you will need to do to stay on course regarding establishing good career skills. Use the BORD method. Balance, Organization, Routine and Discipline (BORD) will maintain the process no matter how your job, school, personal life or professional life might be going (sometimes some areas are going well, sometimes not). You will know that the process is the same, and you can expect an outcome that meets your needs at the time. When you BALANCE all your responsibilities in a series of priorities, you have a healthy approach to accomplishing your goals and objectives while achieving a high level of success. However, being able to correctly balance all your responsibilities requires that you become extremely ORGANIZED to assure that you stay on course. When you do this on a regular basis, this becomes a ROUTINE. STUDENT EXERCISES: Help students with the basic prioritizing skills. Have them discuss their own prioritizing practices and discuss both the good habits and what needs improvement. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.31 LECTURE LINKS LECTURE LINK 12-1 Managerial Accounting and the Budgeting Process In addition to the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, managers need other forms of financial information—especially for the budgeting process. They also need this information to help make decisions such as when to replace a machine, whether to hire extra people, how much wages can be raised, and if advertising should be increased or decreased. Detailed reports are needed on such things as departmental costs, special projects, cash flow, financial analyses, taxes, and labor costs. These reports, which are a part of managerial accounting, do not have to be standardized but can be tailored to the firm’s individual needs. BUDGETING AND BUDGETARY CONTROL Two of the primary functions of management are planning and control. When these two functions are combined with the accounting techniques we have studied, they provide one of management’s most useful tools: the budgeting process. This process, in turn, involves both budgeting and budgetary control. Budgeting is simply stating in dollars-and-cents terms what the firm wants to accomplish in a given period of time. Most individuals have some informal plan at the beginning of the month as to how they are going to spend their money. They know, in general, what their expected income is and what expenses they must use that money for. Businesses must use more formal plans, but they follow the same procedure an individual does— determine how much revenue will come into the firm, divide that revenue among the expenses, and determine the expected profit or loss from operations. In essence, the firm is preparing a “planned” income statement when it sets up a budget. The starting point in budgeting is estimating expected revenue, which is the total amount of goods or services that company expects to sell. For management to get an accurate figure, the firm’s sales department must give a realistic estimate of probable sales. This figure will be a blend of past sales figures, expected business conditions, and company objectives. For example, if 1,200,000 units are to be sold, and the expected price per unit is $7.00, the total revenue should be $8,400,000. Next, expected expenses are calculated by the departments in the firm that will be involved. The production department should submit a plan showing how much it will cost to produce those items, including such costs as raw materials, wages, electricity, and maintenance. The marketing department should develop a plan for sales activities such as advertising, personal selling, and sales promotion. Then administrative, depreciation, and other costs must be computed. After all the firm’s departments have submitted their estimates, management can calculate the projected net income by subtracting total expected expenses from expected revenues. At this point, management adds its plans and projections to the raw figures and begins “finetuning” the budget. The departmental budgets may be sent back for further work and the first few steps repeated until a comprehensive budget acceptable to all is created. Each department then develops a departmental budget based on the figures in the comprehensive budget. The budgeting process does not end here. The only thing you have at this point is a plan, stated in monetary terms, of what you expect to do during the next year. Unless budgetary control is added, the 12.32 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual budget becomes useless. Budgetary control involves comparing actual performance against planned performance and taking corrective action if differences are found. For instance, the production department budget may call for spending $490,000 each month to produce one month’s output of 100,000 units. If, at the end of the month, the chief accountant finds that $505,000 has been spent, he or she knows that actual expenses are exceeding planned expenses by $15,000 and can notify the production manager to take corrective action. (CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-1, “Budgetary Control,” gives the student the ability to practice budgetary control.) With this information, the manager can investigate the problem. Are raw materials being wasted? Was there an increase in the cost of these materials? On the basis of the results of this investigation, a change may be made in production methods or a new supplier may be found. If it is found that the original budget was not realistic, the budget itself may be changed to show realistic goals. In this way, management makes adjustments in order to meet the goals it has set. Budgets and budgetary control are excellent planning and control tools. DETERMINING COSTS AND SETTING PRICES The income statement shows an item called “cost of sales” or “cost of goods sold,” which includes various costs—material, labor, and overhead. Analyses that are more detailed can be made to relate these costs to each product, and costs can be compared with the income from the sales of that product. This shows what the present cost/profit situation is at a given level of sales. Another study is usually made to find out what the situation would be if sales increased or decreased. Each company has its own approach to cost accounting. Some emphasize quality, others price. Cost analysis provides a basis for determining which approach to follow. All involve a trade-off of value against cost. DECIDING ON CAPITAL INVESTMENTS Managers must make daily and long-term capital investment decisions. Daily decisions may be made on whether to use machine A or machine B for a given operation. Should a salesperson visit customer X on this trip or the next? Should Jones’s order be produced today to assure on-time delivery, or can it wait? Capital investment decisions are concerned with changes in fixed assets that affect longer periods of time. Should a manual operation be replaced with a machine? Should a piece of equipment be replaced, rebuilt, or discarded? Many of these decisions involve large sums of money and have long-term effects on the company. Special consideration must therefore be given to such decisions, including such factors as interest charges and the unavailability of money for other purposes, called opportunity cost. These and other capital investment studies consume much time and involve many people. They also involve the use of detailed accounting records to obtain costs for their analysis. LECTURE LINK 12-2 Auditing the Audit Process The independent audit once occupied a lofty spot in corporate reporting. It was perceived as the ultimate business reality check that ensured a company’s financial statements were accurate and prepared according to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Unfortunately, accounting scandals at companies such as Enron, WorldCom, Tyco, and Global Crossing questioned the legitimacy and accuracy of the once respected process. The fallout, however, had much more severe repercussions in the industry. The scandals led to the demise of one of the largest and most respected accounting firms in the United CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.33 States, Arthur Andersen. The company was convicted of obstruction of justice for its actions in the Enron case. The accounting misdeeds also inspired the U.S. Congress and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to impose vast new reporting and auditing requirements on businesses. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 attempts to regulate financial markets and prevent financial fiascos such as Enron and WorldCom from cheating unsuspecting investors. The legislation enacted several key reforms: (1) The law prevents public company auditors from serving as business consultants to firms they audit. However, auditors can provide a tax preparation role at such companies. (2) The Public Company Accounting Oversight Board was created to oversee public company accounting. (3) Roles and duties for audit committees of public companies were to be expanded. (4) Executives of publicly-held companies are required to sign off on their firm’s financial statements and vouch for the effectiveness of financial controls. The roles and duties for audit committees within companies were crafted by the Securities and Exchange Commission. The new rules require accounting firms to follow specific do’s and don’ts in what kinds of non-audit services they can provide firms that they audit. For example: (1) Audit firms must disclose how much money they were paid from audit and non-audit services provided to a client. (2) The top two accounting partners working for a particular client must rotate off the account after a five-year period and wait at least five years before returning to that audit assignment. (3) Outside auditors may not join the client firm and oversee the auditing firm’s work until after a one-year “cooling off” period. (4) Auditors are also barred from offering other services such as the design and installation of financial information systems, appraisal services, actuarial services, investment banking services, legal advice, and management and human resource functions. A result of the new rules set forth by Congress and the SEC is that the role of internal auditors within a company had to be beefed up. In fact, most would argue that when it comes right down to it, the financial and operations policing of company operations should be an “inside job,” done by an internal auditor. Internal auditors need to keep an eye on a company’s “controls” not just its financial operations. In the case of the WorldCom disclosures, it was Cynthia Cooper, an internal auditor at the company, who blew the whistle on the firm for inflating its profits to the tune of $3.8 billion. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act and administrative regulations from the SEC (discussed above) has led to a surge in demand for people trained in the internal-audit field. William Bishop III, president of the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA), said job postings on the organization’s website have more than doubled in the year since the law was passed. Bishop also notes that a company with $3 billion to $4 billion in revenues typically now employs about 16 internal auditors. If you are interested in pursuing a career in the internal-audit field, it’s important to keep a few points in mind. The main goal of the internal audit is to make sure the systems already in place within the company are working correctly. The internal auditor also must know the company inside-and-out but still have enough independence to give honest feedback and advice when it’s needed. Finally, guts also help. Anyone considering a career in internal auditing should have the guts to speak out and most importantly the ability to “tell the truth.”i 12.34 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual LECTURE LINK 12-3 The Power of the Internal Auditor The largest bankruptcy in U.S. history was the 2002 collapse of telecom giant WorldCom. The company’s downfall was caused by a fraudulent $11 billion accounting scheme. The unlikely heroine at the center of this story is an internal auditor who wouldn’t stop asking questions. Cynthia Cooper admits that she was “literally scared to death” during the process of uncovering WorldCom’s fraudulent activities. In the course of a routine internal audit into the obscure area of line cost expenses, Cooper uncovered something that didn’t look right. Other executives told her she was wasting her time and the department’s resources by pursuing the audit. But she never allowed herself to be intimidated. It was the urging to move onto something else that encouraged her to keep looking. Her department eventually discovered $3.8 billion in fraudulent accounting involving line fees—fees WorldCom paid to other telephone companies for the right to use their lines. Cooper said there was a spider web of entries used to disguise the fraud, and after her auditing staff traced them backward and forward, they still couldn’t understand what was happening. When she confronted former controller David Myers about the entries, he was honest and said there was no support to back up the accounting. According to Cooper, the internal audit department never considered backing down once they began the investigation. “We were at a crossroads,” Cooper said of the internal auditing team. “The decision to come forward was easy, but doing the right thing doesn’t come without a cost.” The role of whistleblower isn’t one she relishes. The WorldCom debacle eventually sent several executives to prison. Bernie Ebbers, former chief executive officer and co-founder, was sentenced to 25 years after being found guilty of fraud and conspiracy for his role in the accounting scheme. This is the harshest sentence ever given in a white-collar criminal case. Scott Sullivan, the former chief financial officer who testified against Ebbers, received five years. Cooper has trouble reconciling those sentences. Cooper now runs Cynthia Cooper Consulting Company and spends a great deal of time speaking on the events surrounding the WorldCom scandal. “Small decisions matter. Make sure your moral compass is pointed at true North. Never allow yourself to be intimidated.”ii LECTURE LINK 12-4 It’s the Earnings That Count Marvin Morris’s firm, In-Person Payments, runs payment centers in inner city stores that allow people without checking accounts to pay their bills. His long-standing approach to profit management: when he made enough money, he’d hire somebody. Marketing and expansion efforts were also financed using this bootstrapping approach. Morris’s company has been a financial success, with revenues of nearly $18 million and 3,000 stores in 20 states. But when he approached venture capitalists to fund his expanding enterprise, he was surprised at the bargain basement valuation calculated by the venture capitalists. The VC were impressed with In-Persons’ ability to grow so quickly with so little capital, and they liked the company’s mainly Hispanic customer base, a fast-growing segment of the population. What they didn’t like was the company’s low EBITDA, or earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. EBITDA is basically the firm’s net earnings from normal operations. Morris had always used revenue as his measuring system, and revenue was growing quickly. But most venture CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.35 capitalists look at the bottom line, the company’s earnings after operating expenses are deducted. That figure lets investors determine a company’s profitability, regardless of industry or accounting method. To get a better EBITDA, Morris needed to cut expenses. He cut $100,000 from his marketing budget and dismissed nearly half of his staff. The company even negotiated a lower rate on its phone service. The increase in earnings was almost immediate. The company went from running at breakeven to posting $1.4 million in EBITDA in one year. Investors were also impressed. He has attracted venture capitalists willing to invest up to $3.5 million to expand In-Person Payments nationally.iii LECTURE LINK 12-5 Using the Statement of Cash Flows Rather than studying the income statement, many investors are choosing to look beyond that list of a company’s revenues and expenses to the cash flow statement. And because cash flow is key to financing many takeovers and leveraged buyouts, understanding and profiting from acquisitions often means understanding figures such as “operating cash flow” and “free cash flow.” Companies do not go out of business because they report net losses. They fade away because they run out of cash. Monitoring your ability to generate cash flow is critical to success. To maximize longterm value, a company must continually evaluate its consistent capacity for generating cash. Commercial lenders realize that it is cash flow, not net income, which will repay their loans. The true definition of cash flow is unclear. It is one of the most over used and least agreed upon terms in corporate finance. Cash flows can be divided into three primary categories: Cash flows from operating activities. Cash flows from investing activities. Cash flows from financing activities. Cash flow is often a better measure of company health than earnings, analysts say, because earnings can be puffed up or hidden through accounting changes or other manipulations that don’t reflect the true state of a company’s business. When times are tough, companies can fool around with tax rates and make timing adjustments. Due to such manipulations, many analysts rate the usefulness of cash flow statements far above earnings statements. In today’s competitive environment, it is vital for the owner/operator to monitor current and future cash flow requirements. Careful tracking of cash flow is especially important for industries facing seasonal fluctuations, such as the retail industry. These companies must prepare projections of cash inflows and outflows, preferably on a monthly basis, but certainly no less than on a quarterly basis. A forecast of the company’s monthly balance sheet is also important to show its financial position and available assets, such as accounts receivable and inventory, which can be used as collateral for working capital loans. Based on these projections, periods of negative cash flow will be highlighted and anticipated. To lessen the effect of periods of negative cash flow, many factors should be considered, including the company’s business cycle and its ability to fund the negative cash flow period. In anticipation of these down times, it’s necessary to pay particular attention to cash-producing assets, such as accounts receivable, and cash-flow-draining liabilities, such as accounts payable. Steps to speed up time for collections of receivables might include reducing the time between the sale and mailing the invoice to the customer or changing sales terms to cash on delivery. It may also be worthwhile to meet with the company’s banker to review the cash flow requirements of the company and obtain a seasonal line of credit to cover the negative cash flow periods. 12.36 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual Cash flow can be used in different ways for different types of companies: For developing companies, cash flow and free cash flow are usually negative, because the company is burdened with low sales and one-time expenses necessary to build the business. Matching the cash being lost in a cash flow statement to the assets on hand to pay bills can predict how long the company can survive. Minding cash flow is especially crucial in energy and real estate companies, whose bottom line often is obscured by heavy depreciation and depletion allowances. Companies that recently have made takeovers often have depressed earnings because they must write off massive amounts of goodwill carried on their balance sheet. The goodwill comes from paying a premium over a company’s book value to buy the company. Monitoring cash flows is crucial to a company’s success. As owners and financial statement users become more familiar with the concept and use of cash flow ratios, their decision-making process will improve greatly and become more focused on the cash flow impact of their decisions. LECTURE LINK 12-6 Knowing the Numbers Employees at Setpoint know more about their company’s finances than most investors do. Setpoint is a custom-manufacturing company with 30 employees and a little more than $6 million in sales. Most of its revenues come from designing and building factory-automation equipment, a highly competitive business. In the shop, a spacious, well-lit room, ten employees work on half a dozen machines. Off to one side is a large whiteboard on a wall next to a canteen area. Scribbled across the board are about 20 rows and 10 columns of numbers forming a table, with a few dollar signs sprinkled here and there. Setpoint’s CEO, Joe Knight, says, “That’s our board. It’s how we trace our projects and figure out whether or not we’re making money.” Knight can explain what all the numbers mean, but more surprisingly, so can individual workers. One worker explained how the GP—gross profit—is calculated and how much he and other workers had earned the previous week on each project. He pointed out the column showing each project’s GP per hour and explained the importance of keeping that number in mind. He said he also watched the ratio of overall GP to OE—operating expenses—since that’s how you know if the company was making money. He added that he like to see it running at about 2.0. CEO Knight explained that the people on the shop floor all had it down like that. It was their scoreboard. It was the way they could tell if they were winning or losing. The whiteboard began in November 1998 when Knight was still the Chief Financial Officer. Setpoint had been on a growth binge and was pushing the limits of its credit line. The bank’s loan officer was breathing down his neck. “We’d had three months of losses, and we were running the company on our credit line, but I’d told the bank we’d break even in November and get back to profitability by December. Then I got the numbers for the first week of November, and they were awful. We just had too many projects that were losing money.” Knight didn’t have the board back then, but he was using the same system on a spreadsheet. Knight handed it out to everybody and then talked to Steve Nuetzman, the lead engineer. Knight remembers saying “Look at this, Steve. We’re losing money again. If we don’t do something, we’re going to max out our credit line, and then we’re really going to be in trouble with the bank.” Nuetzman got the message. On the following Monday, when Knight looked at the spreadsheet for the previous week, he was stunned to see that the situation had been turned completely around. Virtually CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.37 no work had been done on the money-losing projects. Instead people had focused almost all their attention on the projects with higher gross-profit margins, so the company had made money for the week. “I went right over to Nuetzman and congratulated him. I was pretty excited because it meant I’d be able to go to the bank and say, ‘See, I said we could turn it around, and we did.’ How many companies can find out they’re losing money in the first week of November and turn it around like that? Not many.” According to Nuetzman, it wasn’t a big idea, really. “We just looked at the projects we had and realized we could shuffle resources around.” They got the delivery dates on the less profitable projects extended and turned them over to contract labor. Then they put their high-powered internal resources on the most profitable projects. The accounting system was developed by Joe Cornwell and Joe VanDenBerghe, who cofounded Setpoint in 1992 and, with Knight, developed its management system. In order to create a projectmanagement system that worked, they realized they’d have to delve into the accounting processes, which plays a major role in the way projects are tracked. Cornwell eventually introduced unconventional accounting ideas. “I didn’t agree with the textbook about the way you should do things. For example, they said you should treat labor as a variable cost. Well, you can’t treat labor as variable ... It’s stupid to treat your regular employees as a variable cost, because the cost doesn’t vary in reality. You can’t hire and fire people as the work comes in and goes out. Even if you were a hard, cruel bastard, you couldn’t do it. Nobody would come to work for you if you did.” Cornwell, VanDenBerghe, and Knight decided early that Setpoint would be an open-book company. To get employee involvement, they put great emphasis on financial training and sharing information. Then in 1998 a project engineer hit upon an idea to communicate the numbers. Instead of the weekly spreadsheet, why not put the same information up where everybody could see it? Thus the board was born. iv 12.38 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual BONUS INTERNET EXERCISES BONUS INTERNET EXERCISE 12-1 Annual Reports Online PURPOSE: The purpose of this exercise is to explore the annual report of a specific company by visiting the company’s website using the principles presented in this chapter. EXERCISE: Locating corporate annual reports is easier than it has ever been. AnnualReports.com hosts a website (www.reportgallery.com) containing annual reports for hundreds of corporations. The site is comprehensive and easy to use. Go to the website (www.reportgallery.com) and choose one company to research. Use the information given in this report to answer the following questions. (Sometimes the web address for a location changes. You might need to search to find the exact location mentioned.) Company name ________________________________ Financial Year ______________________ 1. Locate the report of the independent auditors. a. Who are the auditors? b. Are there any auditor reservations—anything that the auditors flag with the term “except”? 2. Locate the report of management. Since the passage of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act in 2002, corporate management has to certify these financial results. Who signed the management report? 3. Which intangible assets are listed on the balance sheet? 4. How much income tax did the company pay? 5. Using the financial ratios discussed in this chapter, answer the following: 6. a. What is the current ratio? b. What is the debt to owners’ equity ratio? What is the basic earnings per share? Diluted earnings per share? CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.39 BONUS INTERNET EXERCISE 12-2 CPA Certification PURPOSE: To let students investigate the certification examination required to become a Certified Public Accountant. EXERCISE: The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants sponsors a website giving information on the Uniform CPA Examination. Go to the AICPA website (www.cpa-exam.org) and use the information there to answer the following questions. (Sometimes the web address for a location changes. You might need to search to find the exact location mentioned.) 1. What are the requirements to take the CPA exam? 2. The website gives the official statement of purpose for the exam, created by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants. Locate and record this statement of purpose. 3. What are the major areas covered in each section of the exam? 4. Each section is timed. How much time is allocated for each section? 5. Each section is given a percent value adding up to 100%. What percent value is assigned to each section? 12.40 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISES CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-1 Budgetary Control The Weinstein Manufacturing Company prepared a budget for its production department as follows. At the end of the first month, the production manager compared actual results with budgeted amounts and found that some were over and some were under budget. An expenditure is considered exceptional if it varies by more than 10% from the budgeted amount. WEINSTEIN MANUFACTURING COMPANY MONTHLY BUDGETARY CONTROL WORKSHEET ____________________________________________________________________________ EXPENSE BUDGETED ACTUAL DIFFERENCE CATEGORY AMOUNT EXPENDITURE FROM BUDGET ____________________________________________________________________________ Labor $162,500 $195,000 _______________ 172,500 151,500 _______________ Utilities 6,500 6,300 _______________ Maintenance 9,750 8,950 _______________ Other variable expenses 16,750 18,000 _______________ Fixed overhead expenses 25,000 25,000 _______________ Raw materials TOTAL EXPENSES $393,000 $404,750 _______________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.41 CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-1 (continued) 1. Which of the budget items should be investigated? 2. What could be causing the difference? 3. What are some suggestions for improvement? 12.42 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual NOTES FOR CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-1 WEINSTEIN MANUFACTURING COMPANY MONTHLY BUDGETARY CONTROL WORKSHEET ____________________________________________________________________________ EXPENSE BUDGETED ACTUAL DIFFERENCE CATEGORY AMOUNT EXPENDITURE FROM BUDGET ____________________________________________________________________________ Labor $162,500 $195,000 +32,500 +20.0% 172,500 151,500 -21,000 -12.2% Utilities 6,500 6,300 -200 -3.1% Maintenance 9,750 8,950 -800 -8.2% Other variable expenses 16,750 18,000 +1,250 +7.5% Fixed overhead expenses 25,000 25,000 0 0.0% Raw materials TOTAL EXPENSES $393,000 $404,750 +11,750 +3.0% ___________________________________________________________________________________ 1. Which of the budget items should be investigated? If management looked only at the bottom line, this budget report would appear very positive. The total expenditures are over budget by only 3%. However, closer inspection of the individual budget items shows that the actual labor cost is exceeding the budgeted amount by 20%, a significant overage. This item needs to be investigated—what is causing labor costs to increase so much? The second item that needs to be investigated is the expenditure for raw materials. Spending here is 12% below budget. Students may argue that this is good news—why question it? However, the reasons for the decrease need to be identified. Has the cost of raw materials declined? If so, the budget needs to be modified. Are workers using a more efficient production method that uses fewer raw materials? If so, the company needs to make certain that everyone in the organization is using the improved method. 2. What could be causing the difference? The increased labor costs may be due to an increase in the number of workers or an increase in the amount paid each worker. In other words, has the workforce increased or have individual worker earnings increased? The production department may be relying more on expensive overtime, thus increasing costs. Or the company may have added additional workers to meet seasonal increases in demand. A critical financial element is missing here—what is the total revenue earned for this period? This budget overage would be less significant if sales revenue were also increasing. 3. What are some suggestions for improvement? How can workers be used more efficiently? Are there ways to increase productivity? Is automation an option? If the increase is seasonal, how can the company even out the fluctuations? Perhaps the budget report should be prepared more frequently—weekly instead of monthly. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.43 CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-2 Preparing a Balance Sheet As the accountant for Wheatley International, it is your job to prepare the company’s balance sheet. Use the accounts listed below to construct the statement. List of Accounts for Wheatley International Accounts Receivable $120,600 Land 1,500,000 Notes Receivable 61,200 Accounts Payable 45,000 Common Stock 1,896,000 Net Sales 1,053,000 Notes Payable (Long-term) 270,000 Retained Earnings 1,459,800 Cash Short-Term Notes Payable 12.44 72,000 15,600 Buildings (after depreciation) 1,050,000 Equipment & Vehicles (after depreciation) 1,066,000 Inventory 126,600 Goodwill 90,000 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual NOTES ON CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-2 The formula for the balance sheet is assets equal liabilities plus stockholders equity. To prepare a balance sheet, record the assets and liabilities. The difference between the two is stockholders equity. (Note: The format of this statement may be slightly different from the format taught in students’ accounting courses. The exact format is less important than understanding the overall concepts.) Wheatley International Balance Sheet ASSETS Current Assets Cash Accounts Receivable Notes Receivable Inventory Total Current Assets Fixed Assets Land Buildings Equipment & Vehicles Total Fixed Assets Other Assets Goodwill Total Other Assets $72,000 120,600 61,200 126,600 $380,400 $1,500,000 1,050,000 1,066,000 $3,216,000 $90,000 $90,000 TOTAL ASSETS $3,686,400 LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY Current Liabilities Accounts Payable $45,000 Short-Term Notes Payable 15,600 Total Current Liabilities Long-Term Liabilities Notes Payable (Long-Term) Total Long-Term Liabilities $270,000 $270,000 Total Liabilities Owner’s Equity Common Stock Retained Earnings Total Owner’s Equity $60,600 330,600 $1,896,000 1,459,800 TOTAL LIABILITIES & STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting $3,355,800 $3,686,400 12.45 CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-3 The Pizza Stand A student organization has been given permission to operate a pizza stand during the upcoming homecoming weekend. The stand will be located just outside the football stadium, making it accessible during the ball game. The location is also convenient for visitors as they tour the campus at other times during the weekend. An estimated 2,500 visitors will be on campus, in addition to the campus population of 1,500. Each pizza requires: 1/2 pound of pizza flour 2 ounces of pizza sauce 1/8 pound of pepperoni 1/2 pound of cheese. Pizza flour costs $8.00 per 10-pound bag; pizza sauce, $4.80 per 64-ounce jar; pepperoni, $18.00 per 5-pound package; and cheese, $15.00 per 5-pound package. Club members will cook the pizzas and staff the stand on a volunteer basis. The university requires each vendor to pay a $25 permit fee and a $50 refundable deposit on the building. Your club plans to donate the profits from the pizza sales to a local children’s hospital. 1. How many pizzas can you anticipate selling? 2. What price should you charge per pizza? 3. How much of each raw material do you need to buy? 4. What will be your probable profit? 5. Develop a financial plan for your weekend enterprise. 12.46 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual NOTES ON CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-3 I have used this exercise several times in my classes. Below are two of the potential solutions, one conservative and one very optimistic. ALTERNATIVE 1 1. How many pizzas can you anticipate selling? On the homecoming weekend, there will be about 4,000 people on campus. The first step in developing a budget is to estimate what percentage of attendees will purchase your pizzas. This can be complicated. Factors such as the weather, time of day, and presence of other food vendors would have to be considered. Obviously, you would have to consider the demand for pizzas at several price points. Perhaps the simplest method is to use a percentage, say 10%. Potential sales: 400 pizzas. 2. What price should you charge per pizza? You could consider several pricing strategies. Chapter 9 covered several possibilities: demandbased pricing, competition-based pricing, cost-based pricing, and break even analysis. What is the price are people willing to pay? What price is our competition charging? What is the break even point? To simplify transactions on the day of the sale, you may want to set the price at a whole dollar amount and not have to bother with coin change. The analysis below uses cost-based pricing. The fixed costs are quite low—the only one given is the $25 permit. Next, calculate the cost of raw materials per pizza, the variable cost. Ounces Cost of ingredient Cost per ounce Cost per pizza ½ pound 8 oz. $8 per 10 lb $0.05 $0.40 Pizza sauce 2 ounces 2 oz. $4.80 per 64 oz $0.075 $0.15 Pepperoni 1/8 pound 2 oz. $18 per 5 lb. $0.225 $0.45 Cheese ½ pound 8 oz. $15 per 5 lb $0.1875 $1.50 Ingredient Amount per pizza Pizza flour $2.50 After determining the cost of raw materials, a price can be set that covers these costs and provides the desired profit. Possible prices: $5.00, $7.00, or $9.00. Setting the price 3. How much of each raw material do you need to buy? Ingredient Amount per pizza Ounces Potential sales units Total ounces needed Total pounds Pizza flour ½ pound 8 oz. 400 3200 200 Pizza sauce 2 ounces 2 oz. 400 800 Pepperoni 1/8 pound 2 oz. 400 800 50 Cheese ½ pound 8 oz. 400 3200 200 CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.47 You will need: Pizza flour Pizza sauce Pepperoni Cheese Total cost 4. 20 10-pound bags 12½ 64-ounce jars 10 5-pound packages 40 5-pound packages 20 x $8.00 13 x $4.80 10 x $18.00 40 x $15.00 $160.00 $62.40 $180.00 $600.00 $1,002.40 What will be your probable profit? Your profit will depend on the price you charge. Using $7.00: Price $7.00 Revenue $2,800.00 (400 x $7.00) Variable costs $1,002.40 Fixed costs $25.00 Total costs $1,027.40 Profit $1,772.60 5. Develop a financial plan for your weekend enterprise. Project Costs: Buy permit: $25.00 Purchase raw materials: Pizza flour 20 10-pound bags 20 x $8.00 $160.00 Pizza sauce 12½ 64-ounce jars 13 x $4.80 $62.40 Pepperoni 10 5-pound packages 10 x $18.00 $180.00 Cheese 40 5-pound packages 40 x $15.00 $600.00 Total cost $1,002.40 (The $50 deposit is a wash, $50 cost, $50 refund. Therefore, it was not used in these calculations.) Project Revenue Assuming sales of 400 pizzas (10% of attendees) and using $7.00 sale price: 400 x $7.00 = $2,800.00 Project Net Profit: Revenue: $2,800.00 Cost of Goods: $1,002.40 Fixed Costs: $25.00 Net Profit $1,772.60 12.48 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual ALTERNATIVE 2 1. How many pizzas can you anticipate selling? Assume that you will sell pizzas to 75% of the people at homecoming (3,000 pizzas.) People will be hungry, and they will want to support the club. 2. What price should you charge per pizza? Charge $10.00 per pizza. 3. How much of each raw material do you need to buy? Ingredient Amount per pizza Ounces Potential sales units Total ounces needed Total pounds Pizza flour ½ pound 8 oz. 3000 24,000 1500 Pizza sauce 2 ounces 2 oz. 3000 6,000 Pepperoni 1/8 pound 2 oz. 3000 6,000 375 Cheese ½ pound 8 oz. 3000 24,000 1500 Supplies needed: Pizza flour Pizza sauce Pepperoni Cheese Total cost 4. 150 x $8.00 94 x $4.80 75 x $18.00 300 x $15.00 $1,200.00 $ 451.20 $1,350.00 $4,500.00 $7,501.20 What will be your probable profit? Price is $10.00 Revenue Variable costs Fixed costs Total costs Profit 5. 150 10-pound bags 93.75 64-ounce jars 75 5-pound packages 300 5-pound packages $30,000.00 (3,000 x $10.00) $7,501.20 $25.00 $7526.20 $22,473.80 Develop a financial plan for your weekend enterprise. Purchase enough raw materials to make 3,000 pizzas and market aggressively. If sales don’t meet expectations by the end of the third quarter, lower the price by half. Even at a $5.00 sales price, you will cover the $2.50 variable cost and make $2.50 profit per pizza. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.49 CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-4 Comparing Industry Ratios You are interested in investing in a regional hotel company and have investigated the financial statements of four potential investments. Use the information in the table below to answer the questions at the bottom of the page. KEY FINANCIAL STATISTICS Hotel N Hotel J Hotel C Hotel W Information from the income statement Total revenue Total expenses $10,099,000 $3,816,000 $428,806 $1,277,550 $9,503,000 $3,618,000 $354,461 $1,822,748 Information from the balance sheet Current assets $1,946,000 $1,020,000 $68,629 $526,549 Total assets $8,668,000 $8,183,000 $262,388 $3,783,127 Current liabilities $2,356,000 $895,000 $101,091 $693,809 Total liabilities $4,587,000 $5,944,000 $456,441 $3,089,318 225,800 389,000 32,312 168,238 Total shares of common stock outstanding (Use the table on the following page for your answers.) 1. What is the net profit (or net loss) for each company? 2. Calculate the return on sales for each company. 3. Calculate the total stockholders’ equity for each company. 4. What is the current ratio for each company? 5. Calculate the return on equity ratio for each company. 6. What is the debt to equity ratio for each company? 7. Calculate the basic earnings per share for each company. 12.50 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual KEY FINANCIAL RATIOS Hotel N Hotel J Hotel C Hotel W 1. Net income (net profit or net loss) 2. Return on sales 3. Current ratio 4. Stockholders’ equity 5. Return on equity 6. Debt-to-equity ratio 7. Earnings per share (basic) 8. Which company would you rather invest in? Why? CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.51 NOTES ON CRITICAL THINKING EXERCISE 12-4 The requested financial information and ratios are given below. KEY FINANCIAL RATIOS Hotel N 1. Net income (net profit or net loss) 2. Return on sales 3. Current ratio 4. Stockholders’ equity 5. Return on equity 6. Debt-to-equity ratio 7. Earnings per share (basic) Hotel J Hotel C Hotel W $596,000 $198,000 $74,345 ($545,198) 5.9% 5.2% 17.3% (42.7%) 0.83 1.13 0.68 0.76 $4,081,000 $2,239,000 ($194,053) $693,809 14.6% 8.8% not meaningful (78.5%) 112% 265% not meaningful 445% $2.64 $0.51 $2.30 ($3.24) Hotel N. Return on sales is in the mid-range for the industry. The current ratio, while less than the ideal 2.0, is in line with two of the other three companies. Return on equity is healthy and at the top of the industry, showing that the company has made good use of the funds invested by the investors. The debt-to-equity is much higher than the ideal ratio of 100%. However, when compared to the other companies in the industry, a 112% debt-to-equity ratio looks good. Earnings per share are also at the top range in the industry. Hotel J. Return on sales is in the mid-range. Current ratio is at the top of the industry, showing a better than average liquidity. Return on equity is not exceptional, but in the mid-range for the industry. The debt-to-equity ratio, however, is alarming. With a debt-to-equity ratio of 265%, the company is heavily leveraged. Creditors provide almost three times as much capital as stockholders do. This would be a relatively risky investment. Hotel C. If you just look at earnings, return on sales, and earnings per share, Hotel C looks like a winner. The 17.3% return on sales is the highest in the industry. Earnings per share is also at the high end. But investors in this company have a significant problem. The company has not only burned through all of the invested capital, but the stockholders’ equity is actually in the red. Not a good sign at all. Calculating the return-on-equity and debt-to-equity ratios is therefore meaningless. Return on a negative is irrelevant. This company is on the edge of bankruptcy, if it has not already filed. Hotel W. Hotel W has the opposite problem from Hotel C. Stockholders’ equity is still in the positive, but the company is hemorrhaging money. The company’s return-on-sales shows that the company is spending almost 43% more than it takes in as revenue—$1.00 in sales costs the company $1.43. 12.52 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual Hotels C and W are horrible investment candidates. That leaves Hotel N and J. Hotel J is heavily leveraged and would be more risky. Hotel N is a steady, safe performer. Knowing that there is a direct relationship between risk and return, the investment decision would depend on the investors’ tolerance for risk. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.53 BONUS CASES BONUS CASE 12-1 Getting Through the Hard Times at Hard Rock In the mid-1990s, the theme-dining business seemed like a path lined with gold. With regularity, celebrity stargazers, enthusiastic press from around the globe, and hungry customers gathered at the openings of theme restaurants like Planet Hollywood and Motown Café. Unfortunately, the situation changed. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, Planet Hollywood filed for bankruptcy protection and Motown Café closed units across the country. Consumer boredom, a slowing economy, and a saturated market were blamed. The changing “eatertainment” market raised eyebrows at the granddaddy of theme restaurants, the Hard Rock Café (HRC). HRC knew its market position was shaky due to increased competition and shifting consumer attitudes. The company also felt growing financial pressures, and speculated that a change in financial management might be needed. HRC had operated with a traditional, competent accounting department that made sure the company paid its bills, had money left at the end of the day, and could state how much it was earning. The problem was that HRC lacked the ability to analyze its financial information fully and use it to improve operations. To address these concerns, the company recruited a new chief financial officer (CFO) and dedicated itself to changing the financial reporting and information structure at the company. Hard Rock Café believed that it had a tremendous undervalued asset—a premium global brand. The company dedicated itself to protecting and expanding that asset. However, it was evident that the company could have brand loyalty but that, without revenue, doesn’t matter. Hard Rock’s CFO was astonished to find that HRC sold $180 million a year in merchandise (primarily its well-known T-shirts) in addition to food, yet could not explain exactly how these individual items contributed to the firm’s profit. It was then the company realized that Hard Rock Café’s accounting and financial management had to change. To start things off, the company piloted a food and beverage management system to track usage and item profitability. This system included information such as daily and seasonal buying patterns, profitability of one menu versus another, average weekly guest counts per café, and specific cost of sales and profit margins per item. The company then shifted the responsibility of the firm’s accountants. Instead of company accountants being responsible for profit-and-loss statements for a certain number of cafés, they now were responsible for one major financial category only, such as cost of goods sold, for all the company’s operations. The objective was to compile companywide information for sound financial decision making. Hard Rock Café also broke down the barriers that existed between the finance and accounting departments and operations, merchandising, and marketing. Today, financial information is shared directly with managers who can execute the recommendations at the restaurant level. Still, the company realized this was not going to be a quick fix for the company but instead an ongoing challenge. Each year about 25 million people visit a Hard Rock Café at the company’s 103 locations. Even so, competitors such as Rainforest Café, Cheesecake Factory, Dick Clark’s Bandstand Café, and House of Blues promise to make the fight for eatertainment customers an interesting one. 12.54 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-1 1. Why is it important for Hard Rock Café to know how different products contribute financially to overall company profits? 2. Do you think Hard Rock Café’s focus on improved financial reporting helped its company planning capabilities? How? 3. Have you ever visited one of Hard Rock Café’s restaurants? Describe your experience. ANSWERS TO DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-1 1. Why is it important for Hard Rock Café to know how different products contribute financially to overall company profits? If a company knows which products are unprofitable, it can drop them from its offerings. On the other hand, if a company knows which items are most profitable, it can focus promotional efforts on those items to raise profits. The problem is that cost accounting is difficult to manage on an item-by-item basis. One must charge each item with costs such as rent, utilities, etc. That is very difficult to do. But the payoff is worth the effort, as the Hard Rock Café is learning. 2. Do you think Hard Rock Café’s focus on improved financial reporting helped its company planning capabilities? How? Absolutely. The company now knows how much effort should go into nonfood promotions for things like T-shirts. It also knows which food items to drop and which to promote. Furthermore, restaurant locations that are not proving profitable can be closed, and others revamped. 3. Have you ever visited one of Hard Rock Café’s restaurants? Describe your experience. Students will have different experiences. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.55 BONUS CASE 12-2 Survival of the Financially Fittest Are you the kind of person that likes to live life to the fullest? Are you looking for a career that’s challenging, with opportunities for advancement, and a large number of openings? Then welcome to the world of financial management in non-profit organizations. Non-profits are crying out for the talents of skilled financial managers who often overlook non-profits in favor of profit-seeking firms. As the availability of public funding becomes scarcer, the demand for financing expertise has soared among nonprofits. The call for innovative and experienced financial managers has grown louder. Don’t be fooled, however, into thinking that “non-profit” means “no money.” The size and scope of the non-profit sector often surprises even seasoned business professionals. Also, misconceptions abound about work in non-profits. For starters, many people assume that the non-profit sector of the economy is quite small. In reality, it is valued at approximately $665 billion per year. This makes the U.S. non-profit sector twice as large as the U.S. construction industry. Also, the term “non-profit” is sometimes deceiving, bringing to mind church-sponsored bingo games or bake sales. Unfortunately, people forget that the - sector contains such notables as the American Red Cross, Harvard University, the Smithsonian Institution, and the National Audubon Society, none of which sponsors bingo or bake sales. In the United States today, the non-profit sector includes over 1.24 million institutions, including schools, hospitals, human service organizations, religious groups, museums, and more. Over 15 million people are employed in the non-profit sector of the economy. Work in non-profits often includes important interactions with the profit-seeking sector. For example, Sandy Boutin works as the director of Great Dane Rescue in Plymouth, Michigan. Her organization is always in need of dog food but has a very small budget. Boutin decided to invite dog food manufacturers to participate in her group’s fund-raising efforts. The companies got their name exposed to a large group of prospective customers in return for donating dog food to the rescue program. Through Boutin’s efforts, both groups got what they wanted. Often large non-profits, like the Smithsonian Institute, actively seek corporate sponsorship programs to help fund such activities as its traveling exhibitions. Many non-profit organizations experience problems at the top of their organizations. David LaGreca, a manager with the Volunteer Consulting Group, says that top management positions at nonprofits are often filled with social workers, former dancers, and musicians. These individuals have creative and artistic skills but often lack the training and business expertise of executives at profit-seeking firms. Chris Perks, president of Perks Reutter Associates, an engineering consulting firm, agrees. According to Perks, “In non-profits you are often dealing with people whose expertise is in the mission of the organization, not necessarily in administration or management. Furthermore, many employees do not come from business backgrounds. They are often hired as staffers because they are committed to what they are doing.” It’s also difficult to recruit qualified individuals to serve on non-profit boards. The corporate scandals of the early 2000s caused waves in the non-profit sector. Many prospective board members fear that the potential of scandal or poor business practices at a non-profit could damage their reputation or business standing in a community. Non-profits have also been severely lacking in another critical aspect of 21st-century business: Most are not taking advantage of the powerful technology of the Web. Financial experts fault non-profits for not taking advantage of such technology tools as tracking software and databases. With the proper financial management and technological expertise, non-profits could use the Internet to enhance their fund-raising capabilities. Non-profits seem to be listening to this advice. The possibilities for non-profits are clearly there if they can attract qualified business and financial expertise.v 12.56 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-2 1. How is the job of a financial manager in a non-profit organization different from that of a financial manager with a profit-seeking firm? 2. Should financial managers in non-profit organizations be compensated equally to their counterparts in profit-seeking firms? Why or why not? 3. Do you see the job of the non-profit financial manager as getting easier or more difficult in the future? Where might you get facts to support your conclusions? 4. How can a financial manager at a non-profit make better use of Web capabilities to enhance the financial position of the organization? ANSWERS TO DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-2 1. How is the job of a financial manager in a non-profit organization different from that of a financial manager with a profit-seeking firm? The financial management of a non-profit organization differs in many ways from that of a profitseeking firm. The financial manager of a for-profit organization usually has a very accurate estimate of sales revenue and its timing. The non-profit financial manager does not have the same planning accuracy—inflows may be donations that cannot be anticipated accurately. The goals of the organization are also quite different. The for-profit organization is in business to make a profit. The non-profit organization’s mission is often to provide a service that cannot be stated in dollars and cents. 2. Should financial managers in non-profit organizations be compensated equally to their counterparts in profit-seeking firms? Why or why not? Non-profit managers tend to have very different motivations those managers of profit-seeking firms. The “non-profit mindset” is well known. Often the need for achievement is high. Monetary compensation is less important than the satisfaction of doing a worthwhile job. While all good managers deserve compensation for their efforts, non-profit financial managers usually expect to receive less in monetary terms. 3. Do you see the job of the non-profit financial manager getting easier or more difficult in the future? Where might you get facts to support your conclusions? The current trend in government is to transfer more and more social services from government to the private sector. This means that there will be increasing need for financial management. There is also growing scrutiny of the way non-profits handle their finances. The position of non-profit financial manager can only get more challenging. 4. How can a financial manager at a non-profit make better use of Web capabilities to enhance the financial position of the organization? Many excellent websites exist for non-profit organizations. One, foundation.org, features articles available to download covering such topics as developing expense categories and completing necessary tax forms. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.57 BONUS CASE 12-3 Chicago Rush: When the Goal Line Meets the Bottom Line (Video Case) (NOTE: This case can be used with the Video on DVD for this chapter.) There are a lot of statistics to gather in any sport. Football is no exception. There are the ones that the average fan follows most closely, like win-loss records and the number of passes completed given the number of tries. For the Chicago Rush of the Arena Football League, the regular season statistics were not so wonderful in the 2006 season. They won only seven games and lost nine. Nonetheless, that record was good enough to win them a wildcard spot in the playoffs. Much to their credit, the team went on the win the Foster Trophy. There are other important statistics for a football team to follow. You can’t keep playing the game unless you make enough money to pay the players and keep the games going. Therefore, like all companies, the Chicago Rush has to keep careful accounting records. At the top of the income statement, revenues are a key. Winning a championship should improve that number and, after all costs and expenses are deducted, that bigger number should carry right down to the bottom line—profit after taxes. A new team in a relatively new sport can’t expect the bottom line to be huge. Investing in a team can be a major commitment. So the bottom line score is often as important as the scores on the field. And the person keeping those scores is a major player. That person at the Chicago Rush is Maggie Wirth. She goes through the same six-step accounting process outlined in this chapter. Accounting can be an interesting and challenging occupation when you consider how important it is to the team and all its owners, players, and fans. When it comes time to be paid, the players are interested in whether or not the cash flow is sufficient. Costs and expenses have to be kept in line—and that includes player salaries. What seem like mere data to the average person turns out to be more important in the long run than wins and losses and championships won. Without the money, the game is over. With increased revenue comes the opportunity to increase marketing. There are many competing sports in Chicago, and many teams have been around for years. To attract fans, the Rush must consistently provide exciting games and fun entertainment during those games. As in any sports program, the team is looking for revenue from all sorts of sources: parking, various food concessions, team merchandise, and more. Growth often is accompanied by more expenses, including higher-cost players. Going international adds its own expenses, for airline fees, hotels, and related items. Keeping track of revenues, expenses, and other details may seem a rather remote part of team planning, but, as you can see from this case, such details are at the heart of the enterprise. Just as the offense and the defense need to have their plans and their appraisals over time, the fiscal health (profit and loss) of the team must be measured as well. And, just as there is a football team, there is a financial team. Keeping score is more than keeping track of first downs and touchdowns. In the background are people keeping score of how many fans are coming vs. last year, how many hot dogs and sodas were sold, and how much it cost to clean the uniforms and clean the stadium. Boring statistics? Hardly. They determine whether or not the team can stay in business. There are lots of people relying on the results. The same is true in all businesses. The managers, employees, investors, and others are all following the accounting scores as closely as whatever score-keeping the company does (usually sales or profit). 12.58 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-3 1. Does accounting seem more interesting and important when analyzed in the context of a major sport? 2. Player salaries are a major expense to a sports team. What role might accounting play in helping managers and coaches talk to the players about salaries? Does the fact that arena football is a relatively new sport have anything to do with such negotiations? 3. Do different groups, like managers and stockholder and players and fans, want different figures compiled by the accounting department? What are those differences? ANSWERS TO DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-3 1. Does accounting seem more interesting and important when analyzed in the context of a major sport? Accounting is interesting and important to all companies. Often students can’t see the big picture because so much focus is placed in accounting statements and things like double-entry bookkeeping. This case offers and opportunity to explore how important accounting is to businesses and how challenging the job is. After all, it is accounting that measures the bottom line—and no figure is more important to a firm or a team. 2. Player salaries are a major expense to a sports team. What role might accounting play in helping managers and coaches talk to the players about salaries? Does the fact that arena football is a relatively new sport have anything to do with such negotiations? This question gives you a chance to talk about costs and expenses in general and specifically the costs associated with employees (players). It might even lead to a discussion of the minimum wage and how raising salaries affects the bottom line and, therefore, hiring practices. Putting accounting into a whole new context opens many new opportunities for a fresh look at the processes involved. 3. Do different groups, like managers and stockholder and players and fans, want different figures compiled by the accounting department? What are those differences? This question creates an opportunity to discuss managerial versus financial accounting. Managers need to know things like whether or not expenses are being kept in line. They should be kept informed about cash flow issues and actual revenues. Investors and players, on the other hand, are more interested in the bottom line (profit after taxes). Fans are concerned about rising parking fees and ticket prices and want to know why such increases are necessary. The difference between managerial and financial accounting has more relevance in this setting. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.59 BONUS CASE 12-4 The Best Laid Plans Often Go Awry How you report revenues on the income statement makes a big difference in how profitable a company looks. The problem is that stockholders are often fooled into investing in a firm that is not nearly as profitable as they think. A good example is that of Thousand Trails Campground. It sold campground memberships for owners of recreation vehicles. It used the usual expensive promotions to get potential buyers to come to the campgrounds. Once a potential customer was at the site, there was a lot of pressure to buy now, and the campgrounds were quite attractive. Once a customer got home and reconsidered the investment, though, some backed out of the commitment, and that is where Thousand Trails got into difficulty. The company recorded the full price of a membership (about $7,500) as revenue, even though members paid only 40% down on average. Marketing expenses were running higher than payments, so more cash flowed out than flowed in. To get cash, Thousand Trails sold its receivables. In one year, Thousand Trails used $52 million more cash than it produced, a definite cash flow problem. Nevertheless, it reported record earnings of $19.1 million, and the stock price went up to over $29. Two years later, the stock had fallen to less than $5, reflecting a 90% drop in earnings reported (from 19 million dollars to less than 2 million dollars). What happened was that a lot of campground members dropped out before paying in full. So Thousand Trails had to write off $11 million in paper revenues. Marketing expenses were two times greater than down payments. Debt reached a horrendous 244% of stockholder’s equity. Meanwhile, stockholders were left wondering what happened to the company that was growing so fast and making such good profits (at least on the income statement). DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-4 1. Thousand Trails did nothing illegal in its reporting of revenues and profits. What does that tell you about the need to carefully read and analyze income statements before you invest? 2. Can you see how cash flow problems can grow to unbelievable proportions in just a short time, even when profits look good? ANSWERS TO DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-4 1. Thousand Trails did nothing illegal in its reporting of revenues and profits. What does that tell you about the need to carefully read and analyze income statements before you invest? The fact is that income statements and balance sheets are very hard to analyze. Auditors go over them to check for legality, but that doesn’t prevent deception of stockholders. One way to invest and not worry about doing your own analysis is to buy mutual funds and leave the digging to professionals. 2. Can you see how cash flow problems can grow to unbelievable proportions in just a short time, even when profits look good? Yes, cash flow problems plague businesses, especially the ones that grow rapidly. The problem is that the fast-growing firms are also the most attractive as investments. A firm cannot keep borrowing and growing without careful cash-flow analysis or they are bound to get caught with too little cash and too 12.60 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual many bills to pay. If the bank refuses the business any more loans, the result, more often than not, is bankruptcy. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.61 BONUS CASE 12-5 Managing by the Numbers Katherine Potter knew a good thing when she saw it. At least, it seemed so at first. She was traveling in Italy when she spotted pottery shops that made beautiful products ranging from ashtrays to lamps. Some of the pottery was stunning in design. Katherine began importing the products to the United States, and sales took off. Customers immediately realized the quality of the items and were willing to pay top price. Katherine decided to keep prices moderate to expand rapidly, and she did. Sales in the second three months were double those of the first few months. Sales in the second year were double those of the first year. Every few months, Katherine had to run to the bank to borrow more money. She didn’t really discuss her financial situation with her banker because she had no problems getting larger loans. You see, she always paid promptly. To save on the cost of buying goods, Katherine always took trade discounts. That is, she paid all bills within 10 days to save the 2% offered by her suppliers for paying so quickly. Most customers bought Katherine’s products on credit. They would buy a couple of lamps and a pot, and Katherine would allow them to pay over time. Some were very slow in paying her, taking six months or more. After three years, Katherine noticed a small drop in her business. The local economy was not doing well, and many people were being laid off from their jobs. Nonetheless, Katherine’s business stayed level. One day, the bank called Katherine and told her she was late in her payments. She told them she had been so busy that she didn’t notice the bills. The problem was that Katherine had no cash available to pay the bank. She frantically called several customers for payment, but they were not able to pay her, either. Katherine was in a classic cash flow bind. Katherine immediately raised her prices and refused to make sales on credit. She started delaying payment on her bills and paid the extra costs. Then she went to the bank and went over her financial condition with the banker. The banker noted her accounts receivable and assets. He then prepared a cash budget and loaned Katherine more money. Her import business grew much more slowly thereafter, but her financial condition improved greatly. Katherine had nearly gone bankrupt, but she recovered at the last minute. DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-5 1. How is it possible to have high sales and high profits and run out of cash? 2. Why did Katherine do better when she raised her prices and refused to sell on credit? 3. What was the nature of Katherine’s problem? Was she correct to go to the banker for help, even though she owed the bank money? How could she have prevented some of the problems she eventually found herself faced with? ANSWERS TO DISCUSSION QUESTIONS FOR BONUS CASE 12-5 1. How is it possible to have high sales and high profits and run out of cash? That is the classic description of a poor cash flow. A firm sells lots of merchandise on credit and buys more, paying promptly. Credit sales are great, and the firm buys more merchandise on credit. One day the creditors ask for money, and the firm cannot collect its accounts receivable fast enough; it is cash 12.62 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual poor. It could go bankrupt if it can’t borrow money someplace to cover until accounts receivable are collected. 2. Why did Katherine do better when she raised her prices and refused to sell on credit? Higher prices increase cash flow when the terms are cash and slow the need to borrow funds to buy on credit. Too rapid growth often leads to cash flow problems because the growth is all financed and there is not enough cash available to back it up. 3. What was the nature of Katherine’s problem? Was she correct to go to the banker for help, even though she owed the bank money? How could she have prevented some of the problems she eventually found herself faced with? Katherine had a classic cash flow problem, and, yes, a bank is an excellent place to turn for help. The bank can provide funds, help in designing a cash budget, and provide further guidance to avoid cash flow problems in the future. What got Katherine in trouble in the first place was being too free to grant credit to customers and not being more insistent about collecting overdue accounts. To slow business, she could have raised prices and given credit only to her best customers. CHAPTER 12: Understanding Financial Information and Accounting 12.63 ENDNOTES Sources: Andrea L. Charters, “The Sarbanes-Oxley Act Enforces Three Major Stock Market Reforms,” St. Louis Business Journal, April 18-24, 2002, p. 45; “Rules Adopted on Auditing Firm Services,” United Press International, January 23, 2003; Stacy A. Teicher, “Job of Policing Companies May Fall More to Insiders,” The Christian Science Monitor, March 31, 2003, p. 18; “Ex-Andersen Auditor’s Sentencing Delayed,” AP Online, May 8, 2003; Carrie Johnson, “Corporate Audit Panels to Gain Power; SEC Passes New Reforms,” The Washington Post, April 2, 2002, p. E02; Ed McCarthy, “Tips for the Sarbanes-Oxley Learning Curve,” Journal of Accountancy; June 1, 2004; and U.S. Sen. Paul Sarbanes, “Living up to its Promise Sarbanes-Oxley Pays Dividends by Keeping Companies Honest,” Denver Rocky Mountain News; April 8, 2006. i ii Source: Scott Waller, “Whistleblower Tells Her Story,” The Clarion-Ledger, April 29, 2006. iii Source: Bobbie Gossage, “Cranking Up the Earnings,” Inc. Magazine, October 2004. iv Source: Bo Burlingham, “What’s Your Culture Worth?,” Inc. Magazine, September 30, 2001, pp. 124-132 Sources: John Case, “The Surprise Economy,” Inc. Magazine, September 2002, p. 38; and Rachel Brand, “Nonprofits Feel Effects of Corporate Scandals,” Denver Rocky Mountain News, July 30, 2002, p. 24B. v 12.64 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS: Instructor’s Resource Manual