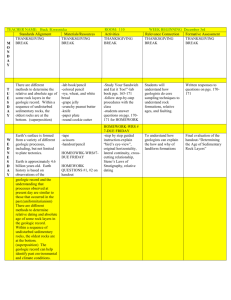
Grade 8 Unit 2 Science Curriculum Map
advertisement
8th Grade Science Unit 2: Inside Earth and Geologic Time Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 LPSS Science Teacher Leader Cadre Debora Ajala – EA Martin Phobe Boutte – LJ Alleman Charlene Jackson – Scott Jodie LeBlanc – Judice Bill Lee – Paul Breaux Bridget Trahan – LPSS Science Lead Teacher Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 8th Science Unit 2: Inside Earth and Geologic Time Time Frame: September 23 – November 11 (7 Weeks) Unit Description and Student Understandings: This unit introduces the layers that form Earth with a focus on the theory of plate tectonics. The unit includes the identification of minerals and rocks and the study of the rock cycle. Students develop an understanding that rocks are made of minerals and use established procedures to identify mineral samples. Research on the rock cycle shows student understandings of the dynamic processes that result in the formation of other rocks. Ending with an awareness of the four density layers of Earth, students gain an understanding of the theory of plate tectonics. This unit focuses on fossils and the evidence of past geologic eras that fossils provide. The methods used to understand the changes experienced by Earth and other planets since their formation are also emphasized. The activities in this unit are also intended to explore Earth’s historical data and geological principles used to study Earth’s composition, age, and processes that affect Earth’s form. Students understand that Earth is always changing, yet ever the same, involving the processes that shape the surface today and throughout geologic time. Students learn that rock layers in outcrops can be correlated and read, revealing the geologic history of an area and the beginnings of life. Students develop an understanding that various types of geologic and biological evidence provide an awareness of the development of life. Guiding Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Can students discuss convection currents as an explanation of plate tectonics? Can students compare causes and locations of earthquakes and volcanoes? Can students classify a given rock or a mineral by its appearance and other physical characteristics? Can students explain what changes the identity of one rock formation to another? Can students describe how certain fossils are indicators of ancient environments and how the evolutionary developments of life forms are inferred from the fossil record? Can students describe how the relative age of a rock is determined? Can students suggest how to correlate discontinuous rock columns from around the world? Can students explain how scientists know what conditions existed on Earth long ago? Can students describe the types of evidence that are available to scientists to interpret the history of Earth? Can students describe how geologists are able to discern the geologic history of a region by using rock layers? Can students distinguish between relative and absolute dating and describe how actual geologic ages can be measured using known rates of radioactive decay? Can students demonstrate their knowledge of the relationships between improvements in technology and subsequent discoveries in space? Key Concepts: Describe the structure of the four density layers of Earth (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core) Identify the effects of convection currents on tectonic plates of Earth’s crust and upper mantle (volcanoes, earthquakes, ocean floor spreading, mountain building, faulting, and folding) Describe natural disasters, predict their effects, and classify them as constructive or destructive forces (earthquakes, hurricanes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, etc.) Identify the characteristics of and classify major rocks and minerals Describe or illustrate the rock cycle and differentiate among igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rock Explain the significance of fossils and why similar fossils are found on two or more separate continents Provide or select examples of changes over time that have allowed various species to survive or that illustrate similarities in structures of animals. Fossil evidence may be used Identify processes and data used to determine the age of Earth Identify the motivation for and value of space exploration 8th Grade Science 2013-2014 Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 8th Science Unit 2: Inside Earth and Geologic Time Time Frame: September 23 – November 11 (7 Weeks) Vocabulary: Interactive Science Textbook Ch. 4 pg. 135 Interactive Science Textbook Ch. 5 pg. 163 Interactive Science Textbook Ch. 6 pg. 209 Interactive Science Textbook Ch. 7 pg. 239 GLEs ES-8 (E) Identify and describe the four density layers of Earth (ESS-MA1) CCSS Literacy Standards NGSS Practices Instructional Strategies Probe: Is it a Rock? Literacy Strategy: Learning Log Prompts: ”What is the difference between rocks and minerals?” “How can you tell if a substance is a mineral?” Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 4 Lesson 1 pgs. 136-141 Discuss Chapter 4 Lesson 2 pgs.142-149 LCC Activity 4: The Layers of Our Earth (2 days) Substitute Earth Model Investigation based on information from http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~braile/indexlinks/educ.htm Differentiation (Enrichment/Remediation Strategies) Scroll down to Plates, Earthquakes and Volcanoes: http://middleschoolscience.com/earth.htm Presentations on the Earth’s Layers: http://science.pppst.com/layers.html http://scienceclass.net/Geology/earth_structure.htm http://scign.jpl.nasa.gov/learn/plate1.htm United Streaming (Discovery Education) – What’s Inside the Earth? ES-10 (E) Illustrate the movement of convection currents (ESS-MA2) Changes 4 Integrated Science video and assessment Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 4 Lesson 3 pgs. 150-153 LCC Activity 5: Convection Currents (1 day) Teacher demo both parts Change 5 Integrated Science video and assessment ES-9 (C) Explain the historical development of the theories of 8th Grade Science 2013-2014 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 5 Lesson 1 pgs. 164-167 Chapter 5 Lesson 2 pgs. 168-173 http://education.sdsc.edu/optiputer/flash/convect ion.htm http://www.cdm.org/i/Resources/Articles/Magic -School-Bus-Convection.pdf http://www.tectonic-forces.org/pt04.htm http://www.absorblearning.com/media/attachme nt.action?quick=12p&att=2775 Make convection currents- from Kids Crossing Hands-on Activities: www.eo.ucar.edu/kids http://scienceclass.net/Geology/plate_tectonics.htm Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 8th Science Unit 2: Inside Earth and Geologic Time Time Frame: September 23 – November 11 (7 Weeks) plate tectonics, including continental drift and sea-floor spreading (ESS-M-A2) ES-11 (E) Illustrate the movements of lithospheric plates as stated in the plate tectonics theory (ESS-M-A2) ES-12 (I) Identify the edges of plate boundaries as likely areas of earthquakes and volcanic action (ESS-M-A3) ES-13 (E) Describe the processes responsible for earthquakes and volcanoes and identify the effects of these processes (e.g., faulting, folding) (ESS-M-A3) ES-16 (I) Compare the physical characteristics of rock and 8th Grade Science 2013-2014 Chapter 5 Lesson 3 pgs. 174-179 LCC Activity 6: Plate Tectonics Part A: (1 day) Plate Tectonic Summary Chart Modeling Lab (1 day) Stages 7, Change 5 Integrated Science video and assessment United Streaming (Discovery Education) - Continents Adrift Also addresses GLE 11 Interactive Science Textbook: pgs. 168-179 Chapter 5 Lesson 2 pgs. 168-173 Chapter 5 Lesson 3 pgs. 174-179 Addressed in LCC Activity 6 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 5 Lesson 5 pgs. 188-191 LCC Activity 3: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Part A: (1 day) a. Literacy Strategy: Student Questions for Purposeful Learning (SQPL) b. Read article Understanding Plate Motions http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html Teacher note: see also My Plate’s Faster Than Your Plate Part B: (1 day) a. Literacy Strategy: Graphic organizer – Ring of Fire http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/historical. html http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/dynamic.html - Dynamic Earth http://scienceclass.net/Geology/plate_tectonics.htm http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078778026/student_view0/unit3/ chapter10/standardized_test_practice.html http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/understan ding.html http://science.pppst.com/platetectonics.html http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/understan ding.html http://www.platetectonics.com/book/index.asp Virtual Seismologist Activity http://www.sciencecourseware.org/Virtual Earthquake/ Change 6 Integrated Science Video and Assessment Also addresses GLE 13 Interactive Science textbook: Chapter 5 Lesson 4 pgs. 180-187 Chapter 5 Lesson 6 pgs. 192-193 http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078778026/student_view0/unit3/ chapter10/internet_lab.html Addressed in LCC Activity 3 http://science.pppst.com/earthquakes.html Interactive Science textbook: Chapter 6 Lesson 2 pgs. 222-225 http://science.pppst.com/rocks.html LCC Activity 2: Rocks and the Rock Cycle Classifying and Identifying Rocks Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 8th Science Unit 2: Inside Earth and Geologic Time Time Frame: September 23 – November 11 (7 Weeks) mineral specimens to observe that a rock is a mixture of minerals (ESS-M-A5) Part A: (1 day) a. Categorizing rocks Part B: (1 day) Uses and economic values of rocks (start in class/finish at home) Part C: (1 day) a. Literacy Strategy: Graphic organizer - rock cycle Part D: (1 day) a. Ride the Rock Cycle Game http://geologyonline.museum.state.il.us/tools/lessons/6.4/lesson.p df b. Literacy Strategy: Story Chain – based on experiences in game Relevance in everyday life- http://mii.org http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078778026/student_view0/brain pop_movies.html# Stages 8 Integrated Science Video and assessment ES-18 (E) Describe how sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks form and change in the rock cycle (ESS-M-A6) ES-17 (E) Describe the properties of minerals (e.g., color, luster, hardness, streak) (ESS-M-A5) United Streaming (Discovery Education) - Basics of All About Rocks and Minerals Also addresses GLE 18 Also addresses GLE 17 Interactive Science textbook: Chapter 6 Lesson 2 pgs. 222-225 Chapter 6 Lesson 3 pgs. 226-229 http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/dl/free/0078778026/164213/0004 4683.html Addressed in LCC Activity 2 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 6 Lesson 1 pgs. 210-221 LCC Activity 1: Mineral Identification: Use Mineral Webquest (See LCC) a. Virtual Mineral ID Lab b. Literacy Strategy: Vocabulary Cards Vocabulary Terms: cleavage, color, crystal system, fracture, hardness, luster, Moh’s Hardness Scale, streak, texture Also addresses GLE 16 Probe: Mountaintop Fossil Intro: The Great Fossil Find 8th Grade Science 2013-2014 Geology http://sciencespot.net/Pages/classearth.html Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 8th Science Unit 2: Inside Earth and Geologic Time Time Frame: September 23 – November 11 (7 Weeks) ES-31 (E)Compare fossils from different geologic eras and areas of Earth to show that life changes over time (ESS-M-B1) ES-34 (E) Apply geological principles to determine the relative ages of rock layers (e.g., original horizontality, superposition, cross-cutting relationships) (ESS-M-B3) Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 Lesson 1pgs. 240- 245 http://science-class.net/Geology/geologic_time.htm Literacy Strategy: Learning Log - Prompt: Where have you seen fossils? How does the study of fossils help us to understand Earth’s history? http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/dl/free/0078778026/164155/0007 6703.html LCC Activity 3: Reconstructing Gondwanaland (2 days) - Part A: Literacy Strategy: SQPL Article – Geodiversity Gondwana Part B: Construction of Gondwana and class discussion Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 Lesson 2 pgs. 246-251 http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078778026/student_view0/unit4/ chapter14/standardized_test_practice.html LCC Activity 1: Relative Dating, Just Not Your Cousin - Part A: Random Letter Cards (1 day) - Part B: Index Fossils (1 day) Also Addresses GLE 31 LCC Activity 2: Getting to the Core it - Candy Coring - Note: Students with peanut allergies need to be considered Stages 9 Integrated Science video and assessment Clues 10 Integrated Science video and assessment ES-35 (E) Describe how processes seen today are similar to those in the past (e.g., weathering, erosion, lithospheric plate movement) (ESS-M-B3) ES-30 (I) Interpret a geologic timeline (ESS-M-B1) Also Addresses GLE 35 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 Lesson 2 pgs. 246-251 Addressed in LCC Activity 6 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 Lesson 4 pgs. 256-259 Chapter 7 Lesson 6 pgs. 264-275 LCC Activity 4: Earth’s Timeline (3 days) US: Prehistoric Earth (SRCD) US: Rocks, Fossils and Earth History Also Addresses GLE’s 31, 32 LCC Activity 6: What Came First? (2 days) - Part A: Students collect illustrations (such as pictures of 8th Grade Science 2013-2014 http://science.pppst.com/fossils.html http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078778026/student_view0/unit4/ chapter13/standardized_test_practice.html http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078778026/student_view0/unit4/ chapter13/section_2_self-check_quiz-eng_.html http://www.geosociety.org/educate/LessonPlans /Relative_Age.pdf Adventures at Dry Creek www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explotime.ht ml Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 8th Science Unit 2: Inside Earth and Geologic Time Time Frame: September 23 – November 11 (7 Weeks) - ES-32 (I) Interpret a timeline starting with the birth of the solar system to the present day (ESSM-B2) ES-33 (I) Use historical data to draw conclusions about the age of Earth (e.g., half-life, rock strata) (ESS-M-B2) ES-48 (C) Communicate ways that information from space exploration and technological research have advanced understanding about Earth, the solar system, and the universe (ESS-M-C8) ES-49 (C) Identify practical applications of technological advances resulting from space exploration and scientific and technological research (ESS-MC) themselves as a baby and through the years) Part B: Formation of Louisiana Show video “Vanishing Wetlands, Vanishing Future” from Barataria Terrebonne National Estuary Also Addresses GLE’s 33, 35 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 Lesson 5 pgs. 260-263 Chapter 7 Lesson 6 pgs. 264-275 Addressed in LCC Activity 4 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 Lesson 2 pgs. 246-251 Chapter 7 Lesson 3 pgs. 252-255 LCC Activity 5: Half of What? - Part A: Radioactive Decay Investigation Part B: Penny Half Life Activity can be used – use the version you prefer LCC Activity 7: Technology and Today’s Understandings of Earth - Will be addressed in Unit 7 and 8 Also Addresses GLE 49 LCC Activity 7: Technology and Today’s Understandings of Earth - Will be addressed in Unit 7 and 8 Also Addresses GLE 48 UNIT 2 BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT NOVEMBER 11 8th Grade Science 2013-2014