HWP (Homework Packet) Ecology - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement

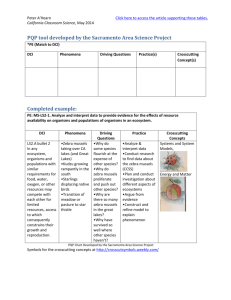
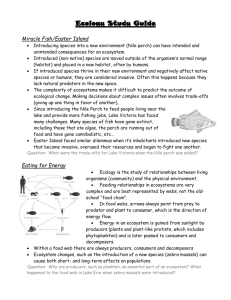
Ecosystems Structure: Key Concept: Ecology is the study of relationships among organisms and their environment. Levels of organization 1. Label this diagram with the correct level 2. Fill in the table below Level Description Example Organism Population Community Ecosystem Biome Main Idea: An ecosystem includes both biotic and Abiotic factors. Use the box below to complete the following sentences. Abiotic Living Plants 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Animals Moisture Temperature Biotic Nonliving Wind All ecosystems are made up of _____ and ______components __________factors are living things, such as ______________ or ____________ _________ factors are nonliving things such as, __________, ___________, or ___________ What is the difference between a biotic and an Abiotic factor? List two (2) Abiotic factors ____________________________________________ List two (2) Biotic factors______________________________________________ Label the biotic and Abiotic parts of the ecosystem in the picture below 1 Key Concept: Life in an ecosystem requires a source of energy. Main Idea: Producers provide energy for other organisms in ecosystems Complete the following sentence with the correct term Autotrophs Consumers eating heterotrophs nonliving producers 10. ___________ are organisms that get their energy from the _________________ resources, meaning they make their own food. These organisms are also called ______________. 11. __________are organisms that get their energy by ______________ other organism. These organisms are also called______________. 12. Why do all ecosystems depend on the producers? 13. Why is the sun important to both producers and consumers? 14. What is the difference between and consumer and a producer? Key Concept: Food chains and food webs model the flow of energy in an ecosystem Main Idea: a food chain is a model that show the sequence of feeding relationships Complete the following sentence with the correct term Carnivore Decomposer Detritivore Herbivore Omnivore Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer Trophic Levels 15. I eat only plants. I am a(n) _____________________. 16. I eat only other animals. I am a(n) _____________________. 17. I eat both plants and animals. . I am a(n) _____________________. 18. I eat dead organic matter. . I am a(n) _____________________. 19. I break down organisms matter into simpler compounds. . I am a(n) _____________________. 20. I am the first consumer, above the producer level. . I am a(n) _____________________. 21. I am a carnivore that eats herbivores. . I am a(n) _____________________. 22. I am a carnivore that eats other carnivores. . I am a(n) _____________________. 23. The levels of nourishment in the food chain are called______________________. Main Idea: Food webs shows complex feeding relationships 24. How is a food web different from a food chain? 25. What happens to the energy at each link in the web? 26. What type of organism is the base of the food web? 2 A Food Web Shows: Types of Consumers: 1. ________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________ 4. _________________________________________________ Trophic Levels Producer __________________ __________________ Primary Consumers __________________ __________________ __________________ _________________ _ Secondary Consumers __________________ __________________ _________________ _ Tertiary Consumer __________________ Key Concept: Pyramids model the distribution of energy and matter in an ecosystem Main idea: Energy pyramids show the distribution of energy among trophic levels. Complete the following sentence with the correct term Heat Biomass Waste 27. The measure of the total dry mass of organism in a given area is called _______________. 28. When a consumer incorporates the biomass of a producer into it’s biomass, a large amount of energy is lost as _______________ and ______________________. 29. Label the four tiers of the energy pyramid with the correct trophic levels. a. Assume you have 50 hawks, how many of each of the following would you have? (Grass, Mice, Snakes) b. Label the pyramid with the numbers and species Main Idea: Other pyramid models illustrate an ecosystem’s biomass and distribution of organisms. 3 30. Fill in the table below Model Description Energy Pyramid Biomass Pyramid Pyramid of numbers 31. What is biomass? 32. Describe how the energy flows from one level to the next? ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION Key Concept: Ecological succession is a process of change in the species that make up a community Main Idea: Succession occurs following a disturbance in an ecosystem. 33. What is ecological succession? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 34. Fill in the chart below with a description and simple sketch of the main steps of primary succession. _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ 35. Fill in the chart below with a description and simple sketch of the main steps of secondary succession. _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ 36. What is the main difference between primary and secondary succession? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 37. What are pioneer species? _____________________________________________________________________________________ a) Why are pioneer species so important in primary succession? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ b) Give an example of a pioneer species _____________________________________________ 38. Why might succession be considered a never-ending process? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4 Population Growth Patterns Key Concept: Populations grow in predictable patterns Main Idea: changes in population size are determined by birth, death, immigration and emigration. Complete the following sentence with the correct term Birth Death Immigration Emigration 39. When resources are abundant in an area, individuals may move into the population in that area. This movement of individuals into a population from a different population is called ______________. 40. A very cold winter has left many deer in a population hungry and sick. By the end of the winter, these populations will likely decrease because of _________________. 41. A deer population experiences growth when the rate of reproduction increases. This change in population size is due to _________________________. 42. As humans move into a territory, many members of the deer population move away and join other herds; this movement of individuals out of a population into a new one is called _________________. 43. How does the availability of resources affect population growth? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 44. In the spaces below, draw and label the two different types of population curves. Write a brief description of each next to the graph and give an example. Description: Description: ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ Example: ___________________ Example: ________________ 45. What type of growth curve shows a carrying capacity? 46. What type of population growth us a risk for a population crash? a) Explain why. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ b) Give an example _______________________________________ 47. Detail the key differences between logistic and exponential growth. Main Idea: Ecological factors limit population growth 48. Define density dependent limiting factor _____________________________________________________________________________________ 49. List three examples of density-dependent limiting factors _____________________________________________________________________________________ 50. Define density- independent limiting factor _____________________________________________________________________________________ 51. List three examples of density-independent limiting factors _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5 Invasive Species---Are zebra mussels really invading? In the mid-1980s a new species found its way to North America. The zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha), a small, clamlike mollusk that grows to about 25 cm as an adult, was introduced into the waters of the Great Lakes, probably carried in the bilge of a Russian freighter. The zebra mussel can reproduce in less than a year, and a single female can release 1 million eggs each year. In the absence of their natural pathogens, parasites, and predators, the zebra mussel populations in the Great Lakes has grown enormously and are now invading eight major river systems, including the St. Lawrence, Hudson, Mississippi, Ohio, Illinois, Tennessee, Susquehanna, and Arkansas rivers. The mussels are spread from one body of water to another by natural flow, carried on the feathers or feet of migrating waterfowl, or by human transport in bait buckets or on trailered boats. Most of the freshwater systems in North America are now threatened by invasion of the zebra mussel. The zebra mussels grow in massive colonies, where nearly a half million individuals may grow on each square meter of substrate. These colonies encrust the hulls and rudders of ships, the hinges of lock gates, and block the drains and intake ducts used by industries and power stations. In 1990, for example, Detroit Edison spent over $500,000 to remove zebra mussels from the intake pipes of its power plants. The zebra mussels also have severe negative effects on the local ecosystem. As filter-feeders, they take in water and filter out algae as food, excreting their waste as sediment. A single individual can filter 1 liter of water each day, and a colony covering 1 square meter of substrate can filter 180 million liters of water per year. Enormous colonies of zebra mussels can reduce the algal populations of lakes and rivers, thus removing a significant portion of the base of the food chain and resulting in a decline in the fish populations. Thus, these mussels are a threat to the local biodiversity. The tremendous filtering capacity of these organisms may have some positive consequences. Zebra mussels have been a major factor in cleaning Lake Erie after a century of pollution from fertilizers and sewage. After the first 10 years of zebra mussel existence in Lake Erie, light penetration in the water has increased from only a few centimeters to nearly 10 meters. If these organisms could be controlled, they may become a useful tool in the treatment of sewage and pollution . 52. Which of the following best summarizes the author's main point? a) Zebra mussels are harmful to the great lakes b) Zebra mussels are harmful to all lakes c) The importation of zebra mussels should be regulated d) Many lakes and river systems are polluted 53. Zebra mussels can move from one lake to another by which method? a. on the feet of birds b. carried by the wind c. moving overland for short periods d. swimming up canal systems 54. Massive colonies of zebra mussels cause problems because: a. they destroy the engines of boats b. they block the flow of water through ducts c. they produce waste that pollutes the water d. they eat large amounts of fish 55. Which of the following is a consequence of the zebra mussel population in the great lakes a. cleaner water b. decline in algae populations c. decline in fish populations d. all of these 56. Why are zebra mussels a problem in the Great Lakes but not in the lake systems where they came from? a. the other lakes are too cold for them to reproduce in large amounts b. they have natural predators in the other lakes c. they cannot leave these lakes d. they cannot grow into colonies 57. How might zebra mussels be used to improve lake systems? a. they can be grown as food for humans b. they can be used to strengthen dams and levies c. they clean the water of pollutants d. they remove algae from the water 58. What do zebra mussels eat? a. algae b. fish c. insects d. water plants 6 Nutrient Cycling Key Concept: Nutrients cycle within ecosystems Main Idea: matter cycles Drawing/Sketch THE WATER CYCLE 59. Name three important needs for water. 60. What draws water back to the Earth? 61. What is transpiration? 62. Name two ways water travels from land to enter the ocean. THE CARBON CYCLE 63. What is the role of each of the following in the carbon cycle? State an example of each. a) Primary producers b) Secondary producers Drawing/Sketch c) Decomposers 64. Where is the most of Earth’s carbon located and in what form? 65. How does carbon enter the biotic part of the ecosystem? 66. What functions do plants have in the forest of the ecosystem? 67. How is carbon dioxide returned to the atmosphere? 68. What is a primary producer? 69. What is a fossil fuel? Drawing/Sketch THE NITROGEN CYCLE 70. What percent of the air is nitrogen? 71. Why is nitrogen essential to life? 72. How do plants and animals get nitrogen if not from the atmosphere? 73. What are nitrogen fixing bacteria? 74. What is denitrification? 7