Chapter 25: Geography and Early History of the Middle East
advertisement

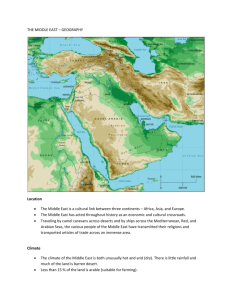
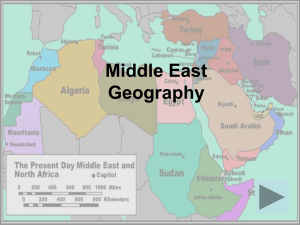
Chapter 25: Geography and Early History of the Middle East Chapter Perspective: 1. Geographic factors, including scarcity of water, have influenced the cultures of the Middle East. 2. Location has made the Middle East a meeting ground for many peoples and a center from which ideas have spread around the world. 3. Ancient civilizations developed in the Tigris-Euphrates and Nile river valleys. 4. The Middle East is the birthplace of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam LEQ(s) How has location affected the peoples of the Middle East? What are the main physical regions of the Middle East? What geographic factors influence population patterns in the Middle East? Which ethnic and religious groups live in the Middle East? I. The Land and the People A. Crossroads of the World 1. Bridges three continents: Africa, Asia, and Europe 2. connects major trade routes, both overland and sea 3. Goods came through from Asia to Europe, also from the east coast of Africa to India 4. Examples of cultural diffusion that originated from the Middle East are iron making, the alphabet, and religious traditions of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam 5. Examples of cultural diffusion that originated from nearby Asia and diffused from the Middle east are numerals (made Arabic) from India and the lateen sail from Southeast Asia 6. The Middle East is a strategic location, important area for military and economic reasons because it is vital for sea routes and some of its countries have huge oil reserves 7. Egypt operates the Suez Canal, linking the Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, and Indian Ocean 8. Turkey controls the Bosporus and Dardanelles two vital straits that link the Black and Aegean Sea 9. The Strait of Hormuz in the Persian Gulf is another strategic location for oil tankers 10. chp909298_256k.asx Movie Clip of Southwest Asia (Middle East) B. Major Regions - there are Five main physical regions 1. The Northern Tier – From present-day Turkey to Iran a. a region of mountains and plateaus b. in the west lies the Anatolian Plateau, ringed by the Pontic and Taurus mountains 2. 3. 4. 5. c. the Anatolian Plateau has fertile soil and supports a large population d. to the east lies the Iranian Plateau, it ringed by the Elburz and Zagros mountain ranges, it is not as fertile as the Anatolian Plateau e. this major region was home to the Ottoman and Persian Empires Arabian Peninsula – a vast plateau about 1/3 the size of the US a. Borders the Red and Arabian Sea, Saudi Arabia is the largest nation in the region b. The region lacks water and fertile soil except for the mountainous southern coast c. Most people live around an oasis, a fertile desert area that has enough water to support plant and animal life d. This region has some of the largest oil reserves e. It also important for the birthplace of Islam and the holy city of Mecca Fertile Crescent –arc-shaped region that stretches from the eastern Mediterranean along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers to the Persian Gulf a. Rich soil and abundant water make it a major population center b. The Tigris-Euphrates valley is home of one of the world’s earliest civilization c. It has few natural barriers, many invaders have conquered its fertile lands and rich cities d. Mesopotamia – “land between the rivers,” usually held the wealthiest cities and other cities developed along the coastline in Syria and Palestine e. The Tigris and Euphrates are sometimes flooded by melting ice in the surrounding mountain ranges f. Governments have always built dikes and canals to control the flooding Nile Valley – a cradle of civilization a. the area has geographic advantages that Mesopotamia did not have such as being surrounded by deserts b. also the flooding of the Nile was more predictable and dependable for farming purposes c. armies and trade caravans usually traveled through the Sinai peninsula from the Fertile Crescent the Maghreb – the North African nations of Algeria, Tunisia, Morocco; five other nations with geographic and cultural links with the Maghreb are Libya, Chad, Niger, Mali, and Mauritania a. means “western isle” in Arabic b. it seemed like an isolated area surrounded by water, mountains, and desert c. in the 600s and 700s A.D., Arab armies carried the religion of Islam to the “western isle” d. an excellent area of trade for West Africa, Europe, and the Middle East e. because of the Sahara desert, most live on the coast with fertile soil and plenty of rain C. Climate and Resources 1. most of the region is desert, therefore people lived in scattered areas that sustain enough water for a population 2. less than 10% receives enough water for farming 3. irrigation has been done since ancient times, including the use of desalination plants (convert salt water into fresh water) 4. the most valuable resource is oil, others include salt, phosphate, and copper D. People 1. home to different peoples with a variety of languages, religions, and traditions 2. the major languages are Arabic, Turkish, Hebrew, Kurdish, Persian, Greek, and Armenian 3. religions include Islam, Christianity, and Judaism 4. 19 countries and almost 350 million people are part of the Maghreb 5. the word Arab – describes anyone whose native language is Arabic 6. other ethnic groups include Turks, Iranians, and Kurds; some of them have migrated to the area from other parts of Asia 7. Islam is the dominant religion in the Middle East 8. most Arabs are Muslims, but most non-Arabs are Muslims as well such as Iranians, Turks, and Kurds 9. Islam itself is broken into different groups, Shiite and Sunni 10. a significant number of Christians live in Egypt, Lebanon, Iraq, and Syria 11. like Muslims they belong to different religious groups or sects, such as Coptic, Greek Orthodox, and Maronite Christians 12. Judaism is the most ancient of the three major religions of Middle East 13. Israel is predominantly Jewish, many of them are descendants of recent European, Asian, and North African immigrants