Exp_2 - UniMAP Portal
advertisement

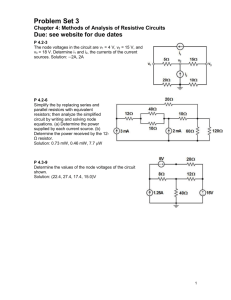
EKT101/4 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY MODULE EXPERIMENT 2 NODAL ANALYSIS AND MESH ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES OBJECTIVES 1. To construct resistive circuits and analyze the circuits using Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis. 2. To test and demonstrate the validity of nodal analysis and mesh analysis through experimental measurements. INTRODUCTION Basic laws such as the Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s laws can solve only a limited number of variables in circuit analysis and are restricted to analyzing simple circuits. To solve for complex circuits with a single source or circuits with more than one source that are not in series or parallel place a need for a more powerful techniques such as Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis. These two techniques can be used to solve almost any kind of circuit analysis problems. The mesh analysis technique will determine the currents of the circuit while the nodal analysis approach will provide the potential levels of the nodes of the circuit with respect to some reference. The application of each technique follows a sequence of steps, each of which will result in a set of equations with the desired unknowns. It is then only a matter of solving these equations for the various variables, whether they be current or voltage. These equations can be either solved by using Cramer’s rule (which allow us to obtain circuit variables as a quotient of its determinants) or by calculator (if not involved complex number) or barely by normal substitutions and eliminations (not suggested for more than two equations). Most of the circuit analysis problems in this course will be limited to the three linear simultaneous equations for conventional hand solutions. EQUIPMENT/COMPONENT Multimeter (1) Variable DC Power Supply (1) Resistor (1/4 W) – 3.9 k, 1 k , 2.2 k, 4.7 k, 6.8 k Breadboard (1) **For all theoretical calculation results students are strictly required to show their work in progress (formula form/complete figures) in the PRE-LAB space provided before the lab session. Otherwise they will be forbidden from participating the session. There will be certain marks allocated for this part. 1 Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) Lab 2 : Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis EKT101/4 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY MODULE PROCEDURE 1. Before inserting the resistors to the breadboard, measure the actual value of each resistors by using multimeter. Record all your answer in Table 3.1. PART A: NODAL ANALYSIS METHOD R1 V1 R3 V2 2.2k R5 V3 V4 1k 6.8k _ + R2 VS 1 R4 4.7k _ VS 2 3.9k + Figure 3.1: Circuit to be analyzed using Nodal Analysis method 2. Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 3.1 on the breadboard. Set VS1 and VS2 to 15V. By using multimeter, measure node voltages at V1, V2, V3 and V4. 3. Record all results in Table 3.2. Compare the difference between the measured results and calculated results if any. PART B: MESH ANALYSIS METHOD 4. Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 3.2 on the breadboard. Set VS1 and VS2 to 15V. By using multimeter, measure mesh currents I1, I2 and I3, then branch currents, Ia and Ib. 5. Record all the measurement in Table 3.3. Compare the difference between the measured results and calculated results if any. R1 2.2k + VS 1 _ R2 I1 4.7k R3 R5 6.8k 1k Ia Ib R4 I2 3.9k _ I3 VS 2 + 2 Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) Lab 2 : Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis EKT101/4 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY MODULE Figure 3.2: Circuit to be analyzed using Mesh Analysis method RESULT Resistor Designation Measured Value (k) R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 Table 3.1: Measured Resistor Value Parameter Theoretical Result Experimental (Volts) (PRE-LAB) Result % Difference V1 V2 V3 V4 Table 3.2: Nodal Analysis Method Parameter Theoretical Result Experimental (PRE-LAB) Result (miliamperes) % Difference I1 I2 I3 Ia Ib Table 3.3: Mesh Analysis Method 3 Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) Lab 2 : Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis EKT101/4 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY MODULE PRE-LAB CALCULATION (Show your WIP) (All calculations should be done in rms values. Use measured resistor values) 1. For the circuit shown in Figure 1, write down the nodal equations for the circuit and solve for V2 and V3 if both VS1 and VS2 are 15V. Show all the calculation involved and record your answers in Table 3.2. 2. Consider the circuit in Figure 2. Write down the mesh equations for the circuit and solve for I1, I2 and I3 if both VS1 and VS2 are 15V. From the results, determine branch currents Ia and Ib. Show all calculation involved and record all your answers in Table 3.3. 4 Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) Lab 2 : Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis EKT101/4 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY MODULE EVALUATION QUESTION 1. By observation, what are the values for V1 and V4 if VS1 and VS2 are set to 10V? Verify your answer. Answer: 2. State the relationship between mesh currents (I1, I2 and I3) and branch currents (Ia and Ib). Answer: 3. For the circuit in Figure 2.1 calculate the power absorbed by resistors R2 and R4. Used all measured values. Answer: 5 Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) Lab 2 : Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis EKT101/4 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY MODULE 4. Try to solve V3 using either method of analysis. Given Vs= 20V, R1 = R2 = R5 = 3.3 k, R3 = 2.2 k and R4 = 1.2 k. R1 Vs a R5 R2 b + R3 V3 R4 The method that you used for this analysis is : __________________________________________________________________________________ Show your calculations: 6 Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) Lab 2 : Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis