Unit 1

Directions: Study guides should be typed (single space). All study guides are due on the day of the exam over that/those unit(s). Each unit study guide is worth 25 points.
1.
For each type of single gene abnormality, describe the conditions necessary for a child to be affected and specify any sex differences a.
Autosomal recessive b.
Autosomal dominant c.
X- linked recessive
Metro Community College
Nursing Program
NURS 2410 Unit 1 Study Guide
2.
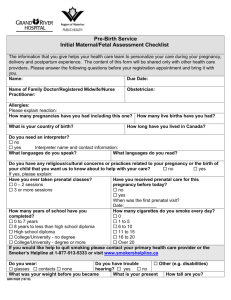
When should a rubella immunization be administered to a woman of child bearing age?
3.
In prescribing drugs for pregnant women, what must the healthcare professional balance?
4.
List factors that may impair the ability of sperm to fertilize the ovum.
5.
List factors that may disrupt the hormonal secretions a woman needs to achieve pregnancy.
6.
List factors that may impair structure and function of the fallopian tubes.
7.
Describe the nursing interventions associated with each of the listed diagnostic tests for infertility. a.
Semen analysis b.
Basal body temperature c.
Post coital test d.
Hystersalpingogram e.
Endometrial biopsy
8.
List two complications associated with medications given to induce ovulation
9.
Complete a table with the description, advantages and disadvantages of the following: a.
IVF (in vitro fertilization) b.
GIFT (gamete intrafallopian transfer) c.
HIT (Husband [doner] intrafallopian transfer) d.
TET (tubal embryo transfer)
10.
Complete a table listing clinical manifestations and therapeutic management of the following types of spontaneous abortions: a.
Threatened b.
Incomplete c.
Complete d.
Recurrent e.
Missed
11.
What teaching is needed for the woman having methotrexate therapy for an early ectopic?
12.
List the typical signs and symptoms of a hydatidiform mole (gestational trophoblastic disease)
13.
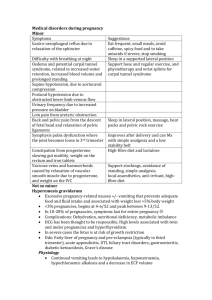
What is the significance of epigastric pain in a woman with pre eclampsia?
14.
List signs of magnesium toxicity. What is the antidote?
15.
Why is maintenance of a normal blood glucose level before and during early pregnancy important?
16.
Do insulin needs increase, decrease or remain stable during the following times? Explain your answer. a.
First trimester b.
Second and third trimester c.
Labor d.
Postpartum
17.
Why are labor and the immediate postpartum period especially dangerous for a woman who has heart disease?
18.
Why does maternal sickle cell crisis make fetal death more likely?
19.
Create a table that defines the maternal effects, fetal effects, prevention and treatment of the following during pregnancy: a.
Rubella b.
Herpes virus c.
Varicella d.
Toxoplasmosis e.
Group B streptococci f.
tuberculosis