Practice Questions Essays
advertisement

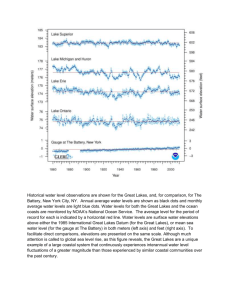
a. ) Two key features of stream and river flow are extreme temporal variability, and the tendency to meander. Explain how these create habitat diversity for aquatic organisms, through its effects on channel morphology, sediment deposition, erosion, and the flood plain. b.) With reference to the hydrological balance equation describe the effects of deforestation and upstream lakes and wetlands on the amplitude and lag-time of the hydrographic responses of a stream to a storm-event. c. )With reference to the hydrological balance equation explain why most streams on the landscape flow continuously (albeit with huge variance) despite the episodic nature of precipitation. Contrast this with the situation you might expect in a storm sewer—a man-made drainage system designed to conduct storm runoff—which has high discharge for a few hours after a storm and then dries up completely. a ) Habitat zonation in lakes is largely dependent on physical processes. Outline the role of wind and wave action, light, and lake basin shape in determining the boundaries of the littoral zone, the thermocline, photic zone depth and the boundaries of the depositional zone. c.) Animals are often herbivorous and prey on plants and plants defend themselves by producing physical and chemical defenses; however, many times mutualistic interactions between animals and plants have evolved. Outline some examples of such mutualisms involving aquatic organisms, and explain why the physiological processes of animals and plants and fundamentally compatible. b. ) Show how the processes of photosynthetis and respiration are linked to changes in O2, and explain how oxygen concentrations in a lake water column change throughout the daily cycle and how these changes can be used to estimate the rates of photosynthesis and respiration of the lake community. c. )Outline the general pattern of seasonal succession in lake phytoplankton, and explain it with reference to seasonal changes in lake temperature and stratification, nutrient availability, and herbivorous zooplankton. Outline the major ways that aquatic ecosystems provide free services to the human economy that are difficult or impossible to replace with human-made substitutes. Outline the role of wind and wave action, light, and lake basin shape in determining the boundaries of the littoral zone, the thermocline, photic zone depth and the boundaries of the depositional zone. With reference to the hydrological balance equation explain why most streams on the landscape flow continuously (albeit with huge variance) despite the episodic nature of precipitation. Contrast this with the situation you might expect in a storm sewer—a man-made drainage system designed to conduct storm runoff—which has high discharge for a few hours after a storm and then dries up completely. With reference to the hydrological balance equation describe the effects of deforestation and upstream lakes and wetlands on the amplitude and lag-time of the hydrographic responses of a stream to a storm-event. Two key features of stream and river flow are extreme temporal variability, and the tendency to meander. Explain how these create habitat diversity for aquatic organisms, through its effects on channel morphology, sediment deposition, erosion, and the flood plain. Most lakes in the world are found in glaciated regions. Explain how glacial processes form lakes. Although there are fewer lakes in non-glaciated regions, in what ways are they different from those in glaciated areas. What are the factors that determine the apparent colour of a water. How would the colour of water be an important environmental factor for photosynthetic organisms? Diatoms by virtue of their siliceous cell walls have higher specific gravities than other small algae and have virtually no ability to control their position in the water column. What are the consequences of this as regard to the types of habitat they live in, their seasonal dynamics, and their responses to the thermal regime. Large colonial Cyanobacteria often bloom during the late summer in lakes. Describe some factors that contribute to this general pattern. What is meant by nitrogen fixation and why is it ecologically important. Explain which organisms can perform this function and how they can exploit this capability in aquatic ecosystems. How have humans exploited this in agriculture? Explain how oxygen concentrations in a lake water column change throughout the daily cycle and how these changes can be used to estimate the rates of photosynthesis and respiration of the lake community.