DNA WORKSHEET
advertisement

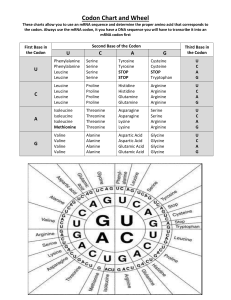
DNA WORKSHEET NAME______________________________ Step 1). Step 2). Step 3). Step 4). back. Replicate the DNA Strand labeled A creating strand B in the left column Transcribe DNA Strand A into mRNA codons Translate the mRNA codons into tRNA anticodons. Decode the tRNA anticodons into amino acids using the tRNA table on the DNA Strand B DNA Strand A T A C G G G C T A C A A C T T A A C A G A C C A Transcribe mRNA Translate tRNA Amino Acid First Base U C A G U SECOND BASE C A G Third Base UUU Phenylalanine UUC Phenylalanine UUA Leucine UUG Leucine UCU Serine UCC Serine UCA Serine UCG Serine UAU Tyrosine UAC Tyrosine UAA STOP UAG STOP UGU Cysteine UGC Cysteine UGA STOP UGG Tryptophan U CUU Leucine CUC Leucine CUA Leucine CUG Leucine CCU Proline CCC Proline CCA Proline CCG Proline CAU Histidine CAC Histidine CAA Glutamine CAG Glutamine CGU Arginine CGC Arginine CGA Arginine CGG Arginine U AUU Isoleucine AUC Isoleucine AUA Isoleucine AUG START ACU Threonine ACC Threonine ACA Threonine ACG Threonine AAU Asparagine AAC Asparagine AAA Lysine AAG Lysine AGU Serine AGC Serine AGA Arginine AGG Arginine U GUU Valine GUC Valine GUA Valine GUG Valine GCU Alanine GCC Alanine GCA Alanine GCG Alanine GAU Aspartate GAC Aspartate GAA Glutamate GAG Glutamate GGU Glycine GGC Glycine GGA Glycine GGG Glycine U C A G C A G C A G C A G To use the amino acid chart: Find the first letter of the tRNA anticodon on the left column. Find the second letter of the tRNA anticodon on the upper column. Draw line from both columns until the lines meet. Now find the third letter from the tRNA anticodon in the right column and draw a line until it intersects with the other 2 lines. Fill in the blank with the terms (1 point each) Phosphate Triplets Deoxyribose Thymine 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Bases Proteins Complementary Helix Amino Acids Cytosine DNA molecules contain information for building specific (1). In a three-dimensional view a DNA molecule looks like a spiral staircase; this is correctly called a (2). The constant parts of DNA molecules are the (3) and (4) molecules, forming the DNA-ladder uprights, or backbones. The information of DNA is actually coded in the sequence of nitrogen containing (5), which are bound together to form the “rungs” of the DNA ladder. When the four DNA bases are combined in different three-base sequences called (6), different (7) of the protein are called for. It is said that the N-containing bases of DNA are (8), which means that only certain bases can fit together or interact together. Specifically this means that (9) can only bind with guanine, and adenine can only bind with (10). Answer in sentences: If a structural gene contains 300 DNA nucleotides, how many amino acids will be used in the protein synthesis? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ If a protein has 150 amino acids, how many DNA nucleotides would make up the structural gene? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Describe in a sentence the relationship between the gene sequence and the tRNA sequence? (Look at both columns how are they similar or different) ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________