Sinusoidal steady
advertisement

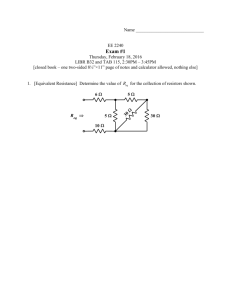
3.1. Introduction Step to analyze AC Circuits: 1. Transform the circuit to the phasor or frequency domain. 2. Solve the problem using circuit techniques (nodal analysis, mesh analysis, superposition, etc.) 3. Transform the resulting phasor to the time domain. 3.2. Nodal Analysis Find 𝑖𝑥 in the circuit of Fig. using nodal analysis. Solution: 3.2. Nodal Analysis 3.2. Nodal Analysis 3.2. Nodal Analysis From node 1 From node 2 3.2. Nodal Analysis 3.2. Nodal Analysis Example 3.2 Compute 𝑽𝟏 and 𝑽𝟐 in the circuit of Fig. Solution: Nodes 1 and 2 form a supernode as shown Fig. Applying KCL at the supernode gives; Example 3.2 Voltage source connected between nodes 1 and 2; 3.3. Mesh Analysis Determine current 𝐼0 in the circuit of fig, using mesh analysis. Applying KVL to mesh 1, we obtain 3.3. Mesh Analysis 3.3. Mesh Analysis 3.3. Mesh Analysis Example 3.4 Solve for 𝑉0 in the circuit in fig, using mesh analysis. As shown fig, meshes 3 and 4 form a supermesh due to the current source between the meshes. Example 3.4 For mesh 1 For mesh 2 Example 3.4 Example 3.4 Example 3.4 Example 3.5 Example 3.5 Example 3.5 Example 3.5 Example 3.6 Example 3.6 Example 3.6