Physical Properties of Matter: Viscosity, Density & More
advertisement

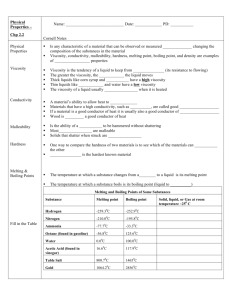
Properties of Matter What is a physical property? • A quality that of the material that can be seen or measured without changing the composition of the material (without changing what its made of) • Physical Properties: – Viscosity – Conductivity – Malleability – Hardness - Melting point - Boiling point - Density Examples of Physical Properties • Viscosity : the tendency of a liquid to keep from flowing, a liquid’s resistance to flowing. – The greater the viscosity, the slower the liquid moves – Examples: honey and corn syrup Discuss Viscosity • Turn to your neighbor…in 30 seconds –Choose two liquids to compare –Explain which of the two has a higher viscosity (which one resists flowing the most) –Listen as your neighbor does the same thing (compares two new liquids) Conductivity • A materials ability to allow heat to flow • Which spoon should you choose for stirring a pot of soup heating on the stove? Wooden spoon or metal Spoon? Why did you choose the spoon that you did? Malleability • The ability of a solid to be hammered without shattering • Most metals are very malleable • Other objects such as glass or fine china are easily broken Hardness • One simple way to compare two materials is to see which one will scratch the other one • Which ever scratches the other is the harder of the two • A Diamond is the hardest known material and a 10 on Mohs scale of hardness Examples Provide an example for each of the following Something with high conductivity Something easily malleable Something that is softer than glass Melting / Boiling Points Melting point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid For water normally occurs at 0o C Boiling point: the temperature at which a substance boils For water normally occurs at 100o C Density Recall that density is the ratio of the mass of a substance and its volume. This ratio can be used to test the purity of a substance Density = mass / volume Sponge Brick Using Physical Properties Physical properties are used to identify a material, to choose a material for a specific purpose, or to separate the substances of a mixture. Using Properties to Choose Materials The properties of a material determine which materials are chosen for which uses. Example: You would not want shoe laces made of wood because they would not be flexible Using Properties to Separate Mixtures Some properties can be used to separate mixtures Filtration and Distillation are two common separation methods Filtration Is a process that separates materials based on the size of their particles Example: Using a strainer to remove tea leaves from a pot of tea Distillation Is a process that separates the substances in a solution based on their boiling points Example: on submarines sea water is boiled, the clean gas collected and cooled for drinking and the undrinkable compound left behind *This works because the clean water has a different boiling temperature than the compounds Recognizing Physical Changes Physical change occurs when some of the properties of a material change, but the substances in the material remain the same. Examples: crumpling a piece of paper and heating butter in a pan *Actions change the shape of the materials but not their composition