Name
advertisement
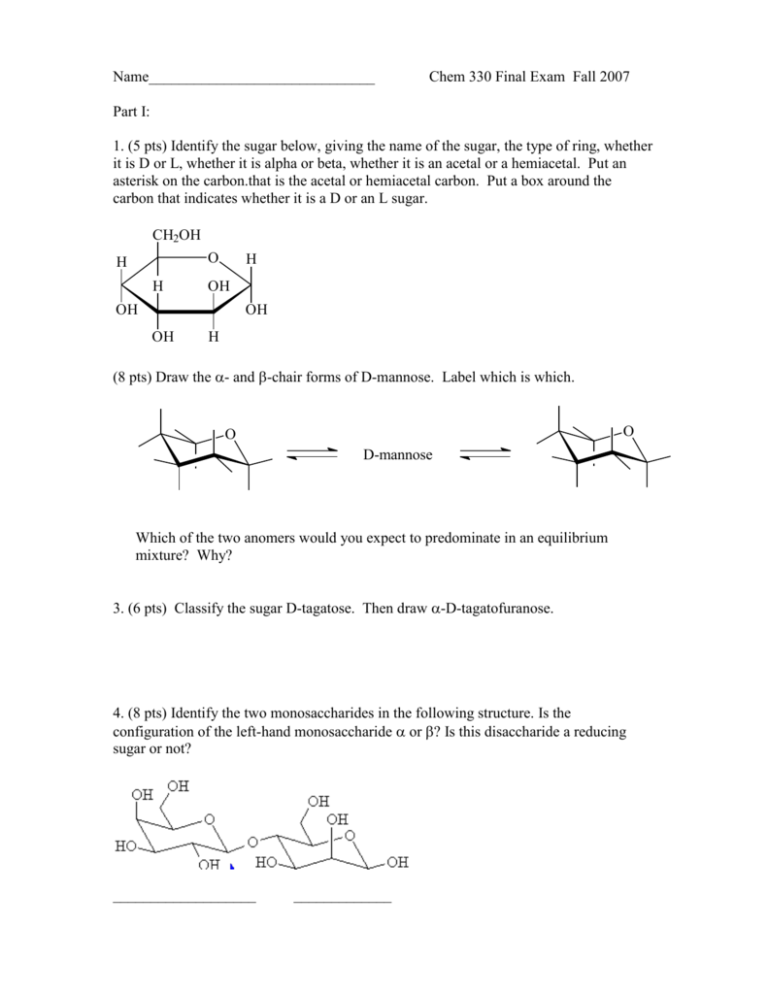
Name______________________________ Chem 330 Final Exam Fall 2007 Part I: 1. (5 pts) Identify the sugar below, giving the name of the sugar, the type of ring, whether it is D or L, whether it is alpha or beta, whether it is an acetal or a hemiacetal. Put an asterisk on the carbon.that is the acetal or hemiacetal carbon. Put a box around the carbon that indicates whether it is a D or an L sugar. CH2OH O H H H OH OH OH OH H (8 pts) Draw the - and -chair forms of D-mannose. Label which is which. O O D-mannose Which of the two anomers would you expect to predominate in an equilibrium mixture? Why? 3. (6 pts) Classify the sugar D-tagatose. Then draw -D-tagatofuranose. 4. (8 pts) Identify the two monosaccharides in the following structure. Is the configuration of the left-hand monosaccharide or ? Is this disaccharide a reducing sugar or not? ___________________ _____________ 5. (4 pts) The following amino acid played a role in a science fiction story about an alien invasion. CO2- CH3S a. Is this amino acid an a-amino acid? Yes No O NH3+ b. Would you expect this amino acid to be: non-polar or polar or acidic or basic 6. (12 pts) Draw the tripeptide phe-thr-glu at physiological pH (~ pH 7). 8. (8 pts) Draw the predominant forms of serine at pH 1.0, 6.0, and 11.0. Calculate the isoelectric point (pI) of this amino acid if pKa1 and pKa2 are 2.00 and 10.60, respectively. pH = 1.0 pH = 6.0 pH = 11.0 pI = 9. (6 pts). Calculate the iosoelectric point (pI) of lysine, given the following pKas: pKa1 =2.18, pKa2 = 8.95, and pKaR = 10.53 10. (5 pts) Explain why acid chlorides are the most reactive carboxylic acid derivative and an amide is the least reactive.. 11. (12 pts) Show how the acid chloride shown below could be converted to the products shown. By each arrow, give the reagents that would accomplish each transformation: O C OH O O O C O C Cl C N O O C O C CH2CH3 12. (16 pts) Indicate how the following compounds could be synthesized using the reaction indicated. OH C CH2 a. CH3 using a Grignard reaction O OH usning an aldol reaction b. O O using a Claissen reaction c. CH3O 13. (14 pts) Predict the product and give a detailed mechanism for the aldol condensation of 2-methylbutanal in base. Show all resonance structures. Part II: Comprehensive 1. (4 pts) Assign R or S to each chiral carbon in the following. CHO O CH3 C H CO2H H C H3C CH2 H OH H OH CH2OH 2. (9 pts) Draw all equivalent resonance structures for the following OCN- anion, including formal charges where appropriate. Indicate which resonance structure would be expected to be the major resonance contributor and explain why. OCN- 3. (10 pts) What are the hybridization and molecular geometries of each of the indicated atoms in the compound shown below? Write the hybridization and molecular geometry right by each arrow. O O C C H 4. (2 pts) Circle the compound in each pair that would be the stronger acid CO2H or CO2H CO2H Cl F or CO2H Cl Br 5. (3 pts) Circle the compound in each pair that: a. is the stronger acid: HBr or b. is the stronger acid HIO3 or c. is the better nucleophile: For HCl HBrO3 I- 6. (6 pts) Draw the two chair conformations of tciss-1-tert-butyl-2-methylcyclohexane. Indicate which conformation would be more stable. 7. (12 pts) Consider the following compounds and their reactivity in SN1 and SN2 conditions:: Br Br Br a. Which would react faster with H2O and heat? ____ b. Which would react faster with NaCN in DMSO? ____ c. Which would give the greatest amount of elimination I II product with CH3ONa? ____ Using the compound you selected for each part a-c, write the product of each reaction a b c III 7. (4 pts) Indicate the relationship between the structures in the following pair (constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or identical). HO H HO H CH2CH3 H3C H OH H3C CH3 CH2CH3 H Br Br H3C CH2CH3 HO H CH2CH3 CH3 H 9. (6 pts) Circle the compounds below that are aromatic: O O N CH3 10. (8 pts) Write a detailed mechanism for the SN1 reaction of (S)-2-bromobutane with propanol. Show all arrows. Clearly indicate the stereochemistry of the product. If more than one product is formed, indicate the relationship between the products. OH CH3 CH3 11. (24 pts) Predict the major product(s) in each of the following reactions. Specify stereochemistry where appropriate. Reactions need not be balanced. Br2 CCl4 (solvent) HBr OH K2Cr2O 7 H2SO 4 OH H+ H2O NaOH Br O 1) MgBr 2) H3O+ O CH3OH (excess) H H+ OH H2SO 4 heat O O OH 1) NaBH4 2) H3O + 12. (12 pts) Give a detailed mechanisms of the acid-catalyzed Fischer esterification of ethanoic acid with methanol, including all resonance structures. O O H+ CH3C OCH3 + H2O CH3C OH + CH3OH CH O CH O CH O H OH HO H OH H OH HO H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH CH2OH OH HO H OH H H OH H CH2OH H CH2OH CH O CH O OH HO H H HO H H HO H HO H H OH CH2OH CH2OH OH H CH2OH CH2OH D-talose CH2OH CH2OH O O H H OH HO H H OH H OH HO H OH H OH H D-fructose Nonpolar Side Chains OH HO H H HO H H OH OH CH2OH CH2OH D-sorbose CH2OH D-tagatose Polar Side Chains - Acidic Side Chains - CO2 HO HO2C NH3+ NH3 valine (val) OH - CO2 HO2C CO2 + isoleucine (ile) phenylalanine (phe) threonine (thr) NH3+ asparagine (asn) NH - H2N + NH3+ arginine (arg) H CO2HO + NH3 tyrosine (tyr) CO2 HN glutamic acid (glu) - O NH3+ lysine (lys) - CO2 H2N - CO2 H2N CO2 NH3 NH3+ NH3+ CO2 NH3+ aspartic acid (asp) serine (ser) CO2- Basic Side Chains - CO2 + OH D-galactose O NH3 HO HO CH2OH D-idose CH2OH D-psicose H OH D-gulose O H D-mannose H H HO HO D-glucose CH O H OH CH2OH D-altrose CH O H H CH2OH D-allose HO H CH O N N CO2+ NH3 histidine (his)










