teacher name: room: week beginning
advertisement
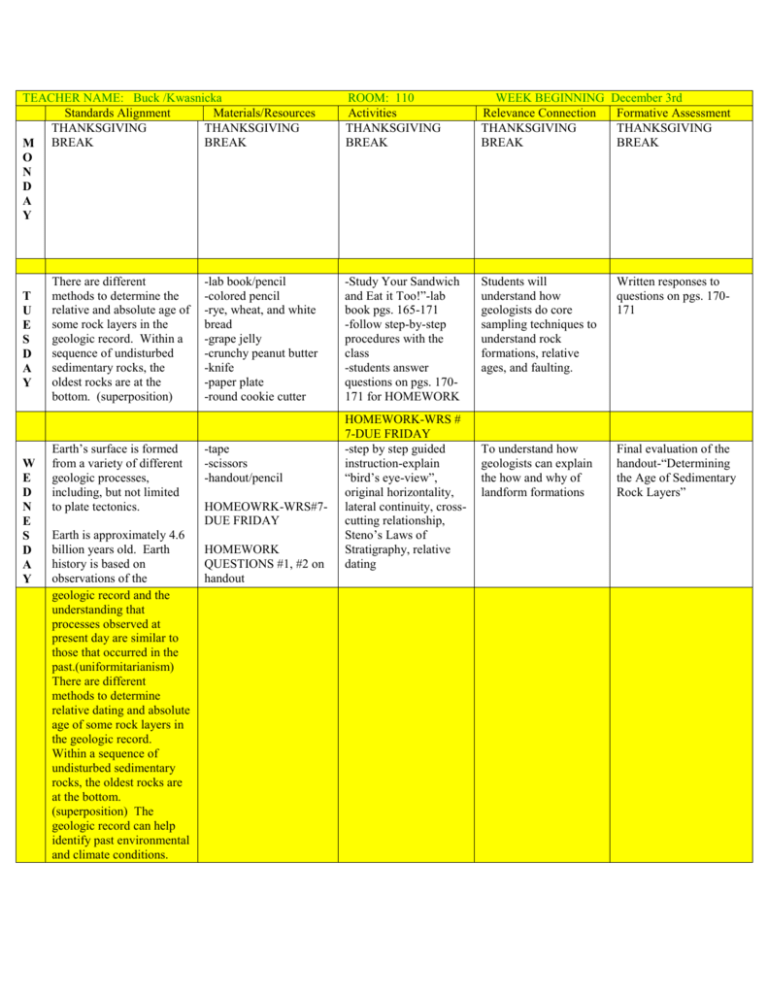
TEACHER NAME: Buck /Kwasnicka Standards Alignment Materials/Resources THANKSGIVING THANKSGIVING BREAK M BREAK O N D A Y T U E S D A Y W E D N E S D A Y There are different methods to determine the relative and absolute age of some rock layers in the geologic record. Within a sequence of undisturbed sedimentary rocks, the oldest rocks are at the bottom. (superposition) Earth’s surface is formed from a variety of different geologic processes, including, but not limited to plate tectonics. Earth is approximately 4.6 billion years old. Earth history is based on observations of the geologic record and the understanding that processes observed at present day are similar to those that occurred in the past.(uniformitarianism) There are different methods to determine relative dating and absolute age of some rock layers in the geologic record. Within a sequence of undisturbed sedimentary rocks, the oldest rocks are at the bottom. (superposition) The geologic record can help identify past environmental and climate conditions. -lab book/pencil -colored pencil -rye, wheat, and white bread -grape jelly -crunchy peanut butter -knife -paper plate -round cookie cutter -tape -scissors -handout/pencil HOMEOWRK-WRS#7DUE FRIDAY HOMEWORK QUESTIONS #1, #2 on handout ROOM: 110 Activities THANKSGIVING BREAK WEEK BEGINNING Relevance Connection THANKSGIVING BREAK -Study Your Sandwich and Eat it Too!”-lab book pgs. 165-171 -follow step-by-step procedures with the class -students answer questions on pgs. 170171 for HOMEWORK Students will understand how geologists do core sampling techniques to understand rock formations, relative ages, and faulting. Written responses to questions on pgs. 170171 To understand how geologists can explain the how and why of landform formations Final evaluation of the handout-“Determining the Age of Sedimentary Rock Layers” HOMEWORK-WRS # 7-DUE FRIDAY -step by step guided instruction-explain “bird’s eye-view”, original horizontality, lateral continuity, crosscutting relationship, Steno’s Laws of Stratigraphy, relative dating December 3rd Formative Assessment THANKSGIVING BREAK See Wednesday T H U R S D A Y HOMEWORK-WRS#7DUE FRIDAY -review from Wednesday -construct Model B with teacher step-bystep instruction See Wednesday See Wednesday -lab book pgs. 341-343, ExploreLearning-“Rock Cycle” -answer questions from the Gizmo -if time, students can finish questions from previous ExploreLearnings Students will understand the three types of rock and understand the terms: lithification, deposition, weathering, intrusive/extrusive igneous rock Written responses to pgs. 341-343 HOMEWORKQUESTIONS #3, #4, #5 on handout -6th grade standards F R I D A Y See Wednesday Minerals have specific quantifiable properties. Igneous, meatamorphic, and sedimentary rocks have unique characteristics that can be used for identification and/or classification -computers -lab book/pencil WEEKLY LESSON PLANS Classification. Igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks form in different ways.