Geography of the Nile Basin - Nile River Awareness Kit (RAK)
advertisement

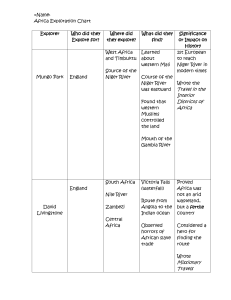
Geography of the Nile Basin The shape of the land and the climate of the different regions of the Nile basin determine flow in the River Nile along its 6,600 km path to the Mediterranean Sea. The geography of the Nile basin was shaped by a long and complex geological history. The Nile River basin covers diverse landscapes and terrain, passing through 10 countries: Burundi, DR Congo, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. The geographic regions of the Nile Basin The important geographic features of this area include mountains, wetlands, rivers, lakes, plains, the Delta, and the desert. The geography of the Nile basin can be divided into: the White Nile, the Blue Nile, the main River Nile, and the Nile Delta in Egypt. ~ The White Nile basin includes the highlands of Burundi and Rwanda, the Equatorial Lakes Plateau, vast areas of tropical swamp systems and the Sobat River. ~ The Blue Nile basin extends from the Ethiopian highlands to the plains of Sudan, and includes Lake Tana as well as numerous tributaries. ~ The White Nile and Blue Nile meet at Khartoum, Sudan. ~ From here the main River Nile flows north through the desert, to the Mediterranean Sea. Facts about the Nile River: Flowing over 6,600 km, the Nile River is the longest river in the world. The river drains an area covering approximately 10% of Africa, extending over 35 degrees of latitude. The Nile River basin ranges in elevation from over 4,500m to sea level. The basin is home to over 160 million people across ten countries. Contact Details: Nile Transboundary Environmental Action Project Gedion Asfaw: gasfaw@nilebasin.org The Nile River Awareness Kit (Nile RAK) project is an educational and awareness raising project designed to increase knowledge and understanding about the environment and resources of the Nile River basin. The Nile Basin Initiative (NBI) is a partnership of nine River Nile countries. For more information about the Nile RAK project visit: www.nileteap.org