The Cell : Structure and Function
advertisement

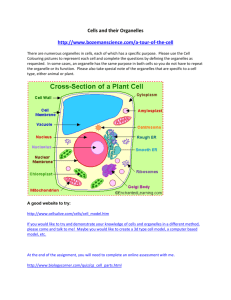
TEACHER MASTER Cells and Systems- Science 8 THE CELL: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Learning Outcomes Addressed B1. demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics of living things B2. relate the main features and properties of cells to their functions - summarize the cell theory - accurately list similarities and differences between cell types - describe the structure and function of cell organelles - recognize and name the parts of a cell using a microscope Master of Template Notes begins on the following page so that it can be easily transferred onto an overhead transparency. Recommended time required for this activity: 30 min as class notes, could also be used as class notes and then have students fill in functions of organelles using the science probe on their own. Materials required: none Suggested “Check your Understanding” questions that correspond from Science Probe 8 (if applicable): o 1.1 #1-4 pg 6 o 1.3 #2-6 pg 13 o 1.6 #1,3,4 pg 21 Suggested “Inquiry Investigations” from Science Probe 8 that correspond: o 1.2 Using a Microscope pg 7 o 1.4 Comparing Plants and Animal Cells pg 14 Notes and Activities – Science 8 TEACHER MASTER Cells and Systems- Science 8 THE CELL: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Cells are the BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS OF ALL LIVING THINGS, the smallest unit that can function on its own. In 1665, HOOKE observed tiny room-like structures while looking at a thin slice of cork through a compound microscope. He called these structures CELLS. The CELL THEORY is how we as biologists gauge whether or not an object is living. It states that: 1. ALL LIIVING THINGS ARE MADE UP OF ONE OR MORE CELLS 2. ALL LIVING CELLS COME FROM PRE-EXISTING CELLS Why was the development of the cell theory important for the progress of science? SCIENTISTS FINALLY HAD A WAY TO DESCRIBE WHAT LIFE WAS! What would have been the limitations of this “new science” when cells were discovered? MICROSCOPES WERE NOT ADVANCED ENOUGH TO SEE THE INNER WORKINGS OF THE CELL Notes and Activities – Science 8 TEACHER MASTER Cells and Systems- Science 8 The inside of the CELL is made up of many structures that we now call ORGANELLES (like mini organs that keep the cell working the way it should) Organelle Structure and Function The organelles inside the cell serve many functions together including: 1. PROVIDING PROTECTION AND SUPPORT 2. FORMING A BARRIER BETWEEN THE CELL AND THE ENVIRONMENT 3. BUILDING AND REPAIRING CELLS 4. TRANSPORTING MATERIALS 5. STORING AND RELEASING ENERGY 6. GETTING RID OF WASTE MATERIAL 7. INCREASING IN NUMBER Most cells share similar characteristics. It is these characteristics that we are going to learn about although there are some major differences between animal and plant cells. Notes and Activities – Science 8 TEACHER MASTER Cells and Systems- Science 8 Take a look at the pictures of animal and plant cells below and see if you can determine any major differences. Write the differences in the space below Typical Animal Cell Typical Plant Cell Notes and Activities – Science 8 TEACHER MASTER Cells and Systems- Science 8 As you learn the functions of the following organelles see if you can find them on the plant and/or animal cell!! Cell Wall: Supporter and Protector - PROVIDES A PROTECTIVE AND SUPPORTIVE BARRIER IN PLANT CELLS - MADE OF CELLULOSE (PLANT FIBRE) Cell Membrane: Doorway to the Cell - CONTROLS NUTRIENTS AND WASTE ENTERING AND LEAVING THE CELL - PROVIDES A PROTECTIVE OUTER BARRIER - HAS TWO LAYERS OF FAT MOLECULES (LIPIDS) THAT INCLUDE PROTIENS Nucleus: The Brain - CONTROLS THE ACTIVITIES OF THECELL (THE BRAIN OF THE CELL) - CONTAINS ALL THE GENETIC INFORMATION b. Nuclear Membrane - DOUBLE LAYERED MEMBRANE THAT CONTROLS MOLECULES ENTERING AND LEAVING THE NUCLEUS Notes and Activities – Science 8 TEACHER MASTER Cells and Systems- Science 8 c. Nucleolus - DARK AREA INSIDE THE NUCLEUS - PLAYS A ROLE IN PROTEIN PRODUCTION d. Chromosomes - GENETIC MATERIAL OF THE CELL (MADE UP OF DNA) Endoplasmic Reticulum: Transportation System - TRANSPORTS AND STORES MATERIAL (PROTEIN) WITHIN THE CELL - CONNECTS ORGANELLES TOGETHER - RUNS THROUGH THE CYTOPLASM LIKE A MAZE OF FREEWAYS! Mitochondria: Powerhouse of the Cell - PRODUCE CHEMICAL ENERGY FORTHE CELL - BEAN SHAPED WITH LOTS OF FOLDS ON THE INSIDE TO INCREASE SURFACE AREA - THEY HAVE THE ABILITY TO REPRODUCE INSIDE THE CELL IF IT NEEDS MORE ENERGY!! - FOUND IN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Notes and Activities – Science 8 TEACHER MASTER Cells and Systems- Science 8 Chloroplast: Energy Producers - PRODUCE CHEMICAL ENERGY FOR THE PLANT CELL - CONTAIN CHLOROPHYLL WHICH ACCOUNTS FOR THEIR GREEN COLOR - OVAL SHAPED Vacuoles: Storage Tanks - USED FOR STORAGE OF WATER AND FOOD - TRANSPORT MATERIALS WITHIN THE CELL - VACUOLES CAN FUSE WITH LYSOSOMES - VERY LARGE IN PLANT CELLS AND HELP WITH STRUCTURE Golgi Body (Complex): Packers and Shippers - COLLECTS PROTIEN FROM THE CELL, PACKAGES IT INTO DIFFERENT TYPES OF VESICLES AND THEN SHIPS THOSE OFF INTO THE CELL (OR OUTSIDE THE CELL) TO WHERE IT IS NEEDED - LOOKS LIKE A STACK OF PANCAKES! Notes and Activities – Science 8 TEACHER MASTER Cells and Systems- Science 8 Ribosomes: Protien Producers - MADE UP OF PROTEIN AND RNA - PRODUCE MORE PROTIEN TO BE USED IN THE CELL - ARE FOUND FLOATING IN THE CYTOPLASM OR ATTACHED TO THE ER. Lysosomes: Suicide Sacs - LITTLE SACS OF DIGESTIVE ENZYMES WHICH ARE USED TO HELP BREAK DOWN UNWANTED PARTS OF THE CELL. (OLD ORGANELLES THAT ARE NOT FUNCTIONING PROPERLY) - CAN EXPLODE AND KILL THE ENTIRE CELL AS WELL Notes and Activities – Science 8