Terrestrial Biome
advertisement
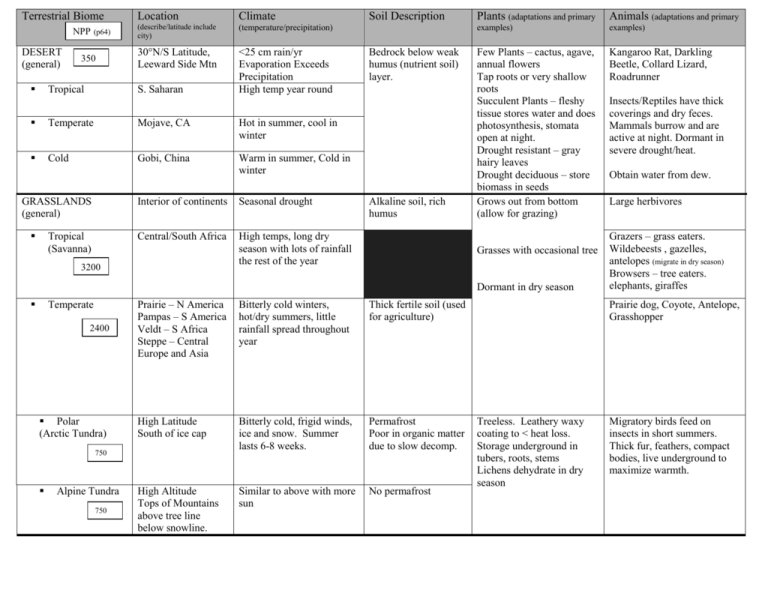
Terrestrial Biome NPP (p64) DESERT (general) 350 Tropical Location Climate (describe/latitude include city) (temperature/precipitation) 30°N/S Latitude, Leeward Side Mtn <25 cm rain/yr Evaporation Exceeds Precipitation High temp year round S. Saharan Temperate Mojave, CA Hot in summer, cool in winter Cold Gobi, China Warm in summer, Cold in winter GRASSLANDS (general) Tropical (Savanna) Interior of continents Seasonal drought Central/South Africa High temps, long dry season with lots of rainfall the rest of the year 3200 Soil Description Bedrock below weak humus (nutrient soil) layer. Alkaline soil, rich humus examples) Few Plants – cactus, agave, annual flowers Tap roots or very shallow roots Succulent Plants – fleshy tissue stores water and does photosynthesis, stomata open at night. Drought resistant – gray hairy leaves Drought deciduous – store biomass in seeds Grows out from bottom (allow for grazing) Kangaroo Rat, Darkling Beetle, Collard Lizard, Roadrunner Dormant in dry season Temperate 2400 Polar (Arctic Tundra) Prairie – N America Pampas – S America Veldt – S Africa Steppe – Central Europe and Asia Bitterly cold winters, hot/dry summers, little rainfall spread throughout year Thick fertile soil (used for agriculture) High Latitude South of ice cap Bitterly cold, frigid winds, ice and snow. Summer lasts 6-8 weeks. Permafrost Poor in organic matter due to slow decomp. High Altitude Tops of Mountains above tree line below snowline. Similar to above with more sun No permafrost 750 Animals (adaptations and primary examples) Grasses with occasional tree 0 Plants (adaptations and primary Alpine Tundra 750 Insects/Reptiles have thick coverings and dry feces. Mammals burrow and are active at night. Dormant in severe drought/heat. Obtain water from dew. Large herbivores Grazers – grass eaters. Wildebeests , gazelles, antelopes (migrate in dry season) Browsers – tree eaters. elephants, giraffes Prairie dog, Coyote, Antelope, Grasshopper Treeless. Leathery waxy coating to < heat loss. Storage underground in tubers, roots, stems Lichens dehydrate in dry season Migratory birds feed on insects in short summers. Thick fur, feathers, compact bodies, live underground to maximize warmth. Terrestrial Biome CHAPARRAL (temperate shrubland) 750 Location Climate Soil Description Plants (adaptations and primary Animals (adaptations and (describe/latitude include city) (temperature/precipitation) (p215) examples) primary examples) Pacific Coast of N. America (S. Cali) S. Texas, Spain, Italy, SW Africa, SW Australia Mild Winters (moderate rain). Long hot/dry summers. Low growing evergreen. Some pines and scrub oak. Leathery leaves, large underground root system, Fire adapted (food reserves in roots, seeds need fire for growth). Coyote (keystone species) Cougar Mule Deer Moderate to high rainfall. Many trees with small vegetation on ground. Broadleaf Evergreens. Low diversity on ground. Waxy coating. Stratified forests Pollinators coevolved with plants Broadleaf deciduous trees. Lose leaves in cold. Oaks, birch, maple. More ground diversity than tropical. Conifers: pine, spruce, fir FOREST (general) Tropical Rainforest 8,800 Temperate Deciduous 5700 Evergreen Coniferous (Boreal/Taiga) Near equator. ITCZ (shifts N/S of equator) 2% of Earth’s surface. Warm year round. Rains every day. Acidic. Nutrient poor humus. (most nutrients are tied up in living things) E. Coast of US, Central Europe, E. China Long warm summers with cool winters. Abundant precipitation. Leaf litter above humus Between 50 & 60N latitude; Canada, Alaska Very cold winters, brief summers, limited precipitation Acidic, thick humus, low nutrients because cold winter & low precip. = slow decomposition In temperate zones near coast; ocean currents provide moisture & moderate temperature; Pacific Northwest Cool winters, warm summers; high precipitation 3400 Temperate Rainforest (Coastal Coniferous) Mountain (Alpine) Conifers: Douglas fir, hemlock, cedar; ferns on forest floor, moss 50-80% Earth’s species. Tapir, bats, birds, monkeys, orangutan, macaw Bears, wolves, wildcats, deer, rabbits. Wolf, warblers, bears, owl, moose Woodpeckers, squirrels, deer Since elevation mimics latitude, Alpine biomes such as alpine forest and alpine tundra have similar adaptations and climate as their counterparts, Boreal forests and tundra respectively. The only difference is that the alpine tundra does not have permafrost. Aquatic Life Zone NPP (p64) Estuary 2500 Coastal Wetland 1700 Intertidal Rocky Shore Salinity Plants/Algae (adaptations Animals (adaptations and (location from shore, depth, examples) (salt/fresh, changes, nutrients) and primary examples) primary examples) Where rivers empty into ocean Brackish water; mixture of fresh & salt water Birds, herring, smelt, water fowl Adjacent to continent Similar to sea water; high nutrients Cattails, salt grass, willow; plants can tolerate salt by eliminating it Salt tolerant trees like mangrove in tropics (roots submerged) Between high & low tide with a rocky substrate Salinity same as ocean; nutrients vary Attach to rocks, flexible, gas bladders; kelp, rock weed, coralline algae Attach to rocks, hard shell; mussels, barnacles, crabs, urchins, anenomes Filter feeders, burrow, smooth shells; clams, sand crabs, sand dollars Calcified structures, narrow bodies; coral, anemones, fish, snail Like Laguna Beach or Dana Point Larval stage of shellfish, crustaceans; spawning fish Important Facts Most productive biome on Earth. Estuaries are salt marshes and swamps Filter contaminants out of water; absorb CO2 Sandy Shore Between high & low tide with a sandy substrate Salinity same as ocean; nutrients vary Phytoplankton; freefloating Coral Reef Warm shallow waters beyond shoreline. Low nutrients, food limited; salinity same as ocean Algae that grows in coral; symbiotic relationship Beyond sunlight; deep Sunlit portion of ocean Little saltier Chemosynthesis; microbes Photosynthesis, phytoplankton Inverts, soft-bodied, bioluminescence Zooplankton, fish Occupies 80% of all ocean water 90% of all ocean animals live here Deep enough to not support vegetation Most are fresh but there are some salt lakes Rooted plants in shallows, phytoplankton in deeper water Fish, freshwater mollusk, insects Flowing fresh water from springs or runoff Same as streams Fresh water with some dissolved solids Nutrients from terrestrial biomes; few plants and algae; leaf litter provide food Insect larvae, crustaceans, fish Deep lakes have a profundal zone where sunlight does not penetrate Fast flowing (rapids) to slow low-oxygen steams OPEN SEA Aphotic Photic 500 STREAMS 500 RIVERS Like Huntington or Newport Most diverse biome on Earth 150 LAKES FRESHWATER Location 3.5% salt Biome/Aquatic Ecosystem Ecosystem services DESERT TROPICAL RF Food, shelter, and nutrients CONIFEROUS FOREST Economic Services Human Impacts Recreation, solar/wind energy, mining Recreation, mining, urbanization Timber, medicine, food supply Conversion to cropland, logging Timber, recreation Logging, recreation, mining DECIDUOUS FOREST Rich soil, migratory bird habitat Timber, recreation Logging, urbanization, road building GRASSLANDS Food for grazing mammals Cropland and grazing Conversion to cropland and grazing ESTUARIES Filters water, removes salt, absorbs CO2, habitat for larvae and immature fish, high productivity Fisheries, protection from tropical storms in E. Coast Urbanization, filled in for building, habitat destruction, run-off form agriculture MANGROVE FORESTS Spawning area for fish, protective Fisheries habitat for larvae and immature fish, high productivity Habitat destruction CORAL REEF Provide protection and food or algae, fish, and invertebrates Recreation, aquaria Coral bleaching due to run-off, over-fishing, pollution WATER SHED (Lakes, Rivers, Streams, Groundwater) Habitat for freshwater organisms Recreation, fisheries, water resource Pollution, run-off from urban areas, habitat destruction for flood control FRESHWATER WETLANDS Productive habitat for animals Fisheries, water resource, recreation Pollution, run-off, salt water infiltration due to over use of water for drinking