Unit-D_-Big-Idea
advertisement

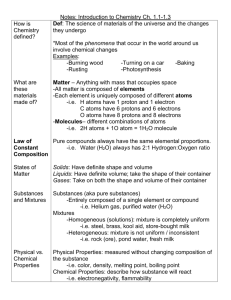
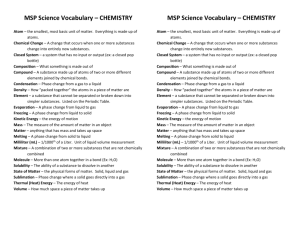
Earth Science Unit D: Elements and Their Combinations Big Idea Elements and their combinations account for all the varied types of matter in the world. Students will understand that all matter is made up of atoms, which may combine to form molecules. Students will take a close look at chemical reactions, as well as the chemical physical properties of mixtures and compounds. Students will examine the properties of certain solid, liquid, and gaseous substances. Chapter 8: Atoms and Elements Lesson 1: Standard 1b, 1d, and 1e Students know all matter is made of atoms, which may combine to form molecules. Students know that the each element is made of one kind of atom and that the elements are organized in the periodic table by their chemical properties. Students know scientists have developed instruments that can create discrete images of atoms and molecules that show that the atoms and molecules often occur in well-ordered arrays. Lesson 2: Standard 1c & 1d Students know metals have properties in common, such as high electrical and thermal conductivity. Some metals, such as aluminum (Al), iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and gold (Au), are pure elements; others, such as steel and brass, are composed of a combination of elemental metals. Students know that the each element is made of one kind of atom and that the elements are organized in the periodic table by their chemical properties. Lesson 3: Standard 1b & 1h Students know all matter is made of atoms, which may combine to form molecules Students know living organisms and most materials are composed of just a few elements. Vocabulary 1. atom – the smallest particle of an element that still has the properties of that element 2. compound – a pure substance that is made of two or more elements that are chemically combined 3. electron – negatively charged particles 4. element – a substance that cannot be broken apart into other substances 5. neutron – a particle that lacks charge 6. nucleus – the structure in the center of an atom 7. proton – a small, positively charged particle 8. chemical symbol – an abbreviation of the element’s name, sometimes from Latin or Greek 9. metal – usually shiny, can be bent or stretched, and conducts electricity 10. noble gas – a substance that cannot be broken apart into other substances 11. nonmetal – a metal that is usually dull in color, does not conduct electricity, does not bend or stretch very much, and breaks easily 12. periodic table – a table in which the elements are arranged by their properties 13. semimetal – a metal that is like metals in some ways and like nonmetals in other ways 14. molecule – a group of two or more atoms that are chemically joined and that act as a single unit Chapter 9: Chemical Compounds Lesson 1: Standard 1a, 1b, & 1f Students know that during chemical reactions the atoms in the reactants rearrange to form products with different properties. Students know all matter is made of atoms, which may combine to form molecules. Students know differences in chemical and physical properties of substances are used to separate mixtures and identify compounds. Lesson 2: Standard 1f & 1g Students know differences in chemical and physical properties of substances are used to separate mixtures and identify compounds. Students know properties of solid, liquid, and gaseous substances, such as sugar (C6H12O6), water (H2O), helium (He), oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), and carbon dioxide (CO2) Lesson 3: Standard 1f & 1i Students know differences in chemical and physical properties of substances are used to separate mixtures and identify compounds. Students know the common properties of salts, such as sodium chloride (NaCl) Vocabulary 1. chemical formula – a shorthand way to describe a compound 2. chemical reaction – process in which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances 3. boiling point – the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas 4. chemical property – the ability or tendency of a material to change its chemical makeup 5. conductivity – the ability to carry energy 6. density – mass per unit volume of a substance 7. melting point – the temperature at which a solid substance changes to a liquid 8. physical property – characteristic that can be measured or detected by the senses 9. solubility – measure of how much of one substance can dissolve in another 10. acid – substance that tastes sour and turns blue litmus paper red when dissolved in water; releases hydrogen ions 11. base – substance that feels slippery, tastes bitter, and turns red litmus paper blue when dissolved in water; receives hydrogen ions 12. indicator – substance that shows whether an acid or a base is present 13. pH – system for measuring the strength of acids and bases 14. salt – what forms when a strong base reacts with a strong acid, typically made from a metal and a nonmetal Chapter 10: Characteristics of Matter Lesson 1: Standard 1g Students know properties of solid, liquid, and gaseous substances, such as sugar (C6H12O6), water (H2O), helium (He), oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), and carbon dioxide (CO2) Lesson 2: Standard 1c & 1f Students know metals have properties in common, such as high electrical and thermal conductivity. Some metals, such as aluminum (Al), iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and gold (Au), are pure elements; others, such as steel and brass, are composed of a combination of elemental metals. Students know differences in chemical and physical properties of substances are used to separate mixtures and identify compounds. Lesson 3: Standard 1f & 1g Students know differences in chemical and physical properties of substances are used to separate mixtures and identify compounds. Students know properties of solid, liquid, and gaseous substances, such as sugar (C6H12O6), water (H2O), helium (He), oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), and carbon dioxide (CO2) Lesson 4: Standard 1a Students know that during chemical reactions the atoms in the reactants rearrange to form products with different properties. Vocabulary 1. gas – form of matter that has no definite shape or volume 2. liquid – form of matter that changes shape to match the shape of its container 3. solid – form of matter that has a definite shape and volume 4. mixture – physical combination of two or more substances 5. solution – homogeneous, mixture, meaning two or more substances that are evenly distributed 6. condensation – a change of state from a gas to a liquid 7. evaporation – the process of becoming vapor 8. sublimation – the process of a solid changing directly to a gas without passing through the liquid state 9. vaporization – the process of a liquid changing into a gas 10. product – substance that results from a chemical change 11. reactant – substance that enters into and is altered through the course of a chemical change Ways to Review for your Test: 1. Study the Vocabulary Words – make flashcards 2. Make an outline for each lesson – noting main ideas, key points, and pictures 3. Understand and use the Visual Summary to help you understand some of the key concepts taught 4. Answer questions at the end of each section of the lesson 5. Answer the Reading Review section at the end of the lesson 6. Answer the Chapter Review and Test Practice Section at the end of each chapter 7. Answer the Unit Review and Test Practice Section at the end of the unit