Chemical Formulae Worksheet: Using Valencies
advertisement
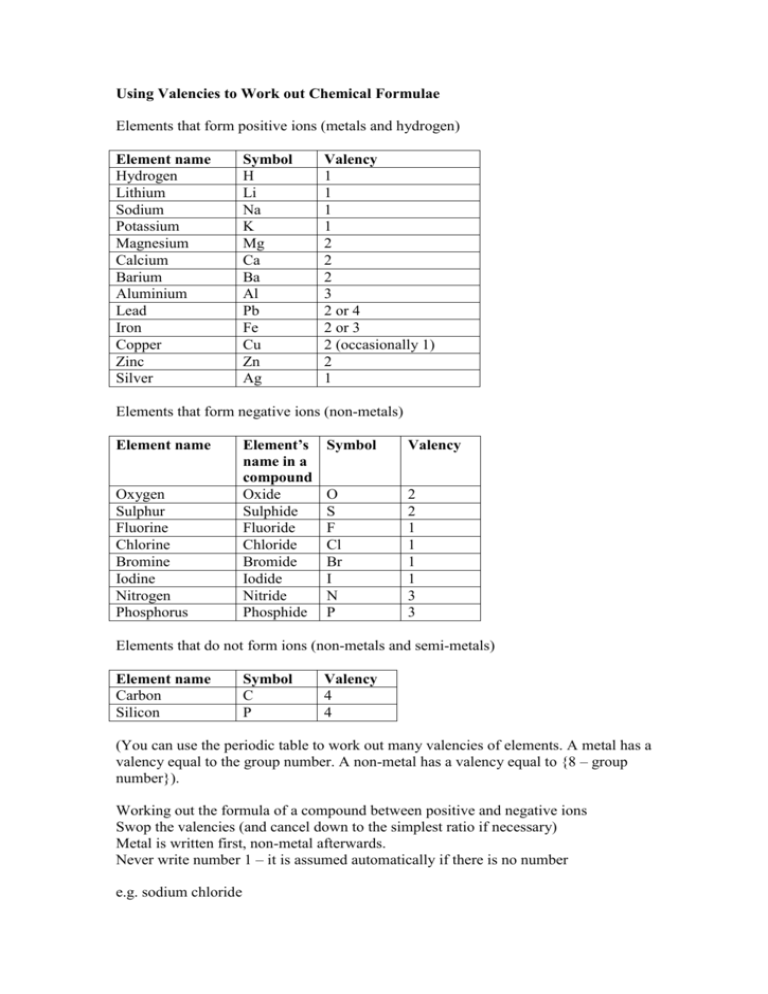
Using Valencies to Work out Chemical Formulae
Elements that form positive ions (metals and hydrogen)
Element name
Hydrogen
Lithium
Sodium
Potassium
Magnesium
Calcium
Barium
Aluminium
Lead
Iron
Copper
Zinc
Silver
Symbol
H
Li
Na
K
Mg
Ca
Ba
Al
Pb
Fe
Cu
Zn
Ag
Valency
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
3
2 or 4
2 or 3
2 (occasionally 1)
2
1
Elements that form negative ions (non-metals)
Element name
Oxygen
Sulphur
Fluorine
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Element’s
name in a
compound
Oxide
Sulphide
Fluoride
Chloride
Bromide
Iodide
Nitride
Phosphide
Symbol
Valency
O
S
F
Cl
Br
I
N
P
2
2
1
1
1
1
3
3
Elements that do not form ions (non-metals and semi-metals)
Element name
Carbon
Silicon
Symbol
C
P
Valency
4
4
(You can use the periodic table to work out many valencies of elements. A metal has a
valency equal to the group number. A non-metal has a valency equal to {8 – group
number}).
Working out the formula of a compound between positive and negative ions
Swop the valencies (and cancel down to the simplest ratio if necessary)
Metal is written first, non-metal afterwards.
Never write number 1 – it is assumed automatically if there is no number
e.g. sodium chloride
Na
Cl
1
1
Formula:
NaCl
(1 sodium atom to 1 chloride atom)
e.g. sodium nitride
Na
N
1
3
Formula:
Na3N
(3 sodium atoms to 1 nitrogen atom)
e.g. lead (IV) oxide
Pb
O
4
2
Formula:
Pb2O4 = PbO2
Positive compound radical
Name
Ammonium
Formula
NH4
Valency
1
Negative compound radicals
Name
Hydroxide
Carbonate
Hydrogencarbonate
Nitrate
Sulphate
Sulphite
Phosphate
Formula
OH
CO3
HCO3
NO3
SO4
SO3
PO4
Valency
1
2
1
1
2
2
3
e.g. sodium hydroxide
Na
OH
1
1
Formula:
NaOH
e.g. magnesium hydroxide
Mg
OH
2
1
Formula:
Mg(OH)2
(brackets needed so that both the O and H of hydroxide are multiplied up)