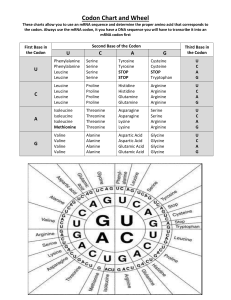
mRNA Codons and Corresponding Amino Acid Chart
advertisement

Biology Student EQ: If there are only four nucleotide types in DNA, why are all living things so different? Genetic Code of Life Amino Acid Codon Chart Target 4. Using descriptions or diagrams of protein synthesis, be able to use the Codon Chart to determine the corresponding amino acid Enduring Understanding Proteins determine the structure and function of living things. Broad Brush Knowledge mutations, protein synthesis Concepts Important to Know and Understand DNA Processes Core Objectives 5. Identify the structure & function of nucleic acids including their role in biodiversity. There are two Genetic Code of Life / Amino Acid Codon Charts in this document. One has the clue of 1st Base, 2nd Base and 3rd Base on the chart. The other does not clue the students as to which base is found in which area of the chart. Identifying the base is helpful in the beginning but students need to be able to use the chart without base indication eventually. What is the Genetic Code of Life The amino acid codon chart is often referred to as the Genetic Code of Life. A unifying feature of life is that cells almost always use the same genetic language to turn DNA codes into RNA, then proteins. This is because the triplet codons that represent certain amino acids are the same in most organisms. In a bacterium, a bean or a dolphin, the same three letters of RNA stand for the same amino acid. UCA, for example, codes for serine. While true for most organisms, as genome projects spread to different species, scientists have found some exceptions. Most of these exceptions occur in the mitochondria of round worms and arthropods. GENETIC CODE OF LIFE - Biology (Revised June 25, 2008) (printed 2/15/2016) p. 1 GENETIC CODE OF LIFE mRNA Codon and Corresponding Amino Acid Chart 2nd Base in Codon C A G C A G Phenylalanine Serine Tyrosine Cysteine U Phenylalanine Serine Tyrosine Cysteine C Leucine Serine Stop Codon Stop Codon A Leucine Serine Stop Codon Tryptophan G Leucine Proline Histidine Arginine U Leucine Proline Histidine Arginine C Leucine Proline Glutamine Arginine A Leucine Proline Glutamine Arginine G lsoleucine Threonine Asparagine Serine U lsoleucine Threonine Asparagine Serine C lsoleucine Threonine Lysine Arginine A Methionine Threonine Lysine Arginine G Valine Alanine Aspartic Acid Glycine U Valine Alanine Aspartic Acid Glycine C Valine Alanine Glutamic Acid Glycine A Valine Alanine Glutamic Acid Glycine G GENETIC CODE OF LIFE - Biology (Revised June 25, 2008) 3rd Base In Codon 1st Base in Codon U U (printed 2/15/2016) p. 2 GENETIC CODE OF LIFE mRNA Codon and Corresponding Amino Acid Chart U C A G U C A G Phenylalanine Serine Tyrosine Cysteine U Phenylalanine Serine Tyrosine Cysteine C Leucine Serine Stop Codon Stop Codon A Leucine Serine Stop Codon Tryptophan G Leucine Proline Histidine Arginine U Leucine Proline Histidine Arginine C Leucine Proline Glutamine Arginine Leucine Proline Glutamine Arginine A G lsoleucine Threonine Asparagine Serine U lsoleucine Threonine Asparagine Serine lsoleucine Threonine Lysine Arginine C A Methionine Threonine Lysine Arginine G Valine Alanine Aspartic Acid Glycine U Valine Alanine Aspartic Acid Glycine C Valine Alanine Glutamic Acid Glycine A Valine Alanine Glutamic Acid Glycine G GENETIC CODE OF LIFE - Biology (Revised June 25, 2008) (printed 2/15/2016) p. 3