AP Biology Vocabulary & Roots: Ch
advertisement

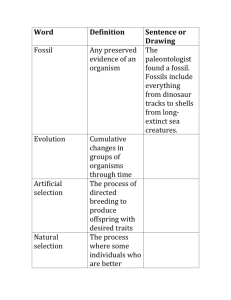
AP Biology Vocabulary & Roots: Ch. 22 1. adaptation-Inherited characteristic of an organism that enhances its survival and reproduction in specific environments. 2. analogous-Having characteristics that are similar because of convergent evolution, not homology. 3. artificial selection-The selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to encourage the occurrence of desirable traits. 4. biogeography-The study of the past and present distribution of species. 5. catastrophism- The principle that events in the past occurred suddenly and were caused by different mechanisms than those operating today. See uniformitarianism. 6. continental drift-The slow movement of the continental plates across Earth’s surface. 7. convergent evolution- the evolution of similar features in independent evolutionary lineages. 8. endemic- Referring to a species that is confined to a specific, relatively small geographic area. 9. evolutionary tree-A branching diagram that reflects a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships among groups of organisms. 10. fossil-A preserved remnant or impression of an organism that lived in the past. 11. homologous structures-Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry. 12. homology- Similarity in characteristics resulting from a shared ancestry. 13. marsupial-mammal, such as a koala, kangaroo, or opossum, whose young complete their embryonic development inside a maternal pouch called the marsupium. 14. natural selection-A process in which organisms with certain inherited characteristics are more likely to survive and reproduce than are organisms with other characteristics. 15. paleontology- The scientific study of fossils. 16. Pangaea- The supercontinent that formed near the end of the Paleozoic era, when plate movements brought all the landmasses of Earth together. 17. stratum- (plural, strata) A rock layer formed when new layers of sediment cover older ones and compress them. 18. trait-Any detectable variant in a genetic character. 19. uniformitarianism-The principle stating that mechanisms of change are constant over time. See catastrophism 20. vestigial structure-A structure of marginal, if any, importance to an organism. Vestigial structures are historical remnants of structures that had important functions in ancestors. Word Roots bio- = life; geo- = the Earth (biogeography: the study of the past and present distribution of species) end- = within (endemic: a type of species that is found only in one region and nowhere else in the world) homo- = like, resembling (homology: similarity in characteristics resulting from a shared ancestry) paleo- = ancient (paleontology: the scientific study of fossils) vestigi- = trace (vestigial organs: structures of marginal, if any, importance to an organism, historical remnants of structures that had important functions in ancestors) 1






![Humerus [ ]Ulna [ ]Radius [ ]Carpals [ ]Metacarpals](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008199621_1-87ac69fffa28dec62383a91f39582f03-300x300.png)



