bio study guide final exam copy
advertisement

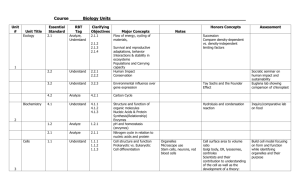
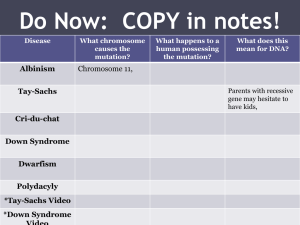
BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE PART 1 AND 2 The following study guide covers all concepts from the ninth grade school year. The material will be covered in two final exams, part 1 and part 2 Consider the concepts covered, and how they relate not only to what we have covered during the year, but also to the diversity of life on earth Concepts covered Test part 1 1. Focus of biology 2. Homeostasis 3. Organization of cells 15. Relative vs. absolute dating 16. Evolution – Darwin and Wallace 17. Ecology 18. Viruses 4. Organelles 5. Eukaryotic vs. prokaryotic 6. Cellular respiration, ATP, and the mitochondria 7. Photosynthesis and the chloroplast 8. Cell division – mitosis vs. meiosis vs. binary fission 9. DNA and (A,T,C,G) 10. Carbs, fats, proteins, and nucleotides 11. Linnaean classification 12. Community vs. population vs. ecosystem 13. Phylogenetic trees vs. clades 14. The species concept Test part 2 1. Inheritance 2. Mendelian genetics 3. Blending theory vs. independent assortment 4. Polygenic vs. co-dominant vs. incomplete dominance vs. recessive and dominant 5. The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology 6. RNA vs. DNA 7. X vs. Y chromosome 8. Mutation types 9. Human genome project 13. Macro vs. Microevolution 10. Autosomal recessive vs. sex-linked, vs 14. Natural selection, mutation, gene flow, gene drift chromosomal disorders 11. Lamarck, Lyell, and Malthus 12. Homologous vs. analogous structures vs. comparative anatomy 15. Autotrophs vs. heterotrophs 16. Producers vs. consumers Notes Biology is the science of? What is homeostasis? Which is the more complex cell, prokaryotic or eukaryotic? What are organelles and what are examples of what they do? Over many generations, what do organisms do as they relate to their environment? What do plant cells have that animal cells do not? What is a phospholipid bi-layer? What organelle “runs” or “directs” eukaryotic cells? Where does DNA reside and what does it do? What does cellular respiration produce? What does photosynthesis produce? What is binary fission? What happens when the cell cycle is no longer regulated? What are taxa, and whose name is connected with binomial nomenclature? Proteins are soooo important in bio; what are the building blocks of proteins? What does a phylogenetic tree show? Relative and absolute dating; which one aims to date in actual calendar years? To what does the term thermo refer? A virus’ protein coat is called a? What does genetics study? Who first discovered laws of (simple) inheritance? What does polygenic mean? Contrast co-dominance and incomplete dominance? What says this: DNA > RNA > protein. Or transcription > translation > protein? Where are sex-linked traits found? If a trait is autosomal recessive, what is someone called who has one dominant and one recessive gene for the condition? Who said that “acquired characteristics” can be passed on to the next generation? Why is the evolution of sexual dimorphism considered disruptive selection? All interacting genes in a population are called a? What are the four mechanisms of biological evolution? Contrast homologous and analogous structures. If organisms move into an open or available niche, what is it called?









![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)