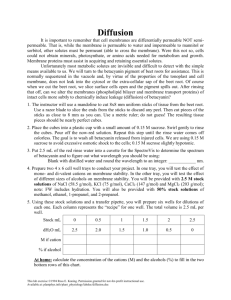
Surface Area to Volume Ratio

Biology
Student Name____________________________Per____
Ms. Buchalski
Date __________________________
LAB
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Modeling a Cell by Building Boxes
Introduction
Cells are limited in how large they can be. This is because the surface area and volume ratio does not stay the same as their size increases. When a cell becomes larger, the need for nutrients increases and the cell excretes more waste. However, it is harder for a cell to pass materials in and out of the cell membrane, and to move materials throughout the cytoplasm of the cell.
In this lab, you will make cube shaped models to represent cells. The dimension along one side will be doubled for each model. You will then calculate the surface area, volume and ratio for surface area and volume.
Materials
Scissors
Colored Pencils
Metric Ruler
Tape
Calculations
Surface area = (length x width) x 6 sides
Volume = length X width x height
Ratio = Surface area
volume
Procedure
1.
Color the paper models of the cells.
2.
Cut out the paper models, making sure to keep the tabs on the outside to assist with folding. Construct five cell models by folding up each side and make a cube (note one side is missing). Use the tabs to fold on the inside of each of the sides. Use tape to hold the sides together.
3.
Record the dimensions in the data table below. The dimensions of a side will double each time, with the sides being
(1 cm, 2 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm and 8 cm).
4.
Make all of the appropriate calculations for each cube, using the equations above. Record all values in the Data
Table below; the first one is done for you.
5.
Answer the questions on the back of the paper.
6.
Stack your cubes together, make sure your name is on each one of them.
Cell Dimensions
# (cm)
Data Table: Cell Size Comparison
Surface Area
(cm 2 )
Volume
(cm 3 )
1
2
3
4
5
1 x 1 x 1 (1 x 1) x 6 = 6 1 x 1 x 1 = 1
Ratio
(Surface Area : Volume)
6:1
Page 1 of 2
Biology
Student Name____________________________Per____
Ms. Buchalski
Date __________________________
Questions
1.
Which cell model has the smallest surface area? ___________________________________
2.
Which model has the largest surface area? ________________________________________
3.
Which model has the smallest volume? ____________________________________________
4.
Which model has the largest volume? _____________________________________________
5.
Which model has the smallest ratio of surface area to volume? _____________________
6.
Which model has the largest ratio of surface area to volume? ______________________
7.
As the cell grows larger, does the Surface Area -to- Volume Ratio get larger, smaller, or remain the same? ________________________________________________________________
8.
Anything that the cell takes in, like oxygen and food, or lets out, such as carbon dioxide, must go through the cell membrane. Which measurement best represents how much cell membrane the models have? ______________________________________
9.
The cell contents, nucleus and cytoplasm, use the oxygen and food while producing the waste. Which measurement best represents the cell content? ___________________
10.
As the cell grows larger and gets more cell content, will it need more or less cell membrane to survive? ____________________________________________________________
11.
To maintain life and carry-out cellular functions, materials must be able to move into and out of the cell. Also, materials need to be able to move within a cell. What might be the advantage of having a large surface area?
___________________________________________________________________________________
12.
What might be the disadvantage of having a large volume?
___________________________________________________________________________________
13.
What happens to a cell if the surface area cannot support the volume of the cell?
___________________________________________________________________________________
14.
Why can't cells survive when the Surface Area -to- Volume ratio becomes too small?
____________________________________________________________________________________
15.
Which size cell has the greatest Total Surface Area -to- Volume Ratio? ______________
16.
Which size cell has the greatest chance of survival? ________________________________
17.
What can cells do to increase their Surface Area -to- Volume Ratio? ________________
Page 2 of 2