BIOTIC RELATIONSHIPS IN THE ENVIRONMENT
advertisement

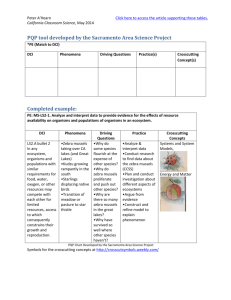
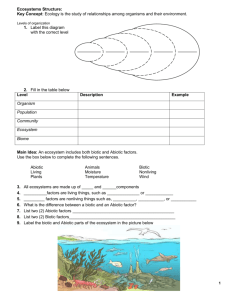
T Key Terms A) abiotic factor: nonliving factors that shapes an ecosystem B) autotroph: or producers organisms that trap sunlight and use it to make sugar C) biosphere: part of the earth in which life exists includes land, water, and air D) biotic factor: living factors that influence and organism E) commensalisms: symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is neither helped or harmed F) community: different populations that live together in the same area G) decomposer: organism that breaks down and obtains energy from dead organic matter H) ecology: study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment I) ecosystem: all the organisms that live in a particular place, with their nonliving environment J) food chain: steps in an ecosystem in which organisms transfer energy by eating or being eaten K) food web: network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships among various organism in a ecosystem L) habitat: area where an organism lives includes biotic and abiotic factors M) heterotroph: or consumer gets energy from eating other organisms N) mutualism: symbiotic relation in which both species benefit from the relationship O) niche: includes the type of food the organism eats, how it gets its food, what other organisms use it for food. Habitat is the address niche is it occupation. P) parasitism: symbiotic relation in which both organism lives in or on another organism and harms the other organism Q) population: group of organisms of the same species that live in an area R) scavengers: organism that obtains energy by feeding on dead organism S) symbiosis: relationships in which two species live closely together T) trophic level: steps in a food chain or food web Ecology Worksheet Page 1 Name ___________________________________ Date _____________ Period _____ PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY Fill in the blank in each sentence below with the correct letter from the terms above. You will not use all the terms. 1. A is a group of organisms that mate with one another and live in the _____ same place at the same time. 2. A producer, or_____, uses the energy from the sun or energy stored in chemical compounds to make its own food. 3. The part of Earth that supports life is called the _____. 4. An organism’s _____ is the place where it lives out its life. 5. The role a species plays in its community is called its _____. 6. The study of the way organisms interact with their environment is called _____. 7. An organism that eats autotrophs is called a _____. 8. Vultures are _____because they eat animals that are already dead. 9. A series of food chains linked together in an ecosystem is known as a _____. 10. Earth worms are a type of _____ returning needed nutrients back to the soil so plants and other autotrophs can use it. 11. The relationship between a flea and the dog it lives on is an example of_____. 12. The nonliving factors in an ecosystem are called _____. 13. Living factors that affect an organism are called _____factors. 14. A _____ is a group of populations that interact with one another. 15. A butterfly pollinates a flower as it try to get nectar from the flower both benefit from their relationship this is an example of _____ symbiosis. Answer the questions below. Use the diagram of a food web to answer questions 16–20. 16. How many food chains make up the food web? __________________ 17. Which organism is an herbivore? _________________________ 18. Which organism is an omnivore? _________________________ 19. Which organism is an autotroph? _________________________ 20. Which organisms belong to more than one food chain? ______________ Ecology Worksheet Page 2 Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Place the letter on the line provided, that best completes the statement. A) Humans F) Ecology B) Soil C) Organisms G) Biotic factors D) Abiotic factors H) Atmosphere E) Environments I) Biosphere J) Nonliving Living organisms in our world are connected to other (21) _____ in a variety of ways. The branch of biology called (22) _____ is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and their (23) _____, including relationships between living and (24) _____ things. All living things on Earth can be found in the (25) _____, the portion of Earth that supports life. It extends from high in the (26) _____ to the bottom of the oceans. Many different environments can be found in the biosphere. All living organisms found in an environment are called (27) _____. Nonliving parts of an environment are called (28) _____. For example, whales, trees, and (29) _____ are biotic factors. Ocean currents, temperature, and (30) _____ are abiotic factors. For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B. Column A _____ 31. A group of organisms of one species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time _____ 32. A collection of interacting populations Column B a. community b. forest _____ 33. Interactions among the populations and abiotic factors in a community c. population _____ 34. Occurs between organisms when resources are scarce e. ecosystem d. competition _____ 35. A terrestrial ecosystem Base your answers to questions 36 through 38 on the food web below and your knowledge of science. _____ 36- Which statement would be true if the owl population disappeared? (A) The mouse population would increase. (B) The rabbit population would decrease. (C) The carrot population would increase. (D) The fox population would decrease. _____ 37- Which organisms in this food web are omnivores? (A) rabbits (B) birds (C) carrots (D) grasshoppers _____ 38- What is the role of the foxes in this food web? Ecology Worksheet Page 3 (A) decomposer (B) carnivore (C) producer (D) herbivore Base your answers to questions 39 and 40 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of science. The diagram represents a pond community containing a variety of plants and animals. _____ 39- Why are the fish able to survive in the pond? (A) The plants use chlorophyll produced by the fish. (B) The fish use oxygen produced by the plants. (C) The plants use oxygen produced by the fish. (D) The fish use carbon dioxide produced by the plants. _____ 40- The main source of energy for this pond community is the (A) plants (B) Sun C) pond water (D) animals Are zebra mussels really invading? In the mid-1980s a new species found its way to North America. The zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha), a small, clamlike mollusk that grows to about 25 cm as an adult, was introduced into the waters of the Great Lakes, probably carried in the bilge of a Russian freighter. The zebra mussel can reproduce in less than a year, and a single female can release 1 million eggs each year. In the absence of their natural pathogens, parasites, and predators, the zebra mussel populations in the Great Lakes has grown enormously and are now invading eight major river systems, including the St. Lawrence, Hudson, Mississippi, Ohio, Illinois, Tennessee, Susquehanna, and Arkansas rivers. The mussels are spread from one body of water to another by natural flow, carried on the feathers or feet of migrating waterfowl, or by human transport in bait buckets or on trailered boats. Most of the freshwater systems in North America are now threatened by invasion of the zebra mussel. The zebra mussels grow in massive colonies, where nearly a half million individuals may grow on each square meter of substrate. These colonies encrust the hulls and rudders of ships, the hinges of lock gates, and block the drains and intake ducts used by industries and power stations. In 1990, for example, Detroit Edison spent over $500,000 to remove zebra mussels from the intake pipes of its power plants. The zebra mussels also have severe negative effects on the local ecosystem. As filterfeeders, they take in water and filter out algae as food, excreting their waste as sediment. A single individual can filter 1 liter of water each day, and a colony covering 1 square meter of substrate can filter 180 million liters of water per year. Enormous colonies of zebra mussels can reduce the algal populations of lakes and rivers, thus removing a significant portion of the base of the food chain and resulting in a decline in the fish populations. Thus, these mussels are a threat to the local biodiversity. The tremendous filtering capacity of these organisms may have some positive consequences. Zebra mussels have been a major factor in cleaning Lake Erie after a century of pollution from fertilizers and sewage. After the first 10 years of zebra mussel existence in Lake Erie, light penetration in the water has increased from only a few centimeters to nearly 10 meters. If these organisms could be controlled, they may become a useful tool in the treatment of sewage and pollution. Ecology Worksheet Page 4 Questions _____41. Which of the following best summarizes the author's main point? a. Zebra mussels are harmful to the great lakes b. Zebra mussels are harmful to all lakes c. The importation of zebra mussels should be regulated d. Many lakes and river systems are polluted _____42. Zebra mussels can move from one lake to another by which method? a. on the feet of birds b. carried by the wind c. moving overland for short periods d. swimming up canal systems _____43. Massive colonies of zebra mussels cause problems because: a. they destroy the engines of boats b. they block the flow of water through ducts c. they produce waste that pollutes the water d. they eat large amounts of fish _____44. Which of the following is a consequence of the zebra mussel population in the great lakes a. cleaner water b. decline in algae populations c. decline in fish populations d. all of these _____45. Why are zebra mussels a problem in the Great Lakes but not in the lake systems where they came from? a. the other lakes are too cold for them to reproduce in large amounts b. they have natural predators in the other lakes c. they cannot leave these lakes d. they cannot grow into colonies _____46. How might zebra mussels be used to improve lake systems? a. they can be grown as food for humans b. they can be used to strengthen dams and levies c. they clean the water of pollutants d. they remove algae from the water _____47. What do zebra mussels eat? a. algae b. fish c. insects d. water plants Predator-Prey Graph Isle Royale National Park on a remote island was established in 1940, and designated a wilderness area in 1976. The only mode of transportation available is by boat or seaplane. Moose first arrived at Isle Royale around 1900. The moose population tends to increase in years with mild winters, early spring green-up, abundant winter forage, low wolf numbers and low levels of tick infestation. Wolves first arrived at the island on an ice bridge from Canada in 1940. Disease has also influenced the wolf population. Between 1980 and 1982, the wolf population declined from 50 to 14, due to canine parvovirus. Ecology Worksheet Page 5 48. What is the greatest moose population? __________ What year did that occur? __________ What was the wolf population when the moose population the greatest? _____________ 49. What would happen to the wolf population if the moose population decreases? __________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 50. What would happen to the moose population if the wolves were removed from Isle Royale? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ Ecology Worksheet Page 6