Biodiversity & Classification Mini-Unit Quiz date: Monday 3/23 or a
advertisement

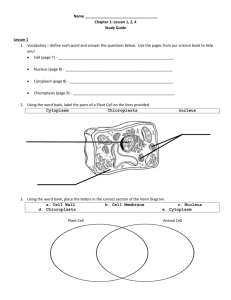
Study Guide Classification and The Six Kingdoms To prepare for the test on this topic: review your homework, study your class notes and worksheets, and know the information on this study sheet. 1. Biologists use classification to organize living things into groups so that they are easy to study. 2. Carolus Linnaeus devised a system of naming organisms called binomial nomenclature, which gives every living thing a two word scientific name. The scientific name is written in the Latin language. This was the language scientists used in the past and since the language is no longer used the names of the organisms will never change. 3. The seven levels of classification of the Linnaean System of Classification are: Kingdom Phylum (Phyla is the plural form) Class Order Family Genus (Genera is the plural form) Species (Kings Play Cards On Fat Green Stools) 4. The modern classification system includes Domain as the broadest classification group. Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (Do Kings Play Cards On Fat Green Stools?) 5. Each kingdom is made up of phyla; each phyla is made up of classes; each class is made up of orders; each order is made up of families; each family is made up of genera; each genus is made up of one or more species; 6. The scientific name of an organism is made up of its genus and species name. The genus name is always capitalized. The species name is not capitalized. Ursus maritimus is the scientific name of the polar bear. 7. When Linnaeus developed his classification system, Charles Darwin had not yet formulated his theory of evolution. Today, the Theory of Evolution has changed the way biologists think about classification. 8. Today, organisms with similar evolutionary histories are classified more closely together. The evolutionary history of a species is based primarily on the chemical makeup of organisms ‘cells. 9. The three domains of living things include Eubacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya (Eukaryota). 10. The domain Eubacteria includes the Kingdom Eubacteria (Bacteria). The domain Archaea includes the Kingdom Archaebacteria. The domain Eukarya includes the Kingdoms of Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. 11. The six kingdoms of living organisms includes: Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protists (Protista) Fungi Plants (Plantae) Animals (Animalia) (Aligators Eat Pizza, Fries, Pepsi, & Antelopes) 12. Some of the characteristics used to classify organisms into kingdoms are: Cell structure – Eukaryotic, with a nucleus vs. Prokaryotic, without a nucleus Number of cells: Unicellular, single celled vs. Multicellular, more than one celled How they obtain food: Autotrophic, makes its own food vs. Heterotrophic, does not make its own food 13. Autotrophs are organisms that can make their own food through the process of photosynthesis. Plants, some bacteria, and some protists are autotrophs 14. Heterotrophs cannot make their own food. They have to get their food. Animals and fungi are heterotrophs. 15. Some organisms have their genetic material enclosed in a nucleus. These organisms are called eukaryotes or eukaryotic. 16. Some organisms do not have nuclei. Their genetic material floats freely in their cytoplasm. These organisms are called prokaryotes or prokaryotic. 17. Unicellular organisms consist of one independent cell, which can carry on all life’s activities. A multicellular organism is made up of more than one cell. 18. Biodiversity is the amazing variety of living things on Earth. Many organisms are in danger of becoming extinct. (no longer living).