Rate of dissolving

Mixtures and
Solutions
Name ______________________
Teacher ____________________
Science Class Period 1 2 3 6 7
Date _______________________
Mixture - 2 or more substances mixed together but not chemically combined
Examples:
Granite – contains feldspar, mica, quartz among other substances
Sand
Soil
Tossed salad
Mixtures are classified according to how well mixed they are
Heterogeneous - substances in which components are not evenly distributed
Examples:
Vinegar and oil
Granola (oats, seeds, coconut, raisins, etc)
Homogeneous - substances in which the components are evenly mixed
Examples:
Paint
Milk
Toothpaste
Perfume
Mixtures can be classified as colloids, suspensions, and solutions.
Colloid - a mixture in which the particles are mixed but not dissolved.
The particles do not settle out.
The particles can be seen when a light is shined through the colloid.
Examples:
Paint
Fog
Smoke
Shaving cream
Suspension - a heterogeneous mixture in which some particles settle out
Example:
Raging river water- silt and particles drop out when water is still
Solution - well-mixed mixture in which the particles are small and dissolved
Examples:
Sea water. 70% of the Earth is covered with a salt water solution
Air is a solution of mostly nitrogen and oxygen
CO
2
is a gas dissolved in soda pop
Physical Science Series Mixtures and Solutions Video Notes 1
Solute - a substance that is dissolved in another substance.
Solvent - a substance in which the solute is dissolved
In sea water, salt is the solute and water is the solvent
Water is called the universal solvent because many substances dissolve in water
Soluble - ability of a substance to dissolve into another substance
Sugar is soluble in water.
Insoluble - inability of a substance to dissolve into a specific substance
Oil is insoluble in water.
Rate of dissolving:
Stirring speeds up rate of dissolving
Particle size- the smaller particles have more surface area that comes in contact with the solvent
Generally, increased temperature speeds the rate of dissolving a solid into a liquid.
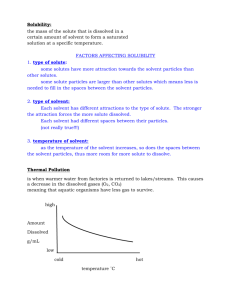
Solubility - measure of how much solute can be completely dissolved in a solvent
A solvent can only dissolve so much solvent
Example:
Copper sulfate, CuSO
4
32 g/ 100 mL water at 20
C
Saturated solution - a solution that has dissolved all the solute it can at a specific temperature.
Label the x-axis
C.
Label the y-axis grams/100g of water.
Draw a curve that shows how much solute can be dissolved in the water at a specific temperature.
Above the curve, the solution is saturated. Below the curve, the solution is unsaturated.
Note: The graph below is not the graph from the video. Notice that the area above the red line shows where a solution is saturated. In other words, not all of the solute would be dissolved.
Some of the solute would settle to the bottom of the beaker.
Physical Science Series Mixtures and Solutions Video Notes 2
Warm lakes dissolve less oxygen, O
2
, than cold lakes.
Label the x-axis [O
2
].
Label the y-axis
C.
Draw a curve that shows how much oxygen, O
2, can be dissolved in the water at a specific temperature. Above the curve, the solution is saturated. Below the curve, the solution is unsaturated.
Alloys - a metal in which 2 or more solids are dissolved together
Example:
Steel, a solution of iron, chromium, and other metals
Sterling silver, a solution of silver, Ag, and copper, Cu.
Quiz:
1. A __ heterogeneous _____ mixture is not well-mixed.
2. A __ homogeneous _____ mixture is the same throughout.
3. In a colloid, the particles are _ mixed but not dissolved _.
4. Muddy river water is an example of a _ suspension ___.
5. In a solution the particles are _ dissolved ___.
6. The _ solvent ___is the part of the solution that does the dissolving.
7. __ Water ____ is often called the universal solvent.
8. The ___ solute ____ is the part of the solution that is dissolved.
9. __ Smaller ____particles tend to dissolve faster than larger ones.
10. An __ alloy ____ is a metal made of two or more solids.
Physical Science Series Mixtures and Solutions Video Notes 3
Physical Science Series Mixtures and Solutions Video Notes 4