Solubility Quiz
advertisement

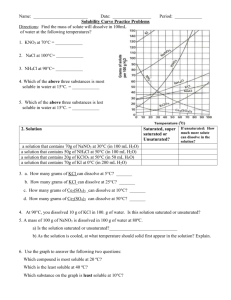
Name: _________________________________ Period__________________ Characteristic Properties Study Guide Solubility 1. In a solution, the substance that is being dissolved is the _____. a. gas b. liquid c. solute d. solvent 2. The oceans are an example of _____ solution. a. an anhydrous b. a gaseous c. a liquid d. a solid 3. A solution that contains all the solute it can hold at a given temperature is _____. a. diluted b. saturated c. supersaturated d. unsaturated 4. Increasing the surface area of a solid _____. a. causes the solid to ionize b. has no effect on the rate of solution c. slows the rate of solution d. speeds the rate of solution 5. When a gas is dissolved in a liquid, the gas dissolves faster if the liquid is _____. a. cooled b. an electrolyte c. heated d. under low pressure 6. The concentration of a solution that contains much solute in the solvent could be described as _____. a. concentrated b. diluted c. polar d. unsaturated 7. An alloy is an example of a _____. a. dilute b. gaseous c. liquid d. solid 8. Adding more solute to a solvent _____. a. decreases its boiling point point c. increases its boiling point b. does not affect its boiling d. increases its freezing point 9. The amount of solute that can be dissolved in a specific amount of solvent at a given temperature is its _____. a. concentration b. density c. dilution d. solubility 10. Which of the following combinations would increase the solubility of a gas in liquid? a. decrease the pressure and decrease the temperature b. decrease the pressure and increase the temperature c. increase the pressure and decrease the temperature d. increase the pressure and increase the temperature 11. Which of the following will speed up the dissolving of a solid in water? a. cool the solution b. freeze the solute c. grind up the solvent d. stir the solution 12. The concentration of a solution, in terms of mass, depends on the _____. a. mass of the solute b. mass of the solvent c. mass of the solution d. volume of solute Matching: Use the letters at the bottom of the page to match the correct terms. 13. A crystal of solute was dropped into a solution and it dissolved. The original solution was _____. 14. If a crystal of solute is dropped into a solution and other crystals appear, the solution was _____. 15. Stirring _____ the rate of dissolving a solid in a liquid. 16. Stirring _____ the rate of dissolving a gas in a liquid. 17. Decreasing temperature _____ the rate of solution for a gas in a liquid. a. b. c. d. e. Increases (yes, there are 2 ‘increases’). Decreases Supersaturated Increases Unsaturated True/False – Write TRUE or FALSE on the provided line. 18. _______________Increasing the temperature always increases the solubility of a solute in a solvent 19. _______________The type of solution depends on the state of the solute. 20. _______________Labels of potentially hazardous materials must contain cautions about possible hazards and instructions for correct and safe use (a common sense question…) Short Answer: Briefly answer the following questions, using words, pictures, diagrams, or whatever else you deem necessary. 21. Explain why increasing the surface area of a solid solute helps to dissolve it more quickly. 22. Explain why the ocean is considered a solution. 23. Explain why cities and towns put salts on icy and snowy streets. 24. List 3 types of solutions AND give and example of each. 25. Identify 2 ways that can be used to make a gas dissolve faster in a liquid. SOLUBILITY CURVES 1. What explains why solids become more soluble as temperature increases and why gasses become less soluble? (You don't need the graph for this one.) 2. Which is more soluble NaNO3 or KCl? 3. How does the line drawn for a particular substance relate to the saturation of a solution of that substance? 4. How many grams of NH4Cl will dissolve in 100 grams of 90°CWater? 5. If I asked you to make a saturated solution of KCl in 100 grams of water, what other piece of information would you need before you could start? 6. At what temperature will 10 grams of KClO3 dissolve? 7. At what temperature will equal amounts of KNO3 and NH3 dissolve? 8. Which substance’s solubility is LEAST affected by increasing temperatures? 9. Which substance’s solubility is MOST affected by increasing temperatures? 10. Which substance is most soluble at 0 Celsius? 11. If half as much water were used how would the amount of solute dissolved be affected for all of these substances? 12. A student has a solution of NaNO3 that contains 90 grams of solute in 100 grams of solution at 30 Celsius. Is this solution unsaturated, saturated or supersatured? Density 1. Calculate the mass of a liquid with a density of 2.8 g/mL and a volume of 35 mL. 2. Calculate the density of a 400 g rectangular block with the following dimensions: length = 9cm, width = 8cm, height = 5cm. 3. Calculate the mass of a solid metal cylinder with a density of 3.6 g/cm3, a diameter of 2.2cm, and a length of 7cm. 4. An irregular object with a mass of 22 kg displaces 3.5 L of water when placed in a large overflow container. Calculate the density of the object. 5. A graduated cylinder has a mass of 90 g when empty. When 30 mL of water is added, the graduated cylinder has a mass of 120 g. If a stone is added to the graduated cylinder, the water level rises to 45 mL and the total mass is now 156 g. What is the density of the stone? Name _________________ Date ______________ Period _________ Heating Curve Worksheet Below is a diagram showing a typical heating curve for water. It reveals a vast wealth of information about the PE and KE of water in all three phases of matter at different temperatures. At the top of the diagram are pictures representing the particle arrangement at each stage of the curve. Answer the following questions using information obtained from the heating curve above. 1. a. What phase(s) is(are) present during segment A? 1a. ____________________________ b. What is happening to the energy being absorbed from the heat source b. _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ 2. c. Is a phase change taking place? If so, which one? c. _____________________________ a. What phase(s) is(are) present during segment B? 2a. ____________________________ b. What is happening to the energy being absorbed? b. _____________________________ _____________________________ c. Is a phase change taking place? If so, which one? c. _____________________________ d. What is the significance of the temperature 0oC? d. _____________________________ _____________________________ 3. a. What phase(s) is(are) present during segment C? 3a. ____________________________ b. What is happening to the energy being absorbed? b. _____________________________ _____________________________ 4. c. Is a phase change taking place? If so, which one? c. _____________________________ a. What phase(s) is(are) present during segment D? 4a. ____________________________ b. What is happening to the energy being absorbed? b. _____________________________ _____________________________ c. Is a phase change taking place? If so, which one? c. _____________________________ d. What is the significance of the temperature 100oC? d. _____________________________ _____________________________ 5. a. What phase(s) is(are) present during segment E? 5a. ____________________________ b. What is happening to the energy being absorbed? b. _____________________________ _____________________________ c. Is a phase change taking place? If so, which one? c. _____________________________