1 - Oxford University Press
advertisement

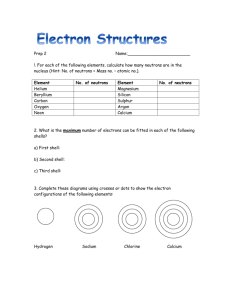
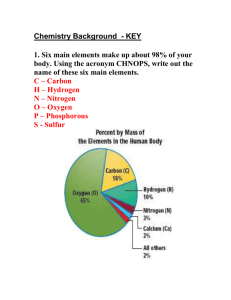
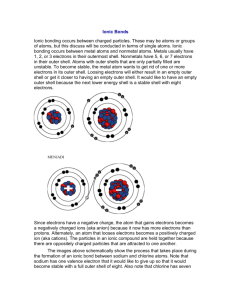
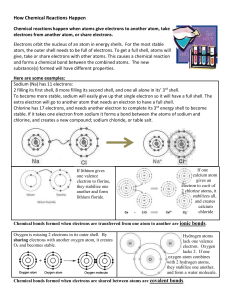
Worksheet answers Chapter 2 It’s all elemental Worksheet 2.1: What are elements made of? 1 • Oxygen is an element. It can be found in the periodic table and has the symbol O. • Gold is an element. It can be found in the periodic table and has the symbol Au. • Aluminium foil is an element. It can be found in the periodic table and has the symbol Al. • Diamond is made up of only carbon atoms. carbon is an element. It can be found in the periodic table and has the symbol C. • Magnesium ribbon contains only atoms of magnesium. Magnesium is an element. It can be found in the periodic table and has the symbol Mg. 2 112 3 As atoms become larger, more neutrons are needed in the nucleus to separate the protons. As the neutrons are much heavier than protons or electrons, the atoms containing large numbers of protons are much heavier than small atoms that contain only a few neutrons in the nucleus. 4 2 5 277 6 Cn (Co and C are already used for other elements in the periodic table). 7 Copernicus – in honour of scientist and astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543). 8 Element 112 will be classed as a metal. 9 A nuclear reaction involving fusing a zinc atom with a lead atom. 10 2 11 An isotope of hydrogen has the same number of protons and electrons in each atom but a different number of neutrons. 12 Hydrogen has a mass number of 1 as there is only one proton in the nucleus. Deuterium has a mass number of 2 as the nucleus of a deuterium atom contains a neutron and a proton. Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia 13 a The element with atomic number 19 is potassium. b There are no electrons in the nucleus of an atom. c There would be 20 neutrons in the nucleus of this atom. d There would be 19 electrons arranged in shells around the nucleus: • 2 electrons in the first shell, • 8 electrons in the second shell • 8 electrons in the third shell • 1 electron in the fourth shell 14 15 16 Lithium 17 92 18 29 19 Uranium 20 The isotope would have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus. 21 The element is sodium. Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia Worksheet 2.2: How do scientists classify elements? 1 2 3 a Best checked in class. b Any vertical column needs to be coloured in green to show a group. c Any horizontal row needs to be coloured purple to show a period. d Magnesium has the atomic number 12. The element with an atomic number which is twice this (i.e. 24) is chromium. e Sodium is in Group 1 as it has one outer shell electron. Chlorine is in Group 7 as it has 7 outer shell electrons. f Helium is listed in Group 18 as it has a full outer shell of electrons. All elements in this group have filled outer shells. Names and symbols of any four metals eg Na Sodium, Cu Copper, Ag Silver, Au Gold, Zn Zinc, Mg a Magnesium, etc. b Properties of metals: • lustrous (shiny) • able to conduct heat • able to conduct electricity • malleable (able to be beaten or hammered into thin sheets or a new shape) • ductile (able to be made into thin wires) c Ductile means that the metal is able to be made into thin wires. d Malleable means that the metal is able to be beaten or hammered into thin sheets or a new shape e Gold is less reactive than copper. It remains in pure form and does not react with many other elements or substances. Copper is more reactive. It will react with oxygen in the air or with chemicals on the hands of people holding the coins. a Oxygen and nitrogen are both colourless gases found in the atmosphere of Earth. b Oxygen has the atomic number 8, so it has 8 electrons that orbit the nucleus. In the nucleus there are 8 protons. Nitrogen has the atomic number 7. Each atom has 7 electrons orbiting the nucleus. In the nucleus there are 7 protons. c The non-metals are found in Groups lll,lV, V, Vl, Vll and Vlll. d All elements in Group 18 have filled shells of electrons. e Any of the non-metals listed in Group 18 would be acceptable here, eg helium, neon, argon etc. f Arrangement of electrons for a fluorine atom: Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia For a chlorine atom there would be another shell of electrons after the first shell. This second shell would contain 8 electrons. 4 Symbol Atomic number Name Description Number of outer shell electrons O 8 Oxygen A colourless gas that makes up 20% of the atmosphere 6 Na 11 Sodium A silvery grey metal that is very reactive 1 He 2 Helium A colourless gas that is very stable. Often used in party balloons. 2 H 1 Hydrogen A colourless but highly flammable gas 1 S 16 Sulfur A yellow powder 6 5 6 a Silicon has 4 outer shell electrons. b A semi conductor allows electricity to flow through it in one direction only, whereas a conductor will conduct electricity travelling in any direction. c Silicon is not classified as a metal because it is a better conductor of electricity than non-metals, but not as good a conductor as a metal should be. In chemical reactions silicon behaves like the nonmetals boron and carbon. Answers found within online game Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia 7 Gold (Au), Element 79, is the golden metal and copper (Cu), Element 29, is the red-brown, shiny metal. 8 a Violet b Yellow-green c Bromine is a purple-brown gas a No b Yes, element 36 Krypton c No. It is a colourless gas. 9 10 They are all silvery-grey solids . As they are so reactive they usually have a dull appearance but when freshly cut the surface is shiny. Cesium reacts much more vigorously and more rapidly with water than sodium. 11 All of these elements have a grey, metallic appearance. At room temperature boron does not conduct electricity but at higher temperatures it is able to do so. Silicon is a semi conductor – it can conduct electricity in one direction only. Arsenic occurs in three distinct solid forms: • Grey arsenic is the most common. It has a metallic sheen and conducts electricity. • Yellow arsenic is metastable, is a poor electrical conductor and does not have a metallic sheen. It is prepared by cooling gray arsenic vapor in liquid air. It reverts to gray arsenic at room temperature. • Black arsenic can be prepared by cooling arsenic vapour at 100oC–200oC. It is glassy, brittle and a poor electrical conductor. Tellurium is a semi-conductor. Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia Worksheet 2.3: What happens when elements come together? 1 The electron transfer that takes place when an atom of sodium reacts with an atom of chlorine. 2 The outer shell electron from potassium is transferred to the outer shell of fluorine, causing the formation of the potassium ion (K+) and the fluoride ion (F-). 3 Atom Number of electrons in outer shell of atom Number of electrons gained or lost Ion formed Name of the ion Na 1 Loses one Na+ Sodium K 1 Loses one K+ Potassium Mg 2 Loses 2 Mg2+ Magnesium Ca 2 Loses 2 Ca2+ Calcium 2- O 6 Gains 2 O S 6 Gains 2 S2- Sulfide Fl 7 Gains 1 F- Fluoride - Oxide Cl 7 Gains 1 Cl Chloride I 7 Gains 1 I- Bromide N 5 Gains 3 N3- Nitride P 5 Gains 3 P3- Phosphide Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia 4 a Lithium donates and electron to chlorine and lithium ions (Li+) and chloride ions are formed (Cl-) b Each magnesium atom donates two electrons to an oxygen atom. The magnesium ion (Mg 2+) and the oxide ion (O2) are formed. c There will be no reaction as argon is inert – it does not react. 5 Formula of ionic compound Name of ionic compound Cation present Anion present NaCl Sodium Chloride Na+ Cl- MgO Magnesium Oxide Mg2+ O2- CaI2 Calcium Iodide Ca2+ I- AlF3 Aluminium Fluoride Al3+ F- ZnO Zinc Oxide Zn2+ O2- Na2O Sodium Oxide Na+ O2- LiBr Lithium Bromide Li+ Br - 6 Name Formula Cation Anion Sodium Carbonate Na2CO3 Na+ CO3 2- Sodium Hydroxide NaOH Na+ OH - Potassium Nitrate KNO3 K+ NO3 - Magnesium Nitrate Mg(NO3)2 Mg2+ NO3 - Sodium Sulfate Na2SO4 Na+ SO4 2- Potassium Carbonate K2CO3 K+ CO3 2- Ammonium Chloride NH4Cl NH4+ Cl - 7 Lithium has one outer shell electron that is can give away to bromine to form the bromide ion. A a reaction will take place and lithium bromide will be formed. b Both of these metals have outer shell electrons that they could give away but there is no substance present to accept the electrons, so no reaction will occur. c Potassium can donate an electron to oxygen. Two potassium atoms could each give one electron to oxygen to form the oxide ion. A reaction will occur and potassium oxide will be formed. d Magnesium has two outer shell electrons to donate. Two chlorine atoms could each accept one electron to form two chloride ions. A reaction will occur and magnesium chloride will be formed. e Aluminium and boron are in the same Group. They have three electrons in their outer shells which they could donate to atoms which lack electrons. As there is no electron acceptor present there will be no reaction. Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia 8 f Cesium is in Group 1. It can donate its outer shell electron to another atom. Sulfur has an unfilled outer shell. It can accept two electrons to complete the outer shell. A reaction will take place with two cesium atoms donating one electron each to sulfur atoms, forming sulphide ions. Cesium sulfide will be formed. g Barium atoms can donate two electrons. Nitrogen atoms can accept three electrons to fill their outer shell. A reaction will take place. Barium nitride will be formed. The formula Ba3N2 shows that three barium atoms have donated a total of six electrons to two nitrogen atoms to form the ions. a Na+ ions b The ions are strongly attracted to one another. A lot of energy is required to weaken the bonds so that the solid can become a liquid. c It is soluble in water and it contains ions. d Potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, lithium chlorides etc. Any ionic compound that dissolves in water can be called a salt. e More energy is needed to weaken the bonds between the magnesium ions and oxide ions so that the solid becomes a liquid. 9 Cl- S2- N3- I- O2- Na+ NaCl Na2S Na3N NaI Na2O Mg2+ MgCl2 MgS Mg3N2 MgI2 MgO AlCl3 Al2S3 AlN AlI3 Al2O3 NH4+ NH4Cl (NH4)2S (NH4)3N NH4I (NH4)2O Zn2+ ZnCl2 ZnS Zn3N2 ZnI2 ZnO Al 10 a 3+ X= +2 b X= -2 c X= +1 d X= -1 e X= +3 f X= +3 g X= -1 h X= +2 11 All Group 1 metals have one electron in their outer shell. In a chemical reaction they can donate this electron to an atom that can accept it and in this process they form ions with a charge of +1. Beryllium, magnesium and calcium are in Group 2. This means that they have two outer shell electrons that they can donate to an atom that can accept them, so they will form ions with a +2 charge. Oxford Big Ideas Science 3 ISBN 978 0 19 556453 2 © Oxford University Press Australia