Determination of Solubility Product Constant Ksp
advertisement
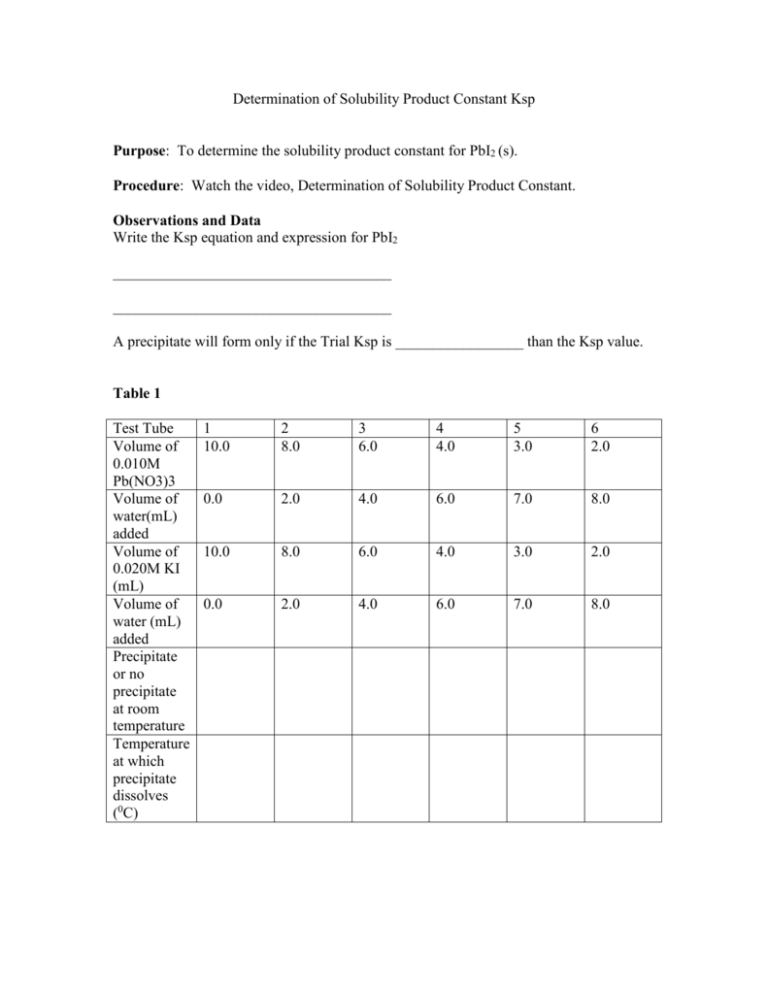
Determination of Solubility Product Constant Ksp Purpose: To determine the solubility product constant for PbI2 (s). Procedure: Watch the video, Determination of Solubility Product Constant. Observations and Data Write the Ksp equation and expression for PbI2 _____________________________________ _____________________________________ A precipitate will form only if the Trial Ksp is _________________ than the Ksp value. Table 1 Test Tube Volume of 0.010M Pb(NO3)3 Volume of water(mL) added Volume of 0.020M KI (mL) Volume of water (mL) added Precipitate or no precipitate at room temperature Temperature at which precipitate dissolves (0C) 1 10.0 2 8.0 3 6.0 4 4.0 5 3.0 6 2.0 0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 10.0 8.0 6.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 Questions 1. For each test tube 1-6 calculate the [Pb2+] in the final mixed solution. Use the appropriate dilution factors; remember that the final volume in each case is the sum of the volumes of both of the solution, total volume for test tube 1 is 20.0mL. __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Calculate the [I-] in the final mixed solution in each test tube. ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 3. Calculate the value of the Trial Ksp for each test tube. ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 4. Find the range of the values in which the experimental Ksp must lie. (This will be between test tube 4, 5). ____________________________________________________________ 4. Find the Ksp for each temperature and the solubility. The solubility is the same as the [Pb2+]. Then make a graph of solubility (moles/litre) against temperature. Test tube 1 Test tube 2 Temperature Ksp Solubility 5. What is the trend in solubility as temperature is increased? Conclusion State all your results and observations. Test tube 3











