Solubility Equilibrium - Practice Problems for Assignment 7
advertisement

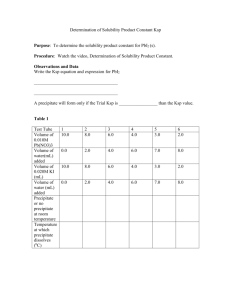
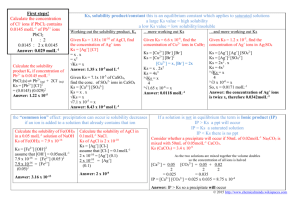
Solubility Equilibrium - Practice Problems for Assignment 7 1. PbCl2(s) is precipitated from a solution containing Pb2+ (aq) and Cl- (aq). Which one of the following describes the concentrations of the ions remaining in solution? (a) [Pb2+]2[Cl-] = Ksp of PbCl2 (s) (b) [Pb2+]2[Cl-]2 = Ksp of PbCl2 (s) (c) [Pb2+][Cl-] = Ksp of PbCl2 (s) (d) [Pb2+] [Cl-]2 = Ksp of PbCl2 (s) 2. Silver acetate, AgCH3COO (s), crystals are in equilibrium with a saturated solution. Which of the following could cause more silver acetate to dissolve? (a) The addition of a few crystals of silver nitrate. (b) The addition of a few drops of concentrated nitric acid. (c) The addition of a few crystals of sodium acetate. (d) The evaporation of some water from the solution with no temperature change. 3. In which of the following would solid AgCl be most soluble? (a) 1 M HCl (b) 1 M MgCl2 (c) 1 M AgNO3 (d) 1 M NH4NO3 4. Consider the following equilibrium system. PbI2 (s) + heat Pb2+ (a) + 2 I- (aq) Which of the following changes would result in more PbI2 dissolving? (a) Add more PbI2 (b) Increase the pressure (c) Add Pb(NO3)2 (d) Increase the temperature 5. A soluble magnesium salt is (a) MgSO3 (b) MgCO3 (c) Mg(NO3)2 (d) Mg3(PO4)2 6. Write the equation for the equilibrium involved in the solubility of barium phosphate. 7. Write the equilibrium law corresponding to Ksp. 8. The solubility of thalium (I) iodide in water at 20oC is 5.9 x 10-3 g/L. What is the Ksp for this compound? 9. The molar solubility of Ag2SO4 in a solution containing 28.4 g Na2SO4 per liter is 4.3 x 10-3 M. What is the Ksp for Ag2SO4? 10. Calculate the molar solubility of Ag3PO4 in water. 11. Calculate the molar solubility of AgI in pure water. 12. Calculate the molar solubility of AgI in 0.20 M CaI2 solution. 13. Will a precipitate of CaSO4 form in a solution if the Ca2+ concentration is 0.0025 M and the SO42- concentration is 0.030 M? 14. When 100.0 mL of 1.0 x 10-3 M Pb(NO3)2 and 100.0 mL of 2.0 x 10-3 M MgSO4 are mixed, what precipitate might be expected? Will some of the precipitate form? 15. Two aqueous solutions of Fe2(SO4)3 and Pb(NO3)2 are mixed. Will a reaction occur? If so, write: (a) the formula equation (b) the complete ionic equation (c) the net ionic equation. (d) Identify the spectator ions. 16. Two aqueous solutions of potassium nitrate and ammonium chloride are mixed. Will a reaction occur? If so, write: (a) the formula equation (b) the complete ionic equation (c) the net ionic equation. (d) Identify the spectator ions. Answers: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. d b d d c Ba3(PO4)2 (s) 3 Ba2+ (aq) + 2 PO43- (aq) 7. Ksp = [Ba2+]3[PO43-]2 8. 3.2 x 10-10 9. 1.5 x 10-5 10. 1.8 x 10-5 M 11. 9.1 x 10-9 M 12. 2.1 x 10-16 M 13. yes 14. PbSO4 (s). A precipitate will form. 15. Yes, a reaction will occur.PbSO4 (s) forms. (a) Fe2(SO4)3 (aq) + 3 Pb(NO3)2 (aq) 2 Fe(NO3)3 (aq) + 3 PbSO4 (s) (b) 2 Fe3+ (aq) + 3 SO4 2- (aq) + 3 Pb2+ (aq) + 6 NO3- (aq) 2 Fe3+ (aq) + 6 NO3- (aq) + 3 PbSO4 (s) (c) Pb2+ (aq) + SO4 2- (aq) PbSO4 (s) (d) The spectator ions are Fe3+ and NO3-. 16. The reaction produces soluble ions. All the ions that are in the solution when the solutions are mixed remain in solution. There is no reaction.