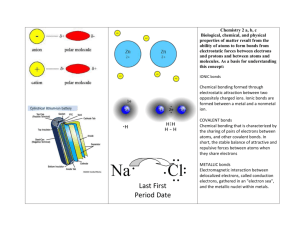
Name
advertisement
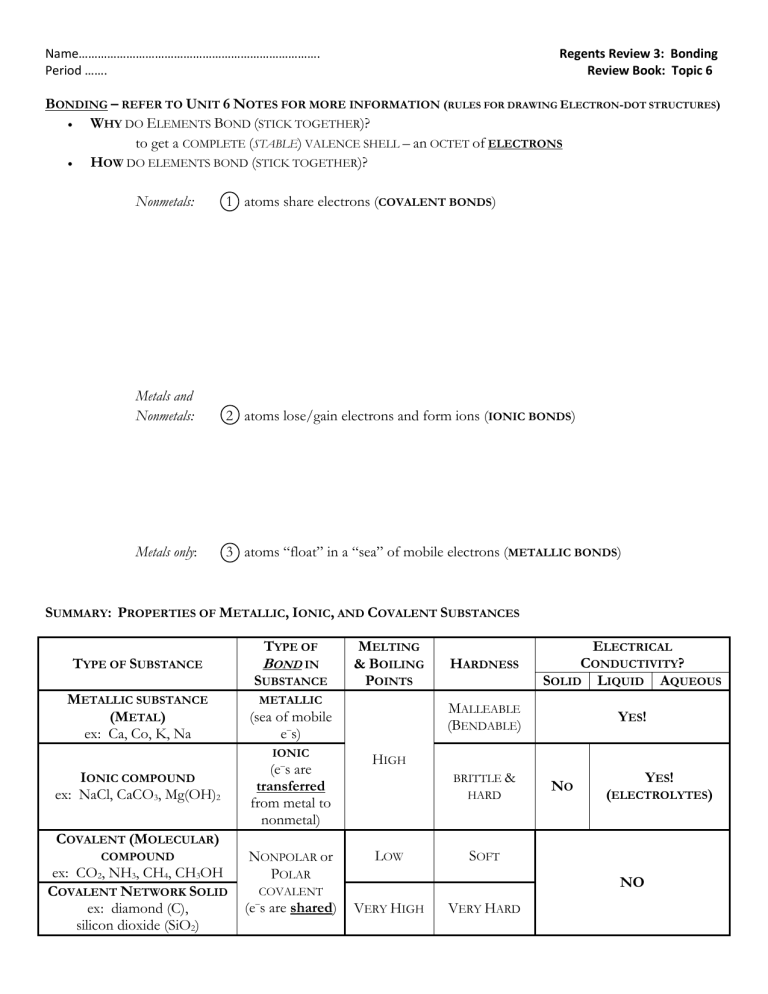
Name…………………………………………………………………. Period ……. Regents Review 3: Bonding Review Book: Topic 6 BONDING – REFER TO UNIT 6 NOTES FOR MORE INFORMATION (RULES FOR DRAWING ELECTRON-DOT STRUCTURES) WHY DO ELEMENTS BOND (STICK TOGETHER)? to get a COMPLETE (STABLE) VALENCE SHELL – an OCTET of ELECTRONS HOW DO ELEMENTS BOND (STICK TOGETHER)? Nonmetals: 1 atoms share electrons (COVALENT BONDS) Metals and Nonmetals: 2 atoms lose/gain electrons and form ions (IONIC BONDS) Metals only: 3 atoms “float” in a “sea” of mobile electrons (METALLIC BONDS) SUMMARY: PROPERTIES OF METALLIC, IONIC, AND COVALENT SUBSTANCES TYPE OF TYPE OF SUBSTANCE METALLIC SUBSTANCE (METAL) ex: Ca, Co, K, Na BOND IN SUBSTANCE METALLIC (e–s are transferred from metal to nonmetal) ELECTRICAL HARDNESS CONDUCTIVITY? SOLID LIQUID AQUEOUS MALLEABLE (BENDABLE) (sea of mobile e–s) IONIC IONIC COMPOUND ex: NaCl, CaCO3, Mg(OH)2 MELTING & BOILING POINTS YES! HIGH BRITTLE & HARD NO YES! (ELECTROLYTES) COVALENT (MOLECULAR) COMPOUND ex: CO2, NH3, CH4, CH3OH COVALENT NETWORK SOLID ex: diamond (C), silicon dioxide (SiO2) NONPOLAR or POLAR LOW SOFT NO COVALENT (e–s are shared) VERY HIGH VERY HARD ***HYDROGEN BONDS*** are a special kind of bond between MOLECULES that contain H bonded to F, O, or N atoms. Hydrogen bonds are a strong INTERMOLECULAR force which cause substances like water to have high melting and boiling points. 1. Which of the following is the correct electron dot diagram for nitrogen? 2. In water, the bond between hydrogen and oxygen is (1) ionic (2) polar covalent (3) nonpolar covalent (4) metallic 3. The bonds in MgSO4 can be described as (1) both ionic and covalent (2) ionic, only (3) covalent, only (4) ionic and covalent 7. The formula for magnesium fluoride is MgF2. The best explanation for this fact is that when they combine (1) each of two magnesium atoms lose an electron and a fluorine atom gains two (2) a magnesium atom loses two electrons and each of two fluorine atoms gains one (3) a magnesium atom shares two electrons with two fluorine atoms (4) each of two magnesium atoms share an electron with a fluorine atom 8. When calcium combines with a nonmetal, it usually (1) loses two electrons (2) gains six electrons (3) shares two electrons (4) shares six electrons 9. Which substance will conduct electricity in both the solid phase and the liquid phase? (1) AgCl (2) H2 (3) Ag (4)HCl 4. Which of the following occurs during covalent bonding? (1) Electrons are lost. (2) Electrons are gained. (3) Valence electrons fall from the excited state to the ground state. (4) Unpaired electrons form pairs. 5. Which of the following is an example of a substance with a nonpolar covalent bond? (1) HCl (2) Cl2 (3) HClO2 (4) NaCl 10. Hydrogen bonds are strongest between molecules of (1) HBr(g) (2) HF(g) (3) HI(g) (4) HCl(g) 11. The strongest hydrogen bonds are formed between molecules of (1) H2Te (3) H2O (2) H2Se (4) H2S 12. What type of bonds are present in a strip of magnesium ribbon? (1) covalent (2) metallic (3) ionic (4) hydrogen bonds 13. Hydrogen bonds are most likely to exist between molecules of (1) H2 (2) HI (3) CH4 (4) H2O 6. Which molecule is polar? (1) H2 (2) CH4 (3) N2 (4) HCl 14. Which substance, in the solid state, is the best conductor ofelectricity? (1) Ag (2) NaCl (3) I2 (4) CO2 15. Which is the predominate type of attraction between molecules of HF in the liquid state? (1) hydrogen bonding (3) metallic bonding (2) ionic bonding (4) covalent bonding 16. Which substance exists as network of covalent bonds? (1) Ar (2) Au (3) SiO2 (4) CO2 17. Mobile electrons are a distinguishing characteristic of (1) an ionic bond (3) an electrovalent bond (2) a metallic bond (4) a covalent bond 18. What kind of bonds are found in a sample of H2O(s)? (1) hydrogen bonds, only (2) covalent bonds, only (3) both ionic and hydrogen bonds (4) both covalent and hydrogen bonds 19. Which substance is made up of molecules that are polar? (1) N2 (2) CH4 (3) H2O (4) CO2 20. Which element consists of positive ions immersed in a "sea" of mobile electrons.? (1) sulfur (2) calcium (3) nitrogen (4) chlorine 21. Which compound contains ionic bonds? (1) CaO (3) SiO2 (2) NO (4) CO2 22. Which of the following solids has the highest melting point? (1) Na2O (3) SO2 (2) H2O (4) CO2 23. Which molecule is nonpolar? (1) CO2 (3) CO (2) H2O (4) NH3 24. Which substance contains metallic bonds? (1) Hg (l) (3) H2O (l) (2) NaCl (s) (4) C6H12O6 (s) 25. Explain, in terms of valence electrons, why the bonding in barium oxide, BaO, is similar to the bonding in magnesium fluoride, MgF2. 26. Draw the Lewis electron-dot structure for the compound magnesium fluoride. 27. Explain, in terms of valence electrons, why the bonding in fluorine, F2, is similar to the bonding in chlorine, Cl2. 28. Draw the Lewis electron-dot structure for fluorine, F2. Questions 29 through 32 refer to the following: Each molecule listed below is formed by sharing electrons between atoms when the atoms within the molecule are bonded together. Molecule A: Cl2 Molecule B: CCl4 Molecule C: NH3 29. Draw the electron-dot (Lewis) structure for the NH3 molecule in the box below. 30. Explain why CCl4 is classified as a nonpolar molecule. 31. Explain why NH3 has stronger intermolecular forces of attraction than Cl2. 32. Explain how the bonding in KCl is different from the bonding in molecules A, B, and C. Questions 33 through refer to the following. Nitrogen and carbon dioxide are gases present in the atmosphere. 33. Draw the electron-dot diagram for a molecule of nitrogen, N2. 34. Draw the electron-dot diagram for a molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2. 35. What is the total number of electron pairs shared between the nitrogen atoms in a molecule of nitrogen, N2? ______ 36. State one similarity and one difference between the bonding within a molecule of nitrogen and the bonding within a molecule of carbon dioxide.