65 Critter Breeding packet_key
advertisement

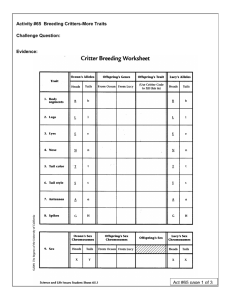
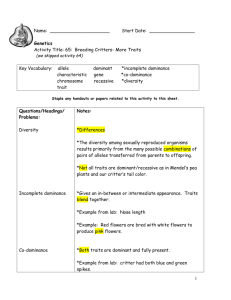
Name _________________________________ Date _______________ Period ________ Lesson 65 – Critter Breeding Packet Ocean’s Alleles Offspring’s Genes Heads Tails From Ocean 1. Body Segments B 2. Legs Trait Offspring’s Phenotype Lucy’s Alleles Heads Tails b B b L l L l 3. Eyes E e E e 4. Nose N n N n 5. Tail Color T t T t 6. Tail Style S s S s 7. Antennas A a A a 8. Spikes G H G H Ocean’s Sex Chromosomes 9. Sex Heads Tails X Y From Lucy Offspring’s Genotype Offspring’s Sex Chromosomes From Ocean From Lucy Offspring’s Genotype (Use Critter Code to fill this in) Offspring’s Phenotype Lucy’s Sex Chromosomes Heads Tails X X Critter Portrait Draw a picture of your critter, color all traits. Offspring Analysis Trait 1. Body Segments 2. Legs 3. Eyes 4. Nose 5. Tail Color 6. Tail Style 7. Antennas Dominant 3 Segments Blue Two Long Blue Curly Two 8. Spikes 1 Short Blue 9. Sex Male Medium 2 Long Green Recessive 2 Segments Red Three Short Orange Straight One 1 Short Blue + 2 Long Green Female Analysis Questions 1. Compare the similarities and differences between the critters (all siblings!) made by your classmates. There are more critters with the dominant traits above in table (3 body segments, blue legs, two eyes etc…)__than the recessive traits___________________________________ 2. List the characteristics that show a simple dominant/recessive pattern (like tail color). Indicate which trait is dominant and which is recessive by underlining the dominant trait. See chart above – everything except nose, spikes and sex will show 3:1 dominance pattern of inheritance Some traits do not show a simple dominant vs. recessive pattern. For example, in some plants, a cross between a red- and white-flowered plant will give pink-flowered offspring. This is called incomplete dominance. A different example is human blood type. A person with Type A blood and a person with Type B blood can have a child with type AB blood. This is called co-dominance, as both traits appear in the offspring. 3. For which characteristics do some offspring have traits in between Skye’s and Poppy’s traits? Explain which kind of dominance this is. _________Nose length is an example of incomplete dominance – medium is in between long and short and that is the phenotype when heterozygous (Nn) for nose ____________________________ 4. For which characteristic(s) do some offspring have both Skye’s and Poppy’s traits? Explain which kind of dominance this is. ______Spikes is an example of co-dominance and you see both traits (short blue and long green) when heterozygous (GH) for spikes 5. Which critter trait is affected by an environmental factor, such as light, temperature, or diet? Explain. Tail style if you have the Ss genotype is affected by diet (critric acid) - _ _ 6. Consider the pattern for sex determination. a. How is a critter’s sex determined? XX is a female and XY is a male_and we determined sex of our critter in class with a toss of the coin for Ocean’s genetic contribution for sex. b. Whose genetic contribution—Ocean’s or Lucy’s—determines the sex of the offspring? Ocean is the male and he contributes either an X chromosome or a Y chromosome to determine sex of the offspring. 7. Who does your critter most look like –Skye, Poppy, Ocean, or Lucy? On which traits did you base your choice? ____________________answers vary 8. Draw a critter with all recessive traits. Assume the recessive trait for spikes is no spikes.