021 Chapter 21
advertisement

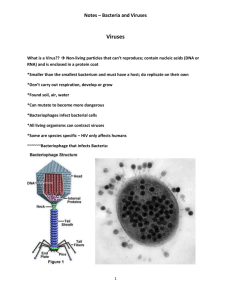
Chapter 21 Student: _________________________________________________________ 1. Which of the following could be used to grow viruses in the laboratory? A. chicken eggs B. cell culture C. bacteria D. all of the choices could be used 2. Which of these diseases could NOT be treated with antibiotics? A. Chlamydia B. plague C. influenza D. scarlet fever 3. Similarities between the archaea and eukarya include: A. same ribosomal proteins B. similar tRNA C. similar initiation of transcription D. all of the choices are correct similarities 4. Which of these is the best description of a virus? A. a noncellular living organism B. one of the smallest bacteria known C. a member of the kingdom Virusae D. a cell at the boundary between living and nonliving things E. chemical complexes of RNA or DNA protected by protein 5. Pasteur chose the Latin root word for "virus" meaning A. extremely small. B. non-living. C. poison. D. contagious. E. particle. 6. Ivanowsky first recognized that something smaller than a bacterium, called a filterable virus, was able to cause disease in the year A. 1865. B. 1874. C. 1892. D. 1910. E. 1935. 7. The innermost portion of a virus's structure is made up of A. a membranous envelope. B. both DNA and RNA. C. either DNA or RNA. D. a protein capsid. E. a protein spore coat. 8. Many animal parasites and bacterial disease agents infect a fairly broad range of hosts, but viruses are often very specific to one type of tissue in one or a few species because A. a virus must be recognized and "taken in" by a host cell. B. different host cells vary greatly in the DNA or RNA they will replicate. C. some viruses may have evolved from nucleic acids from these host cell genomes. D. Both virus must be recognized and the fact that host cells vary greatly in the DNA or RNA they will replicate account for the specificity of viruses. E. All of the choices are correct. 9. Influenza strains that sweep around the world often carry names such as Shanghai H1N1 or Mexico City H2N2. The viruses vary in H and N surface proteins because A. the viruses reproduce on their own and attack people in cities more often. B. these viruses emerged as stray DNA from the genomes of people in these cities. C. this is where the antibodies of immune people began to break down and the old virus was again virulent. D. infected people develop immunity to the present strain, and strains that mutate sufficiently to be outside the range of immunity are soon spread in highly populated areas. 10. Viruses that transform a cell so it undergoes continuous cell divisions–or is cancerous–are A. bacteriophages. B. retroviruses. C. carrying oncogenes. D. viroids. E. preventing DNA transcription. 11. If a virus is latent, it A. cannot be a retrovirus. B. has not entered a lytic cycle. C. has not entered a lysogenic cycle. D. is gaining a new envelope via "budding.'' E. is easy to develop immunity against it. 12. The Greek terms for "rod" and "to eat" underlie the term A. lysogenic. B. bacteriophage. C. prophage. D. eukaryote. E. retrovirus. 13. Some, but not all, viruses contain ______, located on their outer surface. A. a membranous envelope B. both DNA and RNA C. either DNA or RNA D. a protein capsid E. a protein spore coat 14. In order to infect a cell, a virus must A. inject its protein into the cell while the nucleic acid remains attached to the host cell surface. B. have a special protein on its surface that can interact with a protein on the surface of the host cell. C. actively burrow through the cell wall or cell membrane of the host cell to reach the cell's nucleus. D. produce a special extension of its cytoplasm when it comes into contact with the appropriate host cell. 15. The cycle of viral infection of a bacterial cell that will cause its death most rapidly is called the _______ cycle. A. lysogenic B. lysozyme C. lytic D. lysol E. lysosome 16. The cycle of viral infection that will cause the viral DNA to become integrated into the bacterial DNA is called the _______ cycle. A. lysogenic B. lysozyme C. lytic D. lysol E. lysosome 17. The Greek terms for "producing" and "break up" underlie the term A. lysogenic. B. bacteriophage. C. prophage. D. eukaryote. E. lytic. 18. Which statement is NOT true about a retrovirus? A. It may cause cancer or AIDS. B. It contains reverse transcriptase. C. It is known to cause diseases only in animals, not in humans. D. It has the capacity to integrate cDNA into the host DNA of the cell it infects. 19. When an enveloped animal virus enters a cell, then A. the next thing it does is assemble a new virus. B. the envelope is removed after the virus is inside the cell's nucleus. C. the protein capsid is removed through uncoating to expose the viral genome. D. it immediately integrates its nucleic acid genome into the host chromosomes. 20. One bacterial cell passes DNA to a second cell in the process of A. transformation. B. transduction. C. conjugation. D. infection. E. replication. 21. Bacterial cells pick up free pieces of DNA from the medium–pieces that were secreted by live bacteria or released from dead bacteria–in a process called A. transformation. B. transduction. C. conjugation. D. infection. E. replication. 22. Bacteriophages carry portions of bacterial DNA from one cell to another in a process called A. transformation. B. transduction. C. conjugation. D. infection. E. replication. 23. Which statement is true about prokaryotes? A. They contain a nucleus. B. They lack ribosomes. C. They usually lack a cell wall. D. They do not divide by mitosis. E. They contain a single circular DNA molecule as the genetic material. 24. The Latin terms for "break" and "in two" underlie the term A. transduction. B. binary fission. C. conjugation. D. transformation. E. retrovirus. 25. Which of these is a correct description of a form of genetic recombination in bacteria? A. Crossing-over occurs between paired chromosomes in meiosis. B. Conjugation occurs when a cell passes DNA to another cell by means of a sex pilus. C. Transformation occurs when a bacteriophage carries a bit of DNA from a previous host cell to a new host cell. D. Transduction occurs when a live bacterium picks up DNA from dead bacteria that have shed it into the environment of the living cell. 26. Which definition of a relationship between bacteria and other organisms is NOT correct? A. A parasitic bacterium is one that can cause disease in a plant or animal. B. A symbiotic relationship is one in which the bacterium is usually free-living, but may become associated as a parasite in an animal under certain conditions. C. A mutualistic relationship is one in which each of the associated organisms derives benefit. D. A commensalistic bacterium lives on or in another organism without doing it any harm or any good, but the bacterium derives a benefit. 27. Variation in a strain of bacteria A. does not occur, since bacteria are asexual. B. is mainly provided by endospores. C. is produced by genetic recombination, primarily through crossing-over. D. mainly occurs from mutations, which are rapidly replicated and selected in a haploid system. E. is hidden within the many recessive genes and polygenic traits that reside in the diploid genome. 28. The Greek terms for "pertaining to chemicals" and "self" and "food" are the root words for the term A. obligate anaerobe. B. facultative anaerobe. C. chemoautotroph. D. photoautotroph. E. saprophytic heterotroph. 29. The Greek terms for "light" and "self" and "food" are the root words for the term A. obligate anaerobe. B. facultative anaerobe. C. chemoautotroph. D. photoautotroph. E. saprophytic heterotroph. 30. The Greek terms for "life" and "together" are the root words for the term A. obligate anaerobe. B. facultative anaerobe. C. chemoautotroph. D. symbiotic. E. saprophytic heterotroph. 31. The Greek terms for "blue" and "rod" are the root words for the term A. aquificales. B. deinococci. C. cyanobacteria. D. peptidoglycan. E. spirochete. 32. Prokaryotes are now divided into the A. archaea and cyanobacteria. B. bacteria and cyanobacteria. C. photosynthetic bacteria and chemosynthetic bacteria. D. archaea and bacteria. E. autotrophs and heterotrophs. 33. The archaea include all of the following EXCEPT the A. methanogens. B. rickettsia. C. halophiles. D. thermoacidophiles. 34. Which of the following is a characteristic of the photosynthetic cyanobacteria? A. does not release oxygen B. contains only photosystem I C. contains a unique form of chlorophyll D. uses hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide as an electron donor E. contains pigments that may mask the chlorophyll and cause the bacteria to be red or black in color 35. To be sure you have sterilized water, you must boil it for a long time in a pressure cooker because A. bacteria are facultative anaerobes. B. some bacteria produce very resistant endospores. C. peptidoglycan is resistant to boiling water. D. bacteria can otherwise regenerate living cells from nonliving. 36. To which of the following domains do viruses belong? A. Bacteria B. Archae C. Eukarya D. none of the choices 37. Viruses are characterized by all of the following EXCEPT A. they are obligate intracellular parasites B. a specific virus will only infect a specific cell type C. the fact that they most likely evolved after cells D. viruses can mutate E. All of the choices characterize viruses. 38. Which of the following characterize prions? A. prions are simply protein molecules B. they cause Cruetzfeld-Jakob disease C. prions are linked to spongiform encephalopathy and scrapie D. All of the choices are correct. 39. Prokaryotic cells are characterized by A. the lack of an organized nucleus. B. cells that can move by flagella. C. the lack of membrane bound organelles. D. All of the choices are correct. 40. Chemoautotrophs use which of the following compounds to obtain energy? A. hydrogen gas B. hydrogen sulfide C. ammonia D. All of the choices are correct. 41. The only process that bacteria have that is somewhat similar to sexual reproduction is conjugation. True False 42. Bacterial endospores are very easily killed with heat or chemicals. STION] Viruses are capable of replicating by division outside of a cell, but they replicate by assembly within a host cell. True False 43. Most viruses have a wide range of possible hosts: plants, animals, or bacteria. True False 44. A bacteriophage is a virus that attacks only bacteria as its host cells. True False 45. A prophage is a form of virus that attacks only plants as its host cells. True False 46. An environmental change, such as exposure to ultraviolet light, may cause a lysogenic bacterium to enter a lytic cycle. True False 47. One of the most effective ways of controlling a viral disease in animals is to use vaccines. True False 48. The cell wall of the bacteria contains a molecule found nowhere else called peptidoglycan. True False 49. Probably the most important means of gaining new genetic material for prokaryotic evolution is sexual recombination. True False 50. Endospores form in some types of bacteria and allow the cells to survive under unfavorable environmental conditions. True False 51. A facultative anaerobe is an organism that can metabolize effectively in the presence or absence of oxygen. True False 52. A Gram stain will turn a gram-negative cell purple and a gram-positive cell red. True False 53. Lichens are plant-like living systems formed of fungi and cyanobacteria, and they are capable of breaking down rock to help in the formation of soil. True False 54. Because of their ancient origins and abilities to live in extreme environments, the archaea cause a large number of infectious diseases. True False 55. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites. True False 56. During the lytic cycle, bacteriophages commandeer the cells metabolism to produce and release new viral particles. True False 57. Facultative anaerobes grow in the presence or absence of free oxygen. True False 58. Viroids are naked strands of RNA associated with about a dozen plant crop diseases. True False 59. Describe the structure of a virus and explain how it may differ among different kinds of viruses. 60. Many microbiologists prefer to describe viruses as being "activated" rather than "living." Consider again the discussion of "properties of life" and describe at least three distinct reasons why the term "activated" is more appropriate. 61. Describe the lytic cycle of a bacteriophage. 62. Describe the lysogenic cycle of a bacteriophage, and explain how it would be useful to the virus to have this cycle. 63. Describe how a retrovirus's genetic information becomes integrated into a host cell. 64. Give two reasons to explain why mutations in prokaryotes have a more rapid effect on the population than mutations in other organisms. 65. Describe why the heterotrophic prokaryotes are important in the management of the ecosystem. 66. Describe the differences between archaea and bacteria. 67. Describe and explain the importance of the cyanobacteria. 68. There are no antibiotic agents (derived from living sources) and very few chemotherapeutic agents (acyclovir and AZT) that are effective against viruses. Detail why it is so difficult to develop agents that will destroy viruses and not damage host cells, and why it is easier to develop antibiotics against bacteria. 69. Carl Woese and co-workers have proposed that life be divided into three ‘‘domains,'' categories above the level of kingdom, because there appear to be more differences in sequencing of nucleic acids and proteins between the archaea and bacteria than between either prokaryotic group and the rest of life, the eukaryotes! A family tree becomes a complex branched bush with more lengthy stems leading off to bacterial groups than to other ‘‘higher'' forms of life. a) Why do viruses not appear on this phylogeny? b) From your general knowledge of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, why does this system not undermine the idea that all life is still related to common ancestry? c) Will the use of the three-domain (versus the five-kingdom) system make any major operative difference in the day-to-day life of medical practitioners, industrial microbiologists, and others who must work with these organisms? 70. Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology was the standard taxonomic reference in bacteriology until Woese promoted an alternative methodology of identifying and classifying prokaryotes. Describe the differences in the two methodologies. How dramatic were the changes, i.e., were they totally different in their conclusions? 71. Mycoplasmas are very small, almost filterable, organisms that appear to be very stripped-down relatives of Clostridium bacteria. Only 40 or so species are known and they appear to have the smallest genome possible and still code for a membrane and minimal metabolic processes. They are not free-living but are all parasitic; one is a common cause of pleural pneumonia in humans, but others live on specific insects or plants. Why would we place these with the bacteria rather than the viruses? Why would these not be considered an evolutionary link between viruses and bacteria? Chapter 21 KEY 1. D 2. C 3. D 4. E 5. C 6. C 7. C 8. E 9. D 10. C 11. B 12. B 13. A 14. B 15. C 16. A 17. A 18. C 19. C 20. C 21. A 22. B 23. E 24. B 25. B 26. B 27. D 28. C 29. D 30. D 31. C 32. D 33. B 34. E 35. B 36. D 37. E 38. D 39. D 40. D 41. TRUE 42. FALSE 43. FALSE 44. TRUE 45. FALSE 46. TRUE 47. TRUE 48. TRUE 49. FALSE 50. TRUE 51. TRUE 52. FALSE 53. TRUE 54. FALSE 55. TRUE 56. TRUE 57. TRUE 58. TRUE 59. Answers will vary. 60. Answers will vary. 61. Answers will vary. 62. Answers will vary. 63. Answers will vary. 64. Answers will vary. 65. Answers will vary. 66. Answers will vary. 67. Answers will vary. 68. Answers will vary. 69. Answers will vary. 70. Answers will vary. 71. Answers will vary.