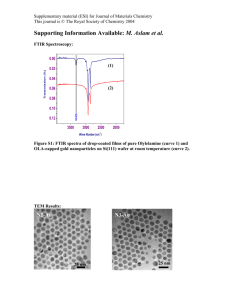
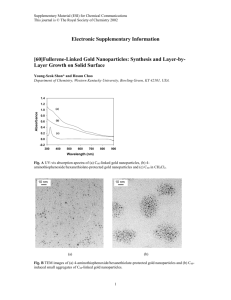
Electronic supplementary information of the paper entitled
advertisement
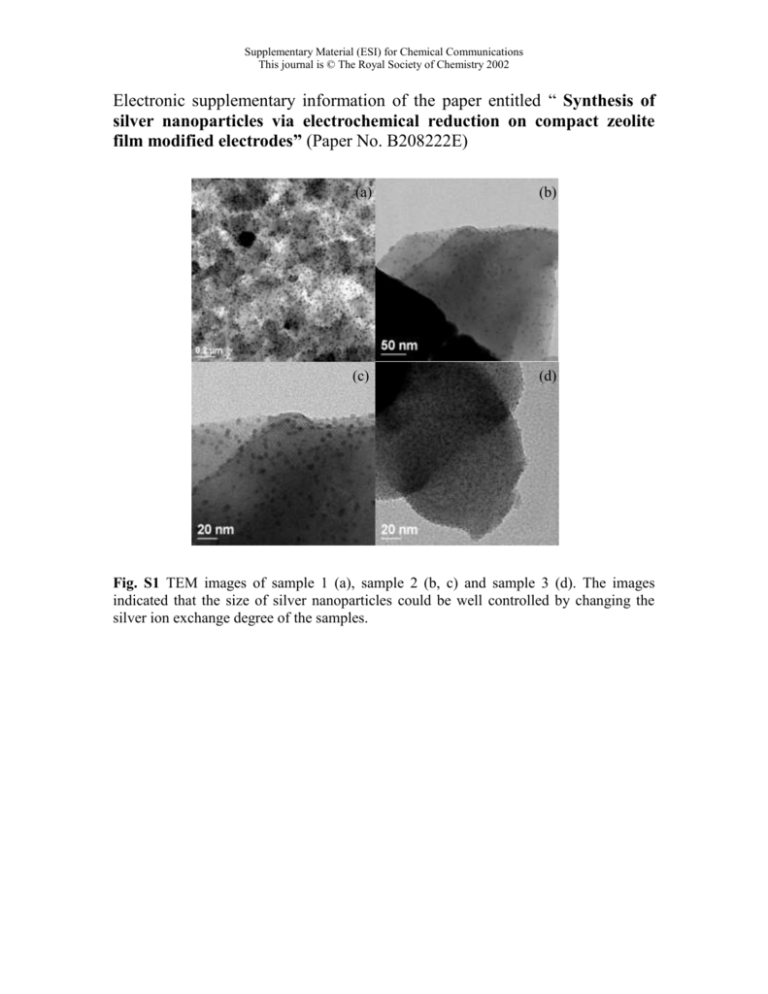
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2002 Electronic supplementary information of the paper entitled “ Synthesis of silver nanoparticles via electrochemical reduction on compact zeolite film modified electrodes” (Paper No. B208222E) (a) (b) (c) (d) Fig. S1 TEM images of sample 1 (a), sample 2 (b, c) and sample 3 (d). The images indicated that the size of silver nanoparticles could be well controlled by changing the silver ion exchange degree of the samples. Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2002 cf25min cf15min (a) 80 (b) 80 60 60 40 40 20 20 0 0 O 64.08 Al 9.72 Na 4.84 O 66.62 Ag 3.07 Al 9.24 Na 3.87 Si 18.29 Mean cf30min Value: Atomic% Ag 3.47 Si 16.8 Mean Value: Atomic% (c) 80 60 40 20 0 O 65.04 Al 9.78 Na .25 Ag 7.94 Si 16.99 Mean Value: Atomic% Fig. S2 Electron dispersive spectrum (EDS) analyses of sample 1 (a), sample 2 (b) and sample 3 (c) before electrochemical reduction, and electron diffraction (ED) analysis of sample 2 (probably containing some diffraction of zeolite-FAU). The EDS results indicate that these samples possess different ion exchange degree from the Ag/Al and Na/Al ratios, as shown in table 1, and ED analysis indicates that the silver nanoparticles might be polycrystals.