Key Terms
advertisement

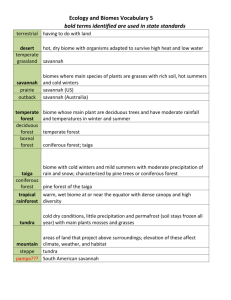
Ecology Key Terms Basic Ecology Ecological Levels of Organization (Organism; Population; Community; Ecosystem; Biome; Biosphere) Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors Consumers vs. Producers (Autotrophs vs. Heterotrops) Types of Autotrophs o Chemotrophs (Chemosynthesis) o Phototrophs (Photosynthesis) Types of Heterotrophs o Herbivores o Carnivores o Omnivores o Detrivores o Scavengers o Decomposers Ecological Diagrams o Food Chains o Food Webs o Food Pyramids (Energy; Mass; Numbers) Ecological Energy Flow o Energy Sources (Sun & Core) o Basic Nutrients for most phototrophs (Solar Energy; Carbon Dioxide; Oxygen; Water; Nitrates; Nitrites; Phosphates; Other trace elements) o Basic Nutrients for chemotrophs vary o Primary Consumption o Consumption Levels (Primary, Secondary, Terciary or Higher Consumption) o Role of Decomposers as Recyclers of Matter/Energy o Reasons for Energy/Mass/Number Reduction Between Levels o Effect of Extinctions on Food Web o Effect of Invasive Species on Food Web o Food Webs, Biodiersity, & Ecosystem Tolerance Level o Bioaccumlation & Biomagnification of Toxins o Benefits / Drawbacks of Eating Lower in the Food Web (More Energy; Less Toxins; More Food; Supports more numbers; May destabilize higher levels of food chain) Biochemical Cycles o Water Cycle (Transpiration; Runoff; Evaporation; Precipitation; Condensation; Seepage; Root Uptake; Carbon Cycle o Carbon Cycle (Human Activity; Volcanic Activity; Photosynthesis; Cellular Respiration; Decomposition; Erosion; Feeding; Settling of the soil; Deposition; Fossilization; Uplift) o Nitrogen Cycle (Nitrogen Fixation; Nitrifying Bacteria; Root uptake of nutrients; Feeding; Decomposition & Amonification; Denitrification) Ecosystems Overview of different types of Biomes and how temperature and precipitation levels sets them apart (no need to know Biome details, but be able to recognize them and tell them apart based on location, temperature, precipitation, and types of adaptations that organism must have to survive on them) o Tropical (Rainforest, Dry Forest; Savanna; Desert) o Temperate (Temperate Forest; Temperate Grassland; Temperate Woodlands / Shrublands; Coniferous Forest) o Artic (Boreal Forest; Tundra; Taiga) o Polar Ice Caps o Mountains Climate & Ecosystems Review o Latitude: Solar Energy & Seasons o Global Wind & Ocean Currents o Land vs. Water (Specific Heat) o El Nino / La Nina o Seasonal Winds o Elevation & Rain Shadow o Greenhouse Gases & Effect o Microclimates Water Biomes (no need to know Biome details, but be able to recognize them and tell them apart based on location, temperature, precipitation, and types of adaptations that organism must have to survive on them) o Salt: Intertidal Zone; Coral Reefs; Open Ocean; Coastal Ocean; Benthic Ocean o Fresh: Rivers & Lakes o Estuaries: Marshes & Mangroves o Photic Zone vs. Aphotic Zone o Aquatic Organisms: Plankton vs. Nekton vs. Benthos Habitat & Organism Tolerance & Adaptation Community Interactions Ecological Relationships o Symbiotic Relationships o Competition for Resources & Nutrients o Predator-Prey Relationships Niche & Competitive Exclusion Principle Succession (Primary vs. Secondary) Population Growth Population Density Population Growth (Immigration & Birth) vs. Decline (Emigration & Death) Types of Population Growth (Linear; Logistic; vs; Exponential) Carrying Capacity Limiting Factors o Density-Dependent Competition Predation Parasitism / Disease o Density-Independent Natural Disasters Habitat Destruction Nutrient Limitation & Algae Bloom R-Selected vs. K-Selected Species Pioneer Species & Succession Human Population Growth Patterns Environmental Science Human Activity & Environment o Hunting & Gathering & Species Conservation o Agriculture & Animal Growth (History; Monocultures, & the Green Revolution) o Industrial Revolution & Urban Development o Habitat Destruction & Conservation o Resource Use vs. Sustainable Development (See more below) Resources o Renewable (Hydroelectric; Geothermal; Plants/Animals; Fusion; Solar; Wind; Current/Tide) o Nonrenewable (Fission & Fossil Fuels: Coal; Tar; Natural Gas; Oil) o Water Resources (Freshwater & Ocean Water Use) o Land Resources (Mining; Soil Erosion; Desertification; Land Creation) o Forest Resources (Deforestation vs. Forest Management) o Fishery (Overfishing vs. Sustainable Fishing & Aquacultures) o Air Resources (Pollution; Smog; Ozone Layer Depletion; Global Warming; Acid Rain; Health Effects) o Animal Resources Biodiversity o Importance of Biodiversity o Ecosystem Diversity o Species Diversity o Extinction o Endanger Species o Habitat Fragmentation & Destruction o Invasive Species o Pollution Bioaccumulation & Biomagnification o Ecological Interdependence & The Value of a Healthy Biosphere