Review for Evolution Test
advertisement

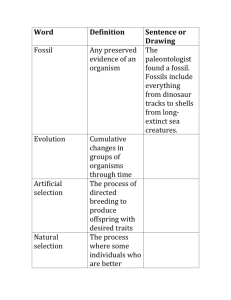
Review for Evolution Test 1. What is a vestigial structure? Give an example of it. A structure that is no longer functional but may have been used by similar ancestral species; ex-tailbone, leg bones in whales 2. What are the 4 evidences of evolution according to our notes/book? Biogeography, embryology, DNA sequences, fossil record, homologous structure 3. Define homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures. Give an example of each. Homologous-similar structures between closely related organisms, may have different functions; ex-horse leg and dog leg Analogous-structures that have a similar function but different structure; ex-butterfly wings and bird wings Vestigial structure-structures that no longer have a function; ex-appendix 4. What is unique about a species? They can reproduce within the species and produce fertile offspring 5. Define these terms: variation, adaptation, fitness. Give an example of each. Variation-differences in traits among individuals within a population Adaptation-inherited traits that help an organism better survive in its environment Fitness-how well an organism is adapted to its environment 6. Describe the theory of common ancestors. All life descended from one common ancestor, but many branches developed from that common ancestor over time 7. What does the theory of Natural selection state? There will be competition within a species for resources and the fittest or best adapted organisms will survive to reproduce and pass on their traits 8. What is artificial selection? Give an example of it. Humans selecting which traits are best and breeding those organisms; ex-dog breeding 9. The ability of an organism to survive and reproduce is called: Fitness 10. What is genetic drift? In which type of populations does genetic drift usually occur? Random change in allele frequency; small populations 11. What is behavioral isolation? Give an example. Members of a population becoming isolated from each other due to different behaviors; ex-bird mating dances 12. What is temporal isolation? Give an example. Members of a population becoming isolated from each other due to reproducing at different times; ex-different species of frogs reproduce at different times of the year 13. What is geographic isolation? Give an example. Members of a population becoming isolated from each other due to being physically separated by a mountain or river; ex-squirrels developing into different species because of separation by a river 14. What is a gene pool? Give an example. All of the alleles present within a population 15. What is adaptation? Give an example. An inherited trait that helps an organism better survive in its environemnt 16. What is the difference between mimicry and camouflage? Give an example of each. Mimicry-copying the appearance of another species that is usually poisonous, provides protection for the species that is not poisonous; ex-monarch and viceroy butterflies Camouflage-blending into the environment to avoid predators; ex-green grasshoppers blending in to green grass 17. What is a mutation? Random changes in DNA that can lead to variation within a species 18. What is relative frequency? Give an example. The number of times a particular allele shows up within a population; ex-the number of recessive alleles in a population of students 19. Make a chart comparing Directional Selection, Stabilizing Selection, and Disruptive Selection, including definition, diagram and examples of each. See notes 20. What is the difference between relative and radioactive dating? Give an example of each. Relative-comparing the age of one fossil to another based on its location in the ground; ex-younger fossils will be closer to the surface than older fossils Radioactive dating-the exact age of a fossil based on carbon decay