Solubility and Concentration Review
advertisement

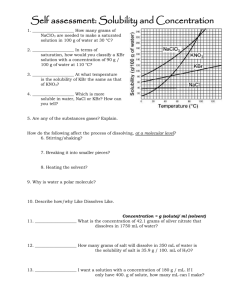
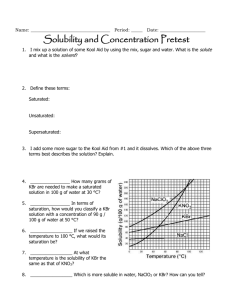
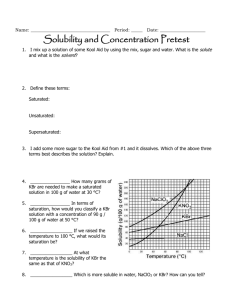
Name: ___________________________________ Period: _____ Date: ____________________ Solubility and Concentration Pretest 1. – 2. I mix up a solution of some Kool Aid by using the mix, sugar and water. What is the solute and what is the solvent? 3. – 5. Define these terms: Saturated: Unsaturated: Supersaturated: 6. I add some more sugar to the Kool Aid from 1. – 2. and it dissolves. Which of the above three terms best describes the solution? Explain. 7. ____________________ How many grams of KBr are needed to make a saturated solution in 100 g of water at 30 °C? 8. ____________________ In terms of saturation, how would you classify a KBr solution with a concentration of 90 g / 100 g of water at 50 °C? 9. ____________________ If we raised the temperature to 100 °C, what would its saturation be? 10. ____________________ At what temperature is the solubility of KBr the same as that of KNO3? 11. ____________________ Which is more soluble in water, NaClO3 or KBr? How can you tell? 12. – 13. As you raise the temperature of a solvent, how does the solubility of a solute change if it is a Solid or liquid? Explain why. Gas? Explain why. 14. Are any of the substances gases? Explain. How do the following affect the process of dissolving, at a molecular level? 15. Stirring/shaking? 16. Breaking it into smaller pieces? 17. Heating the solvent? 18. Why is water a polar molecule? 19. Describe how/why “like dissolves like.” 20. ____________________ What is the concentration of 42.1 grams of silver nitrate that dissolves in 1750 mL of water? 21. ____________________ How many grams of salt will dissolve in 350 mL of water is the solubility of salt is 359 g / 100 mL of H2O? 22. ____________________ If the solubility of KNO3 is 180 g / 100 mL of H2O, will 560 g dissolve in 400 mL of H2O? Name: ___________________________________ Period: _____ Date: ____________________ Solubility and Concentration Pretest 1. – 2. I mix up a solution of some Kool Aid by using the mix, sugar and water. What is the solute and what is the solvent? Solute: Kool Aid, sugar (what gets mixed) Solvent: water (what it’s mixed into) 3. – 5. Define these terms: solvent holds as much solute as it can at that temperature Saturated: solvent holds less than the maxiumum solute it can at that temperature Unsaturated: solvent holds more than the maxiumum solute it can at that temperature Supersaturated: 6. I add some more sugar to the Kool Aid from 1. – 2. And it dissolves. Which of the above three terms best describes the solution? Explain. Unsaturated…it was holding less so it dissolved. If it was saturated or supersaturated, it would fall to the bottom and not dissolve. ~ 72 g__ How many grams of 7. __ KBr are needed to make a saturated solution in 100 g of water at 30 °C? supersaturated_ In terms of 8. _ saturation, how would you classify a KBr solution with a concentration of 90 g / 100 g of water at 50 °C? unsaturated_ If we raised the temperature to 100 °C, what would its 9. _ saturation be? ~ 48 oC _ At what temperature is the solubility of KBr the same as that of 10. _ KNO3? 11. __ NaClO3_ Which is more soluble in water, NaClO3 or KBr? How can you tell? The line on the graph is higher, which means more can dissolve 12. – 13. As you raise the temperature of a solvent, how does the solubility of a solute change if it is a Solid or liquid? Explain why. Increases. As the molecules of both move faster, more solute can dissolve Gas? Explain why. Decreases. As the molecules of both move faster, more solute escapes the solvent 14. Are any of the substances gases? Explain. No. All increase solubility with temperature. How do the following affect the process of dissolving, at a molecular level? 15. Stirring/shaking? Moves around, more interactions between molecules 16. Breaking it into smaller pieces? Increases surface area for interactions to take place 17. Heating the solvent? Moves molecules faster more interactions 18. Why is water a polar molecule? Shares electrons unevenly Has partial charges 19. Describe how/why “like dissolves like.” Partial charges in polar molecules help pull apart the partial charges from other polar molecules. .0241 g/ml_ What is the concentration of 42.1 grams of silver nitrate 20. _ that dissolves in 1750 mL of water? 42.1 / 1750 = .024057142 1000 g_ How many grams of salt will dissolve in 350 mL of water is 21. _ 359 100 the solubility of salt is 359 g / 100 mL of H2O? = x 350 1256.5 yes_ If the solubility of KNO3 is 180 g / 100 mL of H2O, will 560 g dissolve in 22. _ 400 mL of H2O? That concentration is less than its solubility 560/400 = 1.4 g/ml 180/100 = 1.8 g/ml