Biology - Central Lyon CSD
advertisement

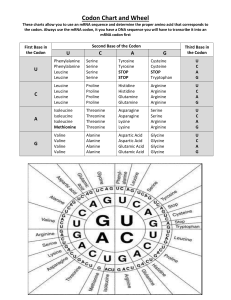
Biology Lab #12 Mutations De Stigter Name/ID_______________ Period _________________ 30 1. Label the following as deletion, point mutation, duplication, insertion, or inversion. Use the definitions found at the end of the assignment. The original code is as follows: The fat cat ate the wee rat. The fat ate the wee rat. ______________ The fat tar eew eht eta tac. ______________ The fat cat xlw ate the wee rat. ______________ The fat caa tet hew eer at. ______________ The fat hat ate the wee rat. ______________ The fat cat ate the wee rat. The fat cat ate the wee rat. _________________ 2. A cell is going through mitosis. As it does so, it copies its DNA. What is the remaining half of DNA code. DNA CODE…CAG – TAT – CCG – AGG – GTA – CAT DNA CODE…___________________________________ 3. The same section of DNA code now needs to make proteins for the cell. In order to do so, the cell undergoes transcription to make RNA. What is the new code found on the RNA? DNA CODE…CAG – TAT – CCG – AGG – GTA – CAT RNA CODE…___________________________________ 4. Where do proteins get made? (2 places) __________________ __________________ 5. Look at the following mRNA codes. Then decipher the type of mutation. One mutation comes from your notes. Normal mRNA Code – AUGAAGUUUGGCGCAUUGUAA 5a. AUGAAGUUGGCGCAUUGUAA ________________________ 5b. AUGAAGUUUGUGCGCAUUGUAA __________________________ 5c. AUGAAGUUUAGCGCAUUGUAA __________________________ 5d. AUGAAGUUUGGCGCAUUGUAAAUGAAGUUUGGCGCAUUGUAA _______________________________ 5e. AAUGUUACGCGGUUUGAAGUA _____________________________ 6. What are the amino acids that should be made from question #5? What are the amino acids that are made from 5a? What are the amino acids that are made from 5b? What are the amino acids that are made from 5c? What are the amino acids that are made from 5d? What are the amino acids that are made from 5e? 7. What are the 4 nitrogen bases and what are their symbols? Deletion Mutations that result in missing DNA are called deletions. These can be small, such as the removal of just one letter, word, or longer deletions that affect a large number of genes on the chromosome. Deletions can also cause frame-shift mutations. Point Mutation A point mutation is a simple change in one base of the gene sequence. This is equivalent to changing one letter in a sentence, but keeping the remaining letters the same. Inversion In an inversion mutation, an entire section of DNA is reversed. A small inversion may involve only a few bases within a gene, while longer inversions involve large regions of a chromosome containing several genes. Duplication A duplication error happens in many different forms. One way is during meiosis where homologous fail to separate to different poles causing offspring to have to duplicate or copied sets of the same gene. (extra copies of a gene) Insertion Mutations that result in the addition of extra DNA are called insertions. Insertions can also cause frame-shift mutations, and generally results in a nonfunctional protein. First Base in Codon A G T C Third Base in Codon Second Base in Codon A Phenylalanine Phenylalanine Leucine Leucine Leucine Leucine Leucine Leucine Isoleucine Isoleucine Isoleucine Methionine Valine Valine Valine Valine G Serine Serine Serine Serine Proline Proline Proline Proline Threonine Threonine Threonine Threonine Alanine Alanine Alanine Alanine T Tyrosine Tyrosine Stop Stop Histidine Histidine Glutamine Glutamine Asparagine Asparagine Lysine Lysine Aspartate Aspartate Glutamate Glutamate C Cysteine Cysteine Stop Tryptophan Arginine Arginine Arginine Arginine Serine Serine Arginine Arginine Glycine Glycine Glycine Glycine A G T C A G T C A G T C A G T C