E1 Rev Fa 03
advertisement

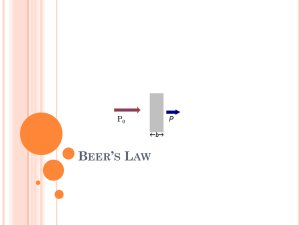
Chem 251 Exam 1 Review I will provide any necessary tables, constants and complicated formulas on the exam. Formulas you should know are c = ; E = h ; Beer’s Law; the formulas for Transmittance and Absorbance; pH; pOH; Kw; the Henderson/Hasselbach equation. There are 63 questions on this review, obviously the exam will be much shorter. I will post the answers to the numerical calculation review questions on the web site by Fri afternoon. Questions 1 – 6 refer to the following data set: Six samples of caffeine are prepared at the same concentration and analyzed spectroscopically. The absorbances at 270 nm were found to be: 0.2625, 0.2635, 0.2590, 0.2700, 0.2610, 0.2715 1. Calculate the mean absorbance. 2. Calculate the standard deviation of the measurements. 3. What is the relative deviation (in the form of a percentage)? 4. What is the 95% confidence limit? 5. A 7th sample is prepared and its absorbance is found to be 0.2439. Use the Q-test to determine if this sample can be rejected. 6. The molar extinction coefficient for caffeine at 270 nm is = 8750 ( 50 ) M-1cm-1. Using Beer’s Law: A = b c with a 1 cm path length cell, calculate the concentration of the caffeine (including error) using the average absorbance. Assume the error in the average absorbance to be equal to its standard deviation calculated in problem #2. Neglect any uncertainty in the path length. 7. Draw a rough sketch of a Gaussian distribution. Label the x and y axis, the mean, and the standard deviation. What % of data points will fall within 1s? 2s? 8. Describe the differences between systematic and random error and give examples of each. How are accuracy and precision related to systematic and random error? 9. The equation of a line of best fit is found to be y = 5.00x – 2.0, where the errors in the slope and intercept are 5% and 15% respectively. What is the predicted value of y (including uncertainty) for an x measurement of 10.0 .4? 10. Describe the processes going on inside the atoms during a) AAS and b) AES. 11. Draw a simple sketch of an AAS instrument and describe the parts. How would the AES instrument sketch differ from the AAS? 12. How would you prepare 250.0 mL of 0.10 M sodium benzoate (molar mass 144.11) ? 13. What is the concentration of the solution in #12 in ppm? 14. How would you prepare 10.0 mL of a 0.020 M sodium benzoate solution from the stock prepared in #12? 15. How would you prepare a 10 % w/w NaCl solution? 16. Assuming typical uncertainties in the measurements, what is the uncertainty in your concentration in #15? 17. Which of the following is a weak acid in aqueous solution? a) HNO3 b) HF c) H2SO4 d) HNO3 18. Which of the following salt solutions would be expected to have the highest pH ? a. NaCN(aq) b. NaClO4 (aq) c. NH4NO3 (aq) d. NaNO3 (aq) e. NaCl(aq) 19. What is the pH of a 0.08 M solution of benzoic acid ? 20. What is the pH of a 0.2 M solution of sodium propionate, NaC 3H5O2 ? 21. What is the pH of a 0.2 M solution of NH4Cl ? 22. What is the hydrolysis reaction of the acetate ion ? 23. Seawater has a pH of 8.10. What is its hydroxide ion concentration? 24. Which of the following mixtures is (are) suitable for making buffers? a. HC7H5O2 and NaC7H5O2 b. NH3 and NH4Cl c. HCl and NaCl 25. What is the pH of a solution which is 0.50 M in acetic acid and 0.10 M in sodium acetate? 26. All the following are acid-base conjugate pairs except a) OH- , O2b) H2CO3 , HCO3c) HNO2 , HNO3 d) HOCl, OCle. HSO4- , SO4227. Which of the following is the strongest acid? a. HC2H3O2 b. HNO2 c. HOCN d. HClO e. HCN 28. Milk of magnesia has a pH of 10.40. What is its [H3O+]? 29. What is the acid dissociation reaction for HS- ? 30. What is the pH of 0.010 M HNO 3 ? 31. What is the [ C2H3O2 - ] / [ HC2H3O2 ] ratio in a buffer of pH 5.00 ? 32. Tris is a base used to make biological buffers. If the pKa of Tris is 8.0, describe how you might make a pH 8.2 Tris buffer. 33. What is the frequency of light with wavelength 254 nm? 34. What part of the spectrum is this light from? 35. What is the light’s energy? 36. Describe what is going on inside a molecule that absorbs light. 37. Why are only certain frequencies of light absorbed by a substance? 38. Why does AES/AAS generally involved line spectra while a typical UV/VIS spectra has broad peaks? 39. Draw a simple diagram of a UV/VIS spectrophotometer; explain each component. 40. What is the relationship between transmittance and absorbance? 41. If a substance has 34% transmittance at 450 nm, what is its absorbance at 450 nm? 42. What is the equation associated with Beer’s Law; define each of the components. 43. Explain in words or pictures how concentration and path length effect absorbance. 44. Explain how a Beer’s Law plot is determined and what it might be used for. 45. What is the difference between a monochromator and a polychromator. 46. When the concentration of chromium in a sample was determined by AES using the method of standard additions, the following data were obtained: Cr added Average (ppb) Reading No Spike 0.000 0.539 Spike 1 2.000 0.664 Spike 2 4.000 0.793 What is the approximate concentration of chromium in the original sample? 48. What information can we obtain from a Boltzmann distribution? 49. Describe a typical type of interference found in flame AES experiments. 50. Why do we have to redo calibration curves every time we use an AS instrument? 51. What is ICP AES? How does it differ from flame AES? 52. What is difference between single and double beam spectrometers? 53. Name 2 typical light sources in UV/VIS spectrometers? What wavenumber range do we typically use in IR spectrophotometry? 54. What are the properties of laser light? 55. What is fwhm and how does it relate to spectrophotometry? 56. Describe the process occurring inside a photomultiplier tube (PMT). 57. Describe the process occurring inside a spectrometer utilizing a photodiode array detector. 58. What type of transitions are occurring inside substances absorbing IR radiation? What IR spectrophotometry tell us about organic molecules? 59. Name 2 types of IR detectors. Describe how one of them works (briefly). 60. What does FTIR stand for? 61. Describe the mechanics of how an interferometer works. 62. How does changing the path length of one light beam in an interferometer affect the beams when they recombine? 63. What is an interferogram and how is it related to the spectrum of light reaching the detector?