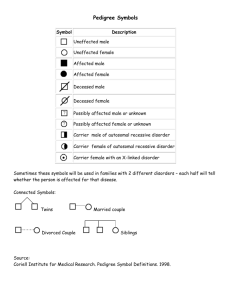
GENETIC DISORDER
advertisement
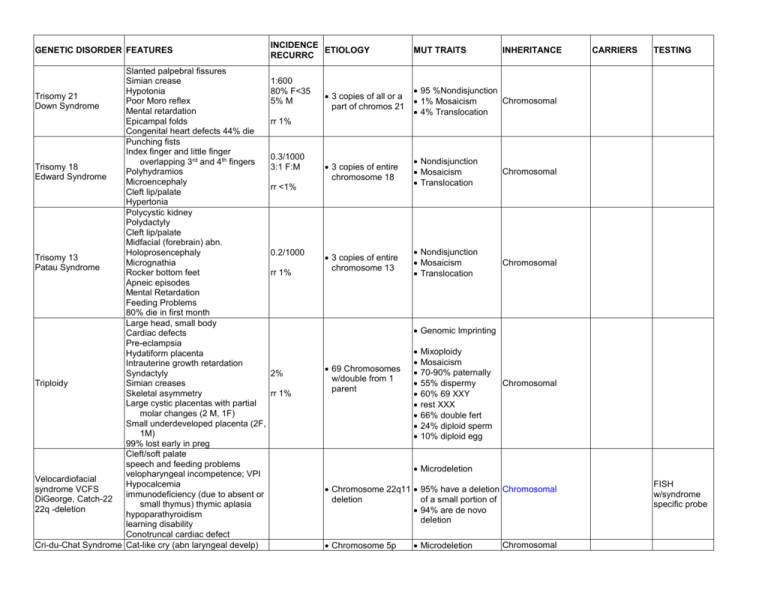
GENETIC DISORDER FEATURES Slanted palpebral fissures Simian crease Hypotonia Trisomy 21 Poor Moro reflex Down Syndrome Mental retardation Epicampal folds Congenital heart defects 44% die Punching fists Index finger and little finger overlapping 3rd and 4th fingers Trisomy 18 Polyhydramios Edward Syndrome Microencephaly Cleft lip/palate Hypertonia Polycystic kidney Polydactyly Cleft lip/palate Midfacial (forebrain) abn. Holoprosencephaly Trisomy 13 Micrognathia Patau Syndrome Rocker bottom feet Apneic episodes Mental Retardation Feeding Problems 80% die in first month Large head, small body Cardiac defects Pre-eclampsia Hydatiform placenta Intrauterine growth retardation Syndactyly Triploidy Simian creases Skeletal asymmetry Large cystic placentas with partial molar changes (2 M, 1F) Small underdeveloped placenta (2F, 1M) 99% lost early in preg Cleft/soft palate speech and feeding problems velopharyngeal incompetence; VPI Velocardiofacial Hypocalcemia syndrome VCFS immunodeficiency (due to absent or DiGeorge, Catch-22 small thymus) thymic aplasia 22q -deletion hypoparathyroidism learning disability Conotruncal cardiac defect Cri-du-Chat Syndrome Cat-like cry (abn laryngeal develp) INCIDENCE ETIOLOGY RECURRC 1:600 80% F<35 5% M MUT TRAITS INHERITANCE 3 copies of all or a part of chromos 21 95 %Nondisjunction Chromosomal 1% Mosaicism 4% Translocation 3 copies of entire chromosome 18 Nondisjunction Mosaicism Translocation Chromosomal 3 copies of entire chromosome 13 Nondisjunction Mosaicism Translocation Chromosomal CARRIERS TESTING rr 1% 0.3/1000 3:1 F:M rr <1% 0.2/1000 rr 1% Genomic Imprinting 2% rr 1% 69 Chromosomes w/double from 1 parent Mixoploidy Mosaicism 70-90% paternally 55% dispermy 60% 69 XXY rest XXX 66% double fert 24% diploid sperm 10% diploid egg Chromosomal Microdeletion Chromosome 22q11 95% have a deletion Chromosomal deletion of a small portion of 94% are de novo deletion Chromosome 5p Microdeletion Chromosomal FISH w/syndrome specific probe GENETIC DISORDER FEATURES XYY Syndrome XXY Klinefelter Syndrome 45XO Turner Syndrome Hemophilia A Hemophilia B Christmas Disease Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD) Microcephaly Intrauterine growth retardation Slow growth, hypotonia Mental retardation Hypertelorism, strabismus, epicampal folds Downward slanting palpebral fiss. Phenotypic normal male Tall thin stature Muscle weakness Poor fine motor coordination Dull mentality, Low IQ Fertile Severe nodulocystic acne Facial asymmetry w/large teeth, long ears, prominent glabella Most common cause of Hypogonadism and Infertility M Testosterone insufficiency Late onset of speech Behavior problems Long limbs w/big upper/lower body Gynecomastia 40% Intention Tremor 20-50% Tall thin stature (obese w/o test) Hyalinization/fibrosis of semi tubule Phenotypic female Small stature Hearing loss Webbed neck – pterygium colli Gonadal dysgenesis Transient congenital Lyphedema w/puffy hands and feet Cubitus valgus Cardiac anomalies More males than females Coagulation deficiency INCIDENCE ETIOLOGY RECURRC INHERITANCE CARRIERS TESTING deletion (short arm) Majority de novo 10% translocation 1:840 Extra Y Chromosome 47 XY Chromosomal 1:500 Extra X Chromosome 75% XXY 22% XXY/XY mosaic few XXYY/ XXXY Chromosomal 1:5000 Paternal set of chromosomes missing 45X 1/10,000 1/5000 M More males than females Coagulation deficiency Young boys Proximal muscle weakness Gower’s maneuver Large calves High blood creatine kinase Milder severity Weakness develops later Survive to mid-adulthood MUT TRAITS 1:4000 M Mosaicism 45X/46XX mosaics Partial deletion of Chromosomal one X chromosome 45X/46XY gonadoblastoma X Chromosome Large inversion Factor VIII mutation Insertion of LINE X Chromosome Xq27.1 Factor IX mutation X Chromosome Xq21 Dystrophin gene Largest gene X Chromosome Dystrophin gene Treat w/testosterone X-Linked Recessive Locus heterogeneity All daughters are carriers X-Linked Recessive Locus heterogeneity >90% deletions Frame shift mut Premature termination X-Linked Recessive Allelic heterogeneity >90% deletions In-frame deletions X-Linked Recessive Allelic heterogeneity F: high blood protein GENETIC DISORDER FEATURES INCIDENCE ETIOLOGY RECURRC Neurological syndrome Nystagmus Severe spastic quadriparesis Cognitive impairment Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Ataxia Disease (PMD) Leukodystrophy Apoptosis of oligodendrocytes Mild: demyelinating peripheral neuropathy Phenotypic females Large breasts Testicular Internal testes Feminization (TFM) Lack of internal female genitalia Androgen Insensitivity Lack of menstruation, pubic, axillary hair, infertile Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy (SBMA) Kennedy Dx X Chromosome Xq21-22 PLP gene Adult onset muscle weakness Gynecomastia Results in hemolytic anemia in response to certain medications such as antimalarials, fava beans and some infections due to a deficiency in G6PD enzyme Drug induced hemolysis: NADPH is one of the products of G6PD. Glucose-6-phosphate NADPH protects the cell against 400 million dehydrogenase def. oxidative damage by affected G6PD regenerating reduced glutathione w/G6PD deficiency, oxidant drugs causes a dramatic severe acute hemolytic anemia Most common disease-producing enzyme defect OTC deficiency Hunter’s Disease Anhydrotic Ectodermal dysplasia Fragile X FRAXX Martin-Bell Severe mental retardation Most common monogenic form of inherited mental retardation Elongated face Macroorchidism Schizophrenia Large testes and ears MUT TRAITS INHERITANCE Gain-of-fcn mut Majority are duplications of PLP region on X Chrm X-Linked Recessive Most are missense mutation (aa sub) Null mutation (miss PLP, less severe) X Chromosome X q 11-12 Androgen receptor 46 XY Mut inactivates androgen receptor Null mutation X-Linked Recessive Trinucleotide repeat Can be dominant Gain-of-function Allelic heterogeneity X Chromosome Xq12 Androgen receptor CAG X-Linked Recessive Allelic heterogeneity Provides some resistance to malaria X chromosome G6PD gene Dosage compensation: equalization of gene activity despite females having twice the gene # of X chromosome Pharamcogenetics X-Linked Recessive X-Linked Recessive X-Linked Recessive Incomplete penetrance Non-mendelian Trinucleotide repeat X-Linked Dominant Shermann Paradox M F Dad normal 9% 5% kids 40% 16% Fragile X Chromo. 1/12-1500 M Xq28 (long arm) 1/2000 F FMR-1 gene 5’UTR CGG CARRIERS X-inactivation Lyonization Expressed to the same degree in RBC of men and women X-Linked Recessive Seen in African, Meditarran ean and Asian descent 1/700 TESTING GENETIC DISORDER FEATURES INCIDENCE ETIOLOGY RECURRC MUT TRAITS INHERITANCE Only females affected Most common form of mental retardation in females (severe) Rett Syndrome (RTT) Hand wringing Spastic paraparesis w/ ataxia Lethal to males fetuses X Chromosome 1:10-15,000 Xq28 F MeCP2 gene Epigenetic Imprinting Binds to methyl bases X-Linked Dominant Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive hexoaminidase A deficiency Autosomal Recessive Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency Osteogenesis Imperfecta Galactosemia Smith-Lemli-Opitz (SLO) Meckel-Gruber Adrenal Insufficiences Urea Cycle disorders Methylmalonc aciduria Biotidinase deficiency Hurler Syndrome Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Dominant Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Autosomal Recessive Acute Intermittant Porphyria (AIP) Achondroplasia Marfan’s Syndrome Huntington’s Disease Myotonic Dystrophy Neurofibromatosis Von Recklinhausen’s Disease Charcot-Marie-Tooth CMT disease ACHOO compelling Autosomal Dominant Autosomal Dominant Autosomal Dominant Autosomal Dominant Cystic Fibrosis Sickle Cell Anemia Thalassemia Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (MLD) Ataxia Telangiectasia (ATM) Freidreich Ataxia Phenylketonuria PKU Spinal Muscular Atrophy Tay-Sachs Storage disease 1/3000 CARRIERS 3% Ashkenazi Jews TESTING GENETIC DISORDER FEATURES helio ophthalmic outburst Familial Hypercholesteremia Polycystic kidney disease Reinoblastoma RBI Wilm’s Tumor Familial Polyposis Coli Li Fraumeni CML Barlatt’s Lymphoma Lip Pits Malignant Hyperthermia Cleidocranial pubodysplasia MODY KS MERRF MELAS NARD LHON Neural Tube Defects Pyloric Stenosis Psychiatric disorders Diabetes Mellitus INCIDENCE ETIOLOGY RECURRC MUT TRAITS INHERITANCE Mitochondrial Multifactorial CARRIERS TESTING