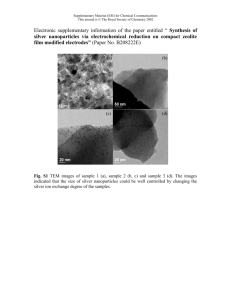
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of
advertisement

Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Peperomia pellucida for enhanced antibacterial activity against clinically isolated human pathogens Konar, S. a, Ojha, D. a, Dam, A. and Bandyopadhyay, T.K.* Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, University of Kalyani, Kalyani -741235, West Bengal, India a Jointly first Author. *Corresponding Author, email address: tapas@klyuniv.ac.in Development of environmentally nontoxic, ecofriendly and cost-effective synthesis of silver nanoparticles is of great importance in the field nanobiotechnology. The unique property of the silver nanoparticles having the antimicrobial activity also drags the major attention in this area. The present study deals with the rapid green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) from silver precursor ( AgNO3) using the aqueous leaf extract of Peperomia pellucida and its activity against clinically isolated human pathogens, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. The formation of silver nanoparticles was observed within 30min under continuous shaking condition. The synthesized silver nanoparticles were characterized by the UV-visible Spectroscopy (Surface Plasmon absorption), Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), High resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM). The EDS analysis of the nanoparticles dispersion confirmed the presence of elemental silver, with no other detectable impurity peaks. The topography and morphology of the particles were determined using HRTEM and the average diameter of the particles was determined as 80–110 nm. Further, the antibacterial activity of the synthesized silver nanoparticles was evaluated by Zone inhibition assay and Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) assay. The biogenic silver nanoparticles showed effective antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.